© 2024 Qualysec.com Disclaimer Privacy Policy Terms & Conditions

As companies keep increasing their usage of cloud services, the risks of cloud computing vulnerabilities also increase. Cloud computing services have become a go-to solution for data storage, business operations, and team collaborations. And why not? They are cost-effective, flexible, and boost productivity. However, it is not always smooth sailing. They too have their fair share of security risks.
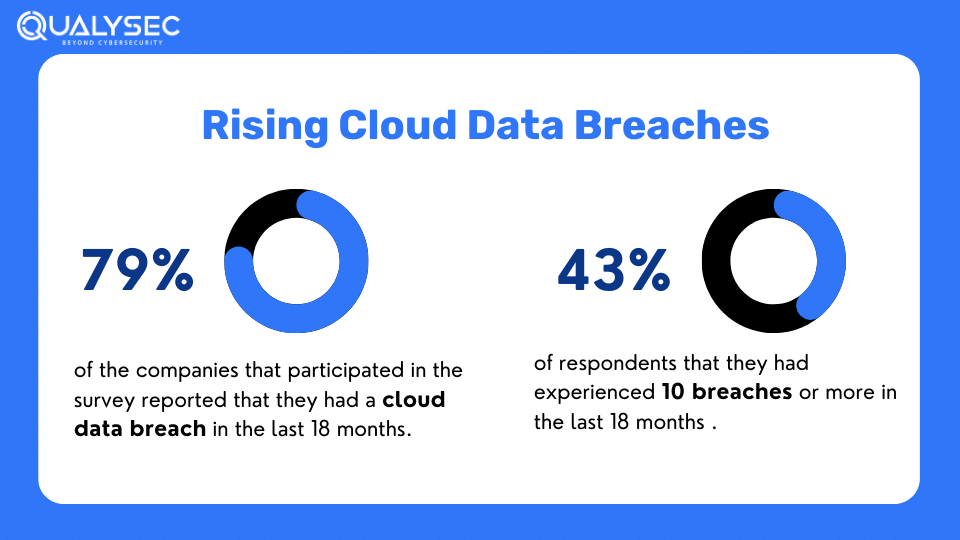
A study by IBM shows that cloud data breaches cost companies $4.8 million on average to recover. This comes when 65% of organizations are defaulting to cloud-based services. So, if your business uses cloud computing services or even offers cloud services, you must be aware of the lingering threats.
This blog lists the top vulnerabilities in cloud computing, what is their impact, and best practices to address them. Remember, proactive prevention is always better than required remediation.
Cloud computing refers to services that are provided over the internet (in this case, “the cloud”) such as servers, storage, networking, analytics, software, and intelligence. It is a cost-effective way where typically pay for the service you want to use.
Most companies use cloud computing for data storage and business operations. Instead of storing files on a device or hard drive, you can save them on the cloud, which you can access from anywhere, as long as you have access to the Internet. Based on the deployment model, the cloud can be classified as a public, private, and hybrid cloud.
Cloud computing is broadly divided into 3 types:
Cloud computing has revolutionized business operations and eliminated storage issues. It will continue to expand to make the services more convenient. However, business owners should stay updated with the evolving vulnerabilities of cloud computation so that they do not face any cyberattacks.
Cloud computing vulnerabilities are security gaps or weaknesses in a cloud computing environment that hackers/attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive data, and interrupt services.
These vulnerabilities can be present anywhere in the cloud environment, including applications, infrastructure, data storage, and communication pathways. These vulnerabilities could be due to bugs in the software, outdated security patches, insecure access controls, lack of encryption, etc. Identifying and promptly addressing these vulnerabilities is key to a secure cloud environment.
The impacts of cloud vulnerabilities include unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. Additionally, these vulnerabilities endanger system integrity, privacy, and the overall security posture of the cloud environment. Here is a brief description of their impact:
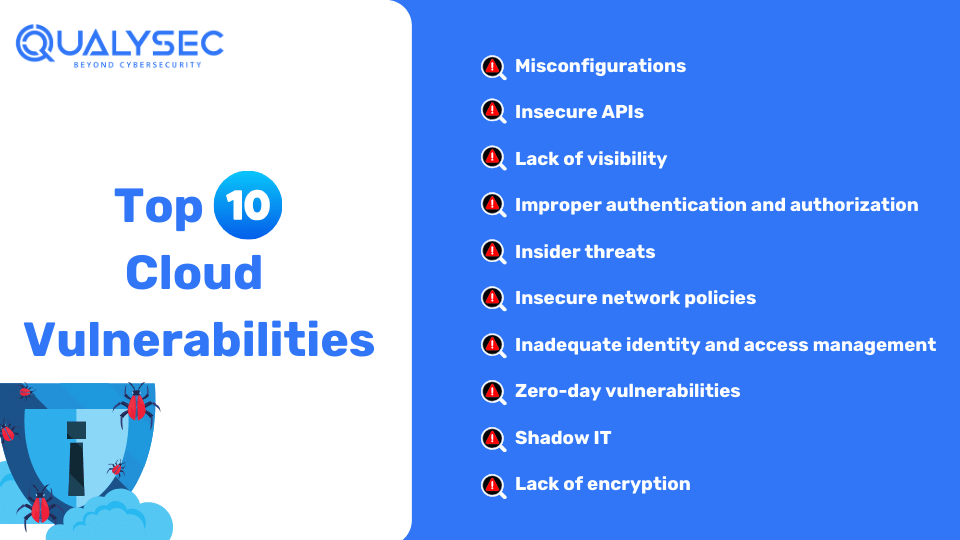
Cloud computing is going to integrate AI in most of its services in the coming years. This means new and unique cloud computing vulnerabilities are going to emerge in the future. Companies face a wide range of risks with the cloud. However, the majority of breaches occur from these 10 vulnerabilities:
As per the National Security Agency (NSA), cloud misconfiguration is probably the most common vulnerability faced by organizations. Cloud misconfigurations refer to incorrect security settings in cloud applications and systems that expose them to various security risks. Misconfigurations can happen in many cloud components, including storage, networking, and access management. These misconfigurations can reveal sensitive data, lead to unauthorized access, increase the attack surface, and pose many other risks.
Common cloud misconfigurations include:
In December 2021, a security breach in Twitter API exposed the personal data of 5.4 million users. In addition, a section of this data was sold on the dark web and the rest was released for free.
Cloud computing relies heavily on application programming interfaces (APIs) for better functioning of the services. However, third-party APIs often lack proper security measures during their design, configuration, and implementation. These weaknesses can lead to injection attacks (SQL injection and XSS), data exposure, and privilege escalation.
There are many API security issues, such as:
In cloud computing, lack of visibility means that the organization struggles to monitor and track activities within the cloud environment. This includes:
Without clear visibility, it can be challenging to detect security breaches. This vulnerability can lead to delayed incident response, unauthorized access, and risk of data loss.
When cloud systems do not effectively verify user identities and manage their access controls, it can result in unauthorized users getting access to sensitive data or resources. Weak password policies and lack of multi-factor authentication are common authentication vulnerabilities.
If users are granted more privileges than necessary, it can lead to misuse or data leaks. Organizations need to ensure that only authorized users can access specific data and resources. Additionally, their identities should be verified through strong authentication measures.
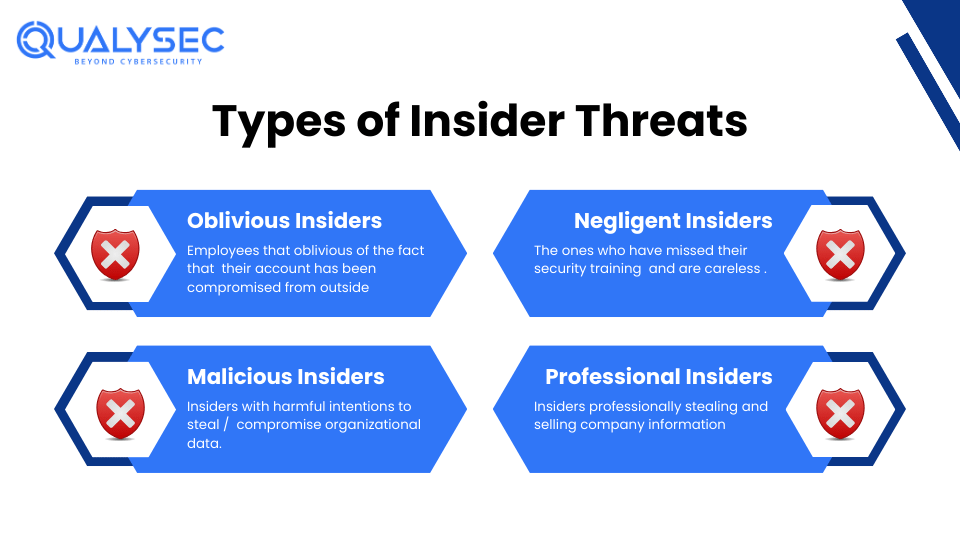
Insider threats involve risks from individuals within the organization, such as employees, contractors, or business partners, who have legitimate access to the cloud environment. These individuals might misuse their access to steal sensitive information, cause damage, or leak confidential data. Such threats can be intentional or accidental.
Shadow IT refers to the use of unauthorized cloud services and applications by employees without the knowledge or approval of the organization’s IT department. This practice can lead to security risks as these unapproved tools may not comply with the organization’s security policies. As a result, it can potentially expose sensitive data to breaches.
Shadow IT can also cause data fragmentation, where data is spread across multiple services that are not monitored.
Insecure network policies are weak or poorly configured rules and settings that manage how data travels across a network. These policies may leave networks open to security threats such as unauthorized access or data interception.
Common issues include:
Inadequate identity and access management (IAM) means that the organization cannot effectively manage user identities and control their access to cloud resources. This often leads to unauthorized access or users having more privileges than needed.
Common IAM practices include:
Strong IAM measures protect sensitive data and resources from potential breaches.
Zero-day vulnerabilities are those security flaws that are unknown to the cloud service provider. As a result, they lack the security patch or necessary remediation. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or cause harm before an organization implements a solution.
Zero-day attacks can be very dangerous because they exploit weaknesses that organizations are unaware of. Therefore, it leaves the cloud environment defenseless.
Data encryption is when data cannot be read without a proper key, even if it is accessed. Lack of encryption means that data (whether at rest or in transit) is not being encoded to prevent unauthorized access. Without encryption, sensitive information can be easily intercepted and read by attackers.
This vulnerability can lead to significant data breaches. Additionally, it can expose confidential information such as personal data, financial details, and intellectual property. Implementing strong encryption methods for both stored data and data being transferred is crucial for protecting sensitive information.

When organizations are looking to migrate or use the cloud, these are the must-have security measures for evolving cloud computing vulnerabilities.
Want to conduct cloud penetration testing to have successful business operations? Qualysec offers hybrid pen testing for in-depth analysis and comprehensive results. Talk to our expert now!

Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Conclusion
On one hand, businesses want to expand their business using cloud computing services. on the other hand, the sheer volume of cloud computing vulnerabilities is giving them nightmares. The dynamic nature of cloud environments provides unique challenges, such as misconfigurations, insecure APIs, and shadow IT. The financial and reputational impacts of these vulnerabilities can be severe, costing companies millions and breaking customer trust.
Partner with a top cybersecurity firm like Qualysec and get customized solutions to address cloud vulnerabilities. Remember, prevention is better than spending millions on recovery.
Q: What are the main security risks of cloud computing?
A: There are several security risks in cloud computing, such as:
Q: How to find cloud vulnerability?
A: The best way to find cloud vulnerabilities is by performing penetration testing. The process involves simulating real-world attacks on the cloud environment to identify where the flaws lie.
Q: What is vulnerability management in the cloud?
A: Cloud vulnerability management refers to the continuous process of identifying, classifying, prioritizing, and addressing security vulnerabilities in a cloud environment.

Pabitra Sahoo is a cybersecurity expert and researcher, specializing in penetration testing. He is also an excellent content creator and has published many informative content based on cybersecurity. His content has been appreciated and shared on various platforms including social media and news forums. He is also an influencer and motivator for following the latest cybersecurity practices.





Plot No:687, Near Basudev Wood Road,
Saheed Nagar, Odisha, India, 751007
No: 72, OJone India, Service Rd, LRDE Layout, Doddanekundi, India,560037
© 2024 Qualysec.com Disclaimer Privacy Policy Terms & Conditions


No: 72, OJone India, Service Rd, LRDE Layout, Doddanekundi, India,560037
© 2024 Qualysec.com Disclaimer Privacy Policy Terms & Conditions