Blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about data security and trust in digital transactions. While blockchain offers numerous benefits, such as transparency, immutability, and decentralization, it is vital to understand and implement robust security measures to protect this innovative technology. In this blog, we will explore the concept of blockchain security, the latest advancements in the field, best practices for building secure blockchain solutions, and the importance of blockchain penetration testing.
What is Blockchain Security?
Blockchain security refers to the protection of data and assets within a blockchain network from unauthorized access, tampering, and fraud. It involves implementing various cryptographic techniques, consensus mechanisms, and protocols to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data stored in a blockchain. By design, blockchain provides a high level of security through its decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms.
Latest on Blockchain Security
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, new security challenges and solutions emerge. Researchers and developers are constantly exploring methods to enhance security measures, address vulnerabilities, and improve privacy within blockchain networks. Regular updates and advancements in blockchain protocols, encryption algorithms, and consensus mechanisms help to bolster security and stay ahead of potential threats.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables the secure recording and verification of transactions across multiple participants in a network. It consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a set of transactions or data. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity has complete control over the network, making it resistant to manipulation and censorship.
What are the Different Types of Blockchains?
There are primarily three types of blockchains:
Public Blockchains:
| Characteristics | Examples |
| Open and permissionless | Bitcoin, Ethereum |
| High level of transparency and security | |
| Slower transaction speeds |
Private Blockchains:
| Characteristics | Examples |
| Restricted to specific participants | Hyperledger Fabric |
| Faster transaction speeds | |
| Sacrifices some decentralization |
Consortium Blockchains:
| Characteristics | Examples |
| Governed by a group of organizations | R3 Corda |
| Offers a balance between security and scalability | |
| Shared control over the network |
Best Practices for Building Secure Blockchain Solutions
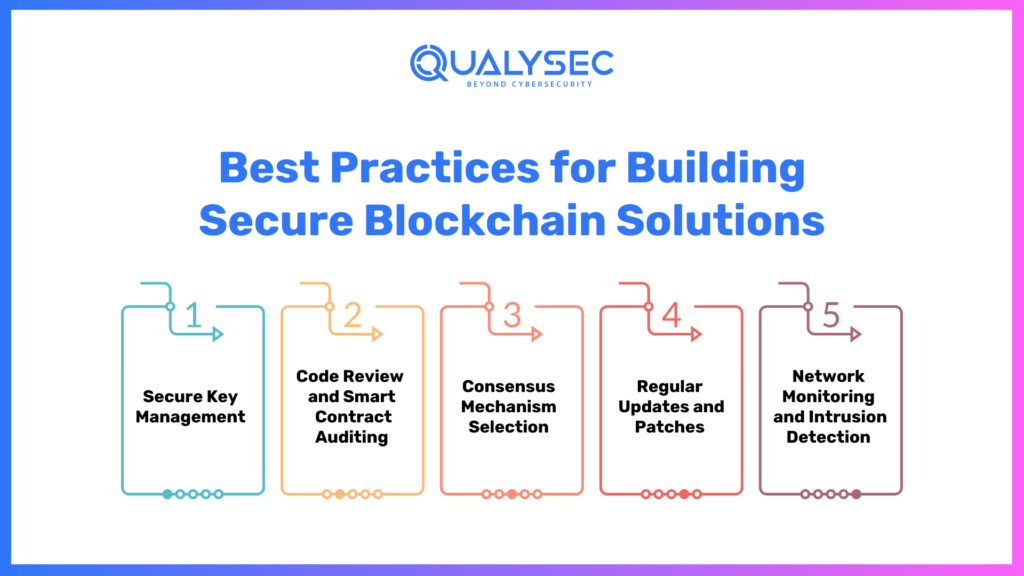
a) Secure Key Management: Implement robust key management practices to protect private keys and digital signatures.
b) Code Review and Smart Contract Auditing: Thoroughly review the code and perform security audits to identify vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
c) Consensus Mechanism Selection: Choose a consensus algorithm that aligns with the security requirements of the network.
d) Regular Updates and Patches: Keep the blockchain software up to date with the latest security patches and enhancements.
e) Network Monitoring and Intrusion Detection: Implement monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities within the blockchain network.
How Blockchain Works?
Blockchain operates through a decentralized network of nodes, each maintaining a copy of the entire blockchain. When a new transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to the network and validated by the nodes using consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Once validated, the transaction is added to a block and linked to the previous block using cryptographic hashes, creating an immutable chain of transactions.
What is Blockchain Penetration Testing?
Blockchain penetration testing is a proactive security assessment that aims to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses within a blockchain system. It involves simulating real-world attacks on the blockchain network to assess its resistance to various threats, including unauthorized access, smart contract vulnerabilities, and denial-of-service attacks. Penetration testing helps organizations strengthen their security posture and proactively address potential risks.
How to Perform Blockchain Penetration Testing?
Performing blockchain penetration testing involves the following steps:
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the scope, objectives, and rules of engagement for the penetration testing exercise.
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the blockchain network, including nodes, smart contracts, wallets, and consensus mechanisms, to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Exploit Vulnerabilities: Attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities to understand the impact and severity of each vulnerability.
- Report and Remediate: Document the findings and provide recommendations for remediation, enabling the blockchain network to strengthen its security defenses.
Professional Blockchain Security Testing by Qualysec
Qualysec is a leading blockchain security company, provider of Cybersecurity and compliance management solutions. Their platform allows companies to conduct continuous monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and compliance management across their entire IT infrastructure with the help of AI.
Qualysec follows a comprehensive methodology that combines manual and automated testing techniques and AI to ensure maximum coverage of vulnerabilities. They also provide detailed reports that include a prioritized list of vulnerabilities, along with recommendations for remediation.
They work closely with organizations to understand their unique needs. Qualysec is also a leading provider of automated vulnerability scanning solutions, offering comprehensive scanning capabilities, advanced reporting and analysis, scalability and performance, industry expertise, and continuous support and updates.
Various services offered:
- Web App Pentesting
- Mobile App Pentesting
- API Pentesting
- Cloud Security Pentesting
- IoT Device Pentesting
- AI /ML Pen-testing
Qualysec offers professional blockchain security audits to help organizations identify and mitigate security risks within their blockchain networks. Their team of experienced experts conducts thorough assessments, code reviews, and penetration testing to ensure the highest level of security for your blockchain solution
The methodologies offered by Qualysec for Blockchain Security Testing are particularly beneficial for businesses that must adhere to industry rules or prove their dedication to security to clients and partners. So, by opting for Qualysec as a reliable service provider, businesses can ensure the safety of their web applications.
Hence, choose Qualysec for a comprehensive and reliable vulnerability scanning report. Also, their penetration testing guide will help you make informed decisions and understand the various factors that impact the cost. Hence, protect your assets and enhance your security posture by choosing us.
Conclusion
It is a crucial aspect of harnessing the full potential of blockchain technology. By understanding the foundations of blockchain security, keeping up with the latest advancements, implementing best practices, and conducting regular penetration testing, organizations can build robust and secure blockchain solutions. With the right security measures in place, blockchain technology can continue to revolutionize various industries while ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of digital transactions.
There are several types of Security Audit solutions one might need, and vulnerability scanners, including network scanners, host scanners, application scanners, cloud scanners, and wireless scanners. Each with its own set of benefits and use cases. Additionally, both internal and external vulnerability scanners are necessary. These cover all devices and systems that are accessible from within and outside of an organization’s network. We are always ready to help, talk to our Experts and fill out your requirements.
FAQs
Q1. Can blockchain be hacked?
A. While blockchain technology is highly secure, it is not entirely immune to hacking. Blockchain networks can be vulnerable to attacks such as 51% attacks, smart contract vulnerabilities, and social engineering attacks. However, the decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain makes it significantly more challenging to compromise compared to centralized systems.
Q2. What is the role of cryptography in blockchain security?
A. Cryptography plays a vital role, by ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data. Techniques such as public-key cryptography, hash functions, and digital signatures are used to secure transactions, verify identities, and protect sensitive information within a blockchain network.
Q3. How does blockchain ensure data integrity?
A. Blockchain ensures data integrity through the use of cryptographic hash functions. Each block in the blockchain contains a hash of the previous block, creating a chain of blocks linked together. Any tampering with the data within a block would result in a change in its hash, breaking the chain and indicating that the data has been compromised.
Q4. What are the common vulnerabilities in blockchain networks?
A. Common vulnerabilities in blockchain networks include smart contract bugs, insufficient validation and authorization mechanisms, consensus algorithm weaknesses, insecure key management practices, and social engineering attacks targeting users or administrators.
Q5. Is blockchain completely secure?
A. While blockchain technology provides a high level of security, it is not immune to all types of attacks. Security breaches can occur due to vulnerabilities in the implementation, human errors, or targeted attacks. It is essential to follow best practices, regularly update the blockchain software, and conduct security audits and penetration testing to maintain a robust and secure blockchain ecosystem.






















![Top 20 Network Security Companies in USA [2025 Updated List]](https://qualysec.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Top-20-Network-Security-Companies-in-USA-2025-Updated-List-scaled.jpg)































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments