The digital world has given a lot of scope for businesses to expand but has also opened more opportunities for cyberattacks. To prepare and mitigate such risks, penetration testing is essential in finding vulnerabilities in current security measures. Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) offers a set of guidelines that tell what should happen in a pentest.
Over 75% of global companies perform penetration testing to measure their security status and compliance reasons. Another study shows that since 2001, financial losses due to cybercrimes have grown 570 times (from $2,000 to nearly $1.2 million per hour). The total loss due to cybercrimes is approximately $36.4 billion in 22 years.
Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) helps companies of all sizes to properly execute effective penetration testing. In this blog, we will discuss PTES in detail, what are its sections so that you know what to expect from a penetration test.
What is Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES)?
PTES is a standardized set of rules that guides all penetration testing processes. In fact, penetration testing has been practiced for a while now, but initially, there weren’t as many rules and regulations in place guiding pen testers. Since businesses did not know what to expect from a pentest, the results were not very consistent. Ethical hacking was still considered hacking that lacked oversight and had little to no quality control.
Then in 2009, a group of cybersecurity experts created the Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES) to address these issues. PTES is a type of penetration testing methodology that provides rules and guidelines that help businesses know what to expect from penetration testing. In addition to that, it also includes how to evaluate penetration testing and whether businesses should conduct penetration testing by themselves or hire third-party service providers.
Before we dive into the details of PTES, let’s understand penetration testing and why it is important.
Our experts at Qualysec have helped secure fintech, SaaS, and enterprise systems across 25+ countries. Manual + Automated Pentesting. No false positives. Actionable reports.

What is Penetration Testing and Why is it Required?
Penetration testing or pentesting is a security testing measure where a cybersecurity professional attempts to find and exploit vulnerabilities in a digital infrastructure. They simulate a real-world attack on the system to identify weak spots in its defenses, which actual attackers or hackers could take advantage of.
It is like a bank hiring someone as a thief and trying to break into their building and access their vault. If the thief succeeds and gets inside the vault, the bank will get valuable insights into their security and which areas need improvement.
Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) allows these third-party testers to conduct a systematic pentesting process for a particular IT environment.
Benefits of Penetration Testing:
- Identify Security Vulnerabilities: As mentioned above, penetration testing detects all those security flaws through which hackers or attackers could gain access to the digital environment.
- Check your Current Security Measures: By doing penetration testing, you can check how strong your current security posture is against potential cyber threats.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Certain industry standards make it mandatory to perform penetration testing to comply with their regulation. These standards include PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 27001, etc.
- Secure Digital Assets from Data Breaches: In 2023, the global average cost of a data breach was $4.45 million. Penetration testing helps find security gaps through which data breaches can occur.
- Maintain Trust Among Clients and Partners: Any type of cyber attack or data breach can significantly hamper the reputation of the company. Therefore, penetration testing is necessary to have strong security.
Are you looking to strengthen your security measures for potential attacks? Do you want compliance with the required industry standards? Book a consultation with us for the best penetration testing service now!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Different Types of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing can be performed in three different ways following the penetration testing execution standard (PTES). However, the type of penetration testing depends on the amount of information provided by the organization for the tested environment. These are:
- White Box Pentesting: Maximum information is given on the tested environment.
- Black Box Pentesting: No information is given on the tested environment.
- Grey Box Pentesting: Limited information is given on the tested environment.
7 Sections of Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES)
Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) consists of seven main sections that cover all aspects of penetration testing. The purpose of PTES is to offer clear technical guidelines to help organizations understand what to expect from a penetration test and guide them throughout the process. The standard doesn’t include every single aspect or scenario that might occur during a pen test. Instead, it focuses on a basic set of rules that outline the minimum requirements for all pen tests.
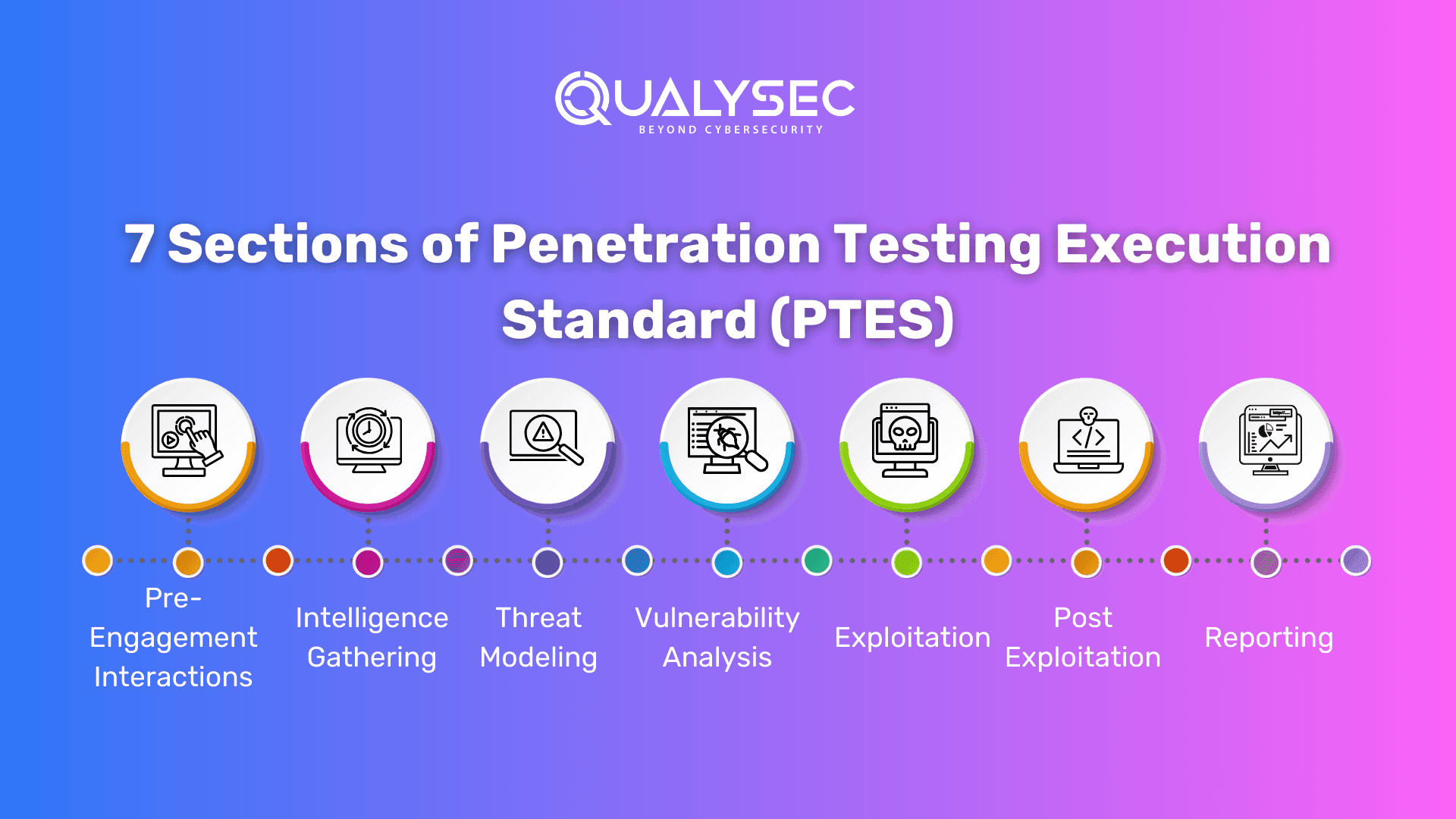
1. Pre-Engagement Interactions
The first section of the Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) deals with the processes involved before starting the pen test. It includes the interactions between the client or organization and the pen testing team, starting from the final negotiation till the pen testing begins.
The guidelines PTES has set for this section are:
Goals of the Pen Test:
Both the testing team and the client establish specific goals for the pen test. The PTES suggests them to prioritize the following:
- The primary goal of the pen test should be security
- The secondary goal should be compliance and legal accountability
Scope of the Analysis:
After setting clear goals, the pen testing team and the client must agree on the scope and scale of the testing. Here are the elements that need to be considered:
- Identifying the areas to be analyzed
- Deciding on the quality and quantity of the test procedures
- Duration and time of the test
Rules of Engagement:
The testing team and the client should also establish clear expectations and limitations, regarding what behaviors are not allowed. This includes:
- Defining particular resources that are “off limits”
- Setting boundaries for social engineering scams
Once these pre-engagement meetings are done and goals are set, then the pen testers can start the first stage of the penetration test, i.e. reconnaissance.
2. Intelligence Gathering
During this phase, the pen testers gather information through sources available publicly and perform basic searches following the rules of engagement. This process, also known as open-source intelligence (OSINT), collects all the information that could be useful for the later stages of the testing process.
The intelligence-gathering stage includes three levels of reconnaissance:
- Level 1: This is a basic level that focuses on the compliance requirement and can often be automated. It only collects the required information about a company’s required security measures.
- Level 2: Going beyond basic requirements, this level explores the organization’s best practices and priorities beyond compliance.
- Level 3: In this advanced level, the pen testers dive deep into the organization’s complexities and business relationships to discover hidden information.
After gathering the necessary information, the pen testing team will then begin planning potential targets for attack.
3. Threat Modeling
After gathering intelligence and understanding the target’s security measures, the next section in the penetration testing execution standard (PTES) is threat modeling. This involves identifying which assets are most likely to be targeted by ethical hackers and what resources might be used to attack them. The pen testers use all the information that has been gathered to plan the attack.
The PTES has outlined a distinct 4-step process for threat modeling:
- Gathering Documentation: Collecting relevant documents and information about the target’s assets and resources.
- Categorizing Assets: Identifying primary and secondary assets that are most valuable or vulnerable.
- Categorizing Threats: Determining primary and secondary threats that pose risks to the assets.
- Mapping Threat Communities: Connecting threats to the assets they target and identifying potential attackers.
By identifying valuable assets and potential vulnerabilities, this section lays the foundation for the next phase, which involves analyzing how to exploit these threats.
4. Vulnerability Analysis
In the vulnerability analysis section, the pentester gathers more information related to specific flaws or weaknesses in the client’s cybersecurity systems. This section uses the information gathered earlier to identify and prioritize specific vulnerabilities.
There are two main modes of vulnerability analysis:
- Passive: This involves automated or minimal activity by the ethical hacker, such as Metadata analysis or traffic monitoring analysis.
- Active: This requires more extensive in-depth activity by the attacker. For example, scanning port-based networks, application flaw scanning, and attempting directory listing or “brute force”.
By using these methods, the attacker creates a targeted list of vulnerabilities to focus on during the attack.
This marks the end of the planning stages, and the ethical hacker is now ready to begin the attack itself.
5. Exploitation
All the preparation done in the previous sections leads to the exploitation phase, which is considered the most important step of penetration testing. This is because it is where the actual attack takes place. The attacker or pen tester will use all the information available to carry out targeted attacks. These attacks may vary depending on the goals outlined in the pre-engagement interactions.
However, there are some general principles set by the penetration testing execution standard (PTES) to guide the attacker:
- Stealth: They aim to avoid detection by security systems.
- Speed: They move quickly to infiltrate the client’s systems.
- Depth: They delve deeply into the systems to find vulnerabilities.
- Breadth: They explore as many paths of attack as possible.
The goal of the attacker is to remain undetected for as long as possible, possibly throughout the entire offensive practice. By following these principles, the pen tester will find maximum weaknesses and get maximum insights into the client’s security system.
6. Post Exploitation
In the post-exploitation phase, the hacker shifts to a different type of attack after penetrating and exploring the full control of any seized systems. This step is vital in some pen tests, especially those focused on internal analysis.
During this phase, the hacker’s goals depend on the agreed scope with the client. However, the main objectives typically involve:
- Identifying the value and functions of compromised resources.
- Creating additional vulnerabilities for potential future exploitation.
- Maintaining ongoing control over the compromised resources.
- Exiting without being detected.
Both parties need to have clear expectations for this stage. If the exploitation reveals deeper weaknesses that the client didn’t see previously, it can lead to changes in scope and potential conflicts.
However, if the initial discussions were thorough, this stage sets the stage for the final step: reporting.
7. Reporting
The final section, reporting, is a straightforward process if the earlier stages have been completed properly.
The client documents all the steps taken during planning and attacking, and this information is compiled into a report. The report includes:
- Assessment of security posture and ranking of risks.
- Breakdown of the risks discovered.
- Detailed plan for fixing any issues.
Once the report is complete, the pen test concludes. This is where the PTES guidelines come to an end.
Want to see what a sample penetration testing report looks like? Follow the link and download one now!
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Penetration testing execution standard (PTES) is important because pen testing is complex, challenging, and sensitive. That’s why it’s crucial to have qualified professionals to ensure a smooth pen testing process for your business.
Conclusion
The Penetration Testing Execution Standard (PTES) provides essential guidelines for conducting effective penetration tests. With the increasing risks of cyberattacks, businesses need to assess their security measures regularly. PTES offers a structured approach to identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities so that you get thorough security testing and comprehensive analysis.
At Qualysec Technologies, we follow penetration testing execution standard (PTES) guidelines to provide the best in the world penetration testing services. Our expert cybersecurity professionals can create a customized testing plan as per your security requirements.
You can choose anything from the following list of services we provide:
- Web application pentesting
- Mobile app pentesting
- Cloud pentesting
- Network pentesting
- IoT device pentesting
- API pentesting
- Source code review
FAQs
Q: What is the execution of a penetration test?
A: The penetration testing execution standard (PTES) offers the guidelines that should be checked during a penetration test. It includes what type of tests should be performed, specific details on each test, and what clients should expect from a pentest.
Q: What is the standard of penetration test?
A: The penetration testing execution standard (PTES) consists of 7 sections covering every key part of a pentest, created to outline what is required for an effective pentest. These sections are:
- Pre-Engagement Interactions
- Intelligence Gathering
- Threat Modeling
- Vulnerability Analysis
- Exploitation
- Post Exploitation
- Reporting
Q: Who created PTES?
A: The penetration testing execution standard (PTES) was created in 2009 by a team of six information security consultants. It was started to address the lack of quality control in the penetration testing process.
Q: What are the benefits of PTES?
A: PTES or penetration testing execution standard is a penetration testing methodology that allows pen testers to evaluate different environments consistently and entirely.




















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments