In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations face an ever-increasing number of cybersecurity threats. Safeguarding digital assets and sensitive information has become paramount. One effective way to fortify your cybersecurity defense is through automated vulnerability scanning. This blog will provide a comprehensive guide to automatic vulnerability scanning, exploring its importance, benefits, best practices for implementation, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to address common concerns.
How does Automated Vulnerability Scanning Work?
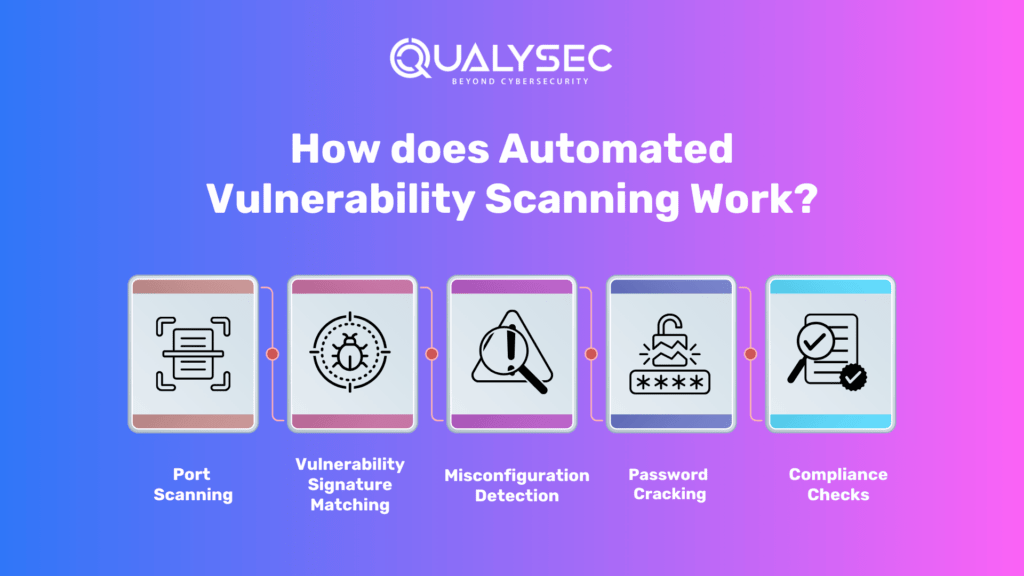
Automated vulnerability scanning works by utilizing specialized software tools that systematically scan networks, systems, applications, and infrastructure for security vulnerabilities. These tools employ various techniques, including port scanning, vulnerability signature matching, misconfiguration detection, password cracking, and compliance checks. Detailed reports are generated, highlighting identified vulnerabilities, their severity levels, and recommended remediation steps.
- Port Scanning: Scanning for open ports and services to identify potential entry points for attackers.
- Vulnerability Signature Matching: Comparing known vulnerability signatures against the target system to identify specific vulnerabilities.
- Misconfiguration Detection: Identifying common misconfigurations that can lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Password Cracking: Attempting to crack weak passwords or identify default credentials used in systems and applications.
- Compliance Checks: Assessing systems against industry standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices.
Automated vulnerability scanning tools generate detailed reports highlighting identified vulnerabilities, their severity levels, and recommended remediation steps.
Types of Automated Vulnerability Scanning
- External vs. Internal Vulnerability Scanning:
- External Scanning: Assessing the security of publicly accessible systems, applications, and networks from an external perspective, simulating attacks from outside the organization.
- Internal Scanning: Assessing the security of internal systems, applications, and networks, focusing on vulnerabilities that can be exploited by insiders or in case of a breach.
- Authenticated vs. Non-Authenticated Scanning:
- Authenticated Scanning: Conduct scans with valid credentials to simulate an attacker with insider access, providing a more comprehensive assessment of vulnerabilities.
- Non-Authenticated Scanning: Conducting scans without credentials and evaluating vulnerabilities that can be identified without authentication.
Factors to Consider While Choosing an Automated Vulnerability Scanning Tool
When selecting an automated vulnerability scanning tool, consider factors such as accuracy and coverage, reporting and analysis capabilities, integration and compatibility with existing infrastructure, scalability and performance, and vendor support and updates.
- Accuracy and Coverage: Look for tools that have wide coverage of vulnerabilities and provide accurate results to minimize false positives and false negatives.
- Reporting and Analysis: Evaluate the reporting capabilities of the tool, including the clarity and comprehensiveness of vulnerability reports and the ability to prioritize and track remediation efforts.
- Integration and Compatibility: Consider the tool’s compatibility with your existing IT infrastructure and whether it can integrate with other security tools for a holistic security approach.
- Scalability and Performance: Assess the tool’s ability to handle large-scale scanning across diverse systems and networks without significant impact on performance.
- Vendor Support and Updates: Ensure that the tool is backed by a reputable vendor that provides regular updates, patches, and responsive support.
Top 5 Open-Source Automated Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Open-source automated vulnerability scanning tools offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for vulnerability scanning. With numerous free and paid options to choose from, finding the top tools can be challenging. To simplify the process, we have compiled a curated list of the finest free and open-source options available.
- NMAP
- Metasploit
- OWASP Zap
- Sqlmap
- OpenVAS
Why Choose Qualysec for Automated Vulnerability Scanning?
Qualysec is a leading provider of Cybersecurity and compliance management solutions. Their platform allows companies to conduct continuous monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and compliance management across their entire IT infrastructure with the help of AI.
Qualysec follows a comprehensive methodology that combines manual and automated testing techniques and AI to ensure maximum coverage of vulnerabilities. They also provide detailed reports that include a prioritized list of vulnerabilities, along with recommendations for remediation.
They work closely with organizations to understand their unique needs. Qualysec is also a leading provider of automated vulnerability scanning solutions in USA, offering comprehensive scanning capabilities, advanced reporting and analysis, scalability and performance, industry expertise, and continuous support and updates.
Qualysec offers various services which include:
- Web App Pentesting
- Mobile App Pentesting
- API Pentesting
- Cloud Security Pentesting
- IoT Device Pentesting
- AI /ML Pen-testing
The methodologies offered by Qualysec for Mobile Application Security Testing are particularly beneficial for businesses that must adhere to industry rules or prove their dedication to security to clients and partners. So, by opting for Qualysec as a reliable service provider, businesses can ensure the safety of their web applications.
Hence, choose Qualysec for a comprehensive and reliable vulnerability scanning report. Also, their penetration testing guide will help you make informed decisions and understand the various factors that impact the cost. Hence, protect your assets and enhance your security posture by choosing us.
Key Features
- Over 3,000 tests to detect and root out all types of vulnerabilities.
- Capable of detecting business logic errors and gaps in security.-
- Ensures zero false positives through manual pen testing.
- Compliance-specific scans for SOC2, HIPAA, ISO27001, and other relevant standards.
- Provides in-call remediation assistance from security experts
Conclusion
Automated vulnerability scanning is an essential component of a proactive cybersecurity strategy. By leveraging specialized tools, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, reduce risks, and prioritize remediation efforts. Consider the types of scanning, choose the right tool, and follow best practices to fortify your cybersecurity defenses. Whether you opt for open-source tools or a reliable vendor like Qualysec, automated vulnerability scanning enhances your ability to detect and address vulnerabilities, ensuring a robust and resilient security posture.
There are several types of Pen testing Solutions one might need, and vulnerability scanners, including network scanners, host scanners, application scanners, cloud scanners, and wireless scanners. Each with its own set of benefits and use cases. Additionally, both internal and external vulnerability scanners are necessary. These cover all devices and systems that are accessible from within and outside of an organization’s network. We are always ready to help, talk to our Experts and fill out your requirements.
With today’s technology, the cybersecurity industry also includes various techniques involving AI. Check out how Artificial intelligence (AI) is creating an impact on the cybersecurity industry, Explore by checking out our article “Impacts of AI on Cybersecurity“.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How often should automated vulnerability scanning be performed?
It is recommended to conduct it at least monthly. However, the frequency may vary based on factors such as the organization’s risk profile, industry regulations, and the rate of system changes. In high-risk environments or rapidly evolving systems, more frequent scans may be necessary.
Q2: Can automated vulnerability scanning replace manual penetration testing?
Automated vulnerability scanning and manual penetration testing serve different purposes. Automated scanning is efficient for identifying known vulnerabilities and common misconfigurations. On the other hand, manual penetration testing involves human expertise to identify complex vulnerabilities and test for security weaknesses that automated tools may miss. Both approaches complement each other for comprehensive security testing.
Q3: What should be done after vulnerabilities are identified?
After vulnerabilities are identified through automated scanning, organizations should prioritize them based on severity and potential impact. Remediation efforts should be planned and implemented promptly. Patching systems, updating software, configuring secure settings, and implementing security best practices are common steps for remediation.
Q4: Are automated vulnerability scanning tools capable of detecting zero-day vulnerabilities?
It primarily relies on known vulnerability signatures and databases. Therefore, they may not detect zero-day vulnerabilities that are unknown or recently discovered. However, some advanced scanning tools may employ techniques like heuristic analysis to identify patterns and behaviors associated with zero-day vulnerabilities.
Q5: Can automated vulnerability scanning tools cause network disruptions?
Its tools are designed to minimize network disruptions. However, in certain cases, aggressive scanning techniques or large-scale scans on resource-constrained systems may cause temporary network disruptions. It is recommended to carefully configure scanning parameters and perform scans during non-peak hours to minimize potential disruptions.
























![Top 20 Network Security Companies in USA [2025 Updated List]](https://qualysec.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Top-20-Network-Security-Companies-in-USA-2025-Updated-List-scaled.jpg)


































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments