In 2017, 83000 data protection officers (DPOs) were assigned to data protection. Now, there are more than 500,000! The 700% increase in demand for DPOs has been mostly ascribed to GDPR compliance requirements. Can you imagine?
GDPR, or General Data Protection Regulation, is regarded as one of the most stringent data protection regulations ever enacted, with a detailed set of standards. There is much to catch up on under GDPR, including the principles, individual rights, breach notification obligations, paperwork, and more.
In this blog, we will demystify the criteria in an understandable language. Continue reading to learn quickly about GDPR compliance fundamentals and how Qualysec can assist you.
Understanding the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the world’s most stringent privacy and security regulation. Though it was designed and passed by the European Union (EU), it imposes duties on enterprises worldwide as long as they target or collect data about EU citizens. The regulation went into force on May 25, 2018. Furthermore, GDPR compliance will impose heavy fines on anyone who breaks its privacy and security regulations, with penalties ranging in the tens of millions of euros.
With the GDPR, Europe is establishing its hard stance on data privacy and security at a time when more individuals are entrusting their data with cloud services, and breaches are a regular occurrence. GDPR compliance is a far-reaching proposition, especially for small and medium-sized organizations (SMEs), due to the regulation’s scale, breadth, and relative lack of specialty.
The GDPR provides extensive definitions of legal words. The following are some of the most notable ones:
-
- Personal Data: This refers to any information about an individual who may be directly or indirectly identified. Furthermore, personal data may include location information, race, gender, biometric data, religious beliefs, online cookies, and political viewpoints.
- Data Processing: GDPR compliance requirements necessitate any action taken on data, whether automatic or human. The literature provides examples of tasks such as gathering, recording, organizing, structuring, storing, utilizing, and wiping data.
- Data Subject: The individual whose information is processed. These are your clients or website visitors.
- Data Controller: This person decides why and how personal data will be handled. Furthermore, this is for you if you are a business owner or employee who works with data.
- Data Processor: This is a third party that processes personal data on behalf of the data controller. The GDPR compliance includes specific requirements for certain persons and organizations.
Are you a business looking for a GDPR service provider? Your wait has come to an end. Schedule a FREE call with our expert consultant to learn how to achieve GDPR compliance.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Why Businesses Need to Pay Attention to GDPR?
While worries about data privacy have existed for many years, many market factors are currently bringing the problem to the forefront:
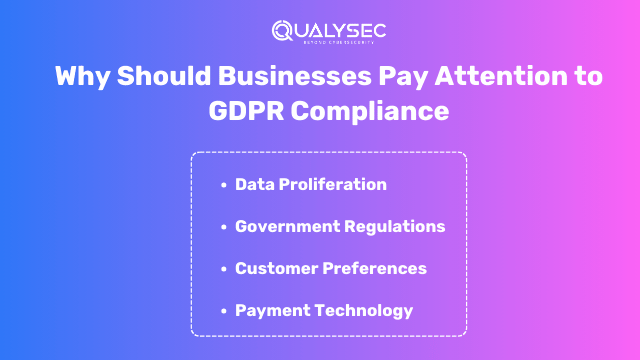
1. The Proliferation of Data
As new techniques, platforms, and applications develop, organizations have to handle an increase in data sources combined with a growth in the volume of data. Furthermore, with more consumer data scattered among providers, personal information is more likely to be exposed.
2. New Government Regulation
In addition to complying with known data privacy requirements such as GDPR compliance and HIPAA, companies must keep up with several new regulations scheduled to be enacted in the coming months.
3. New Customer Preferences
According to recent research, 68% of consumers feel businesses profit more from data use than customers. Furthermore, customers becoming more aware of how data is gathered and utilized may be more likely to distrust firms and restrict the amount of information they are ready to contribute.
4. New Payment Technology
The digitization of trade accelerates payment innovation more than ever. Customers are becoming more comfortable with various innovative payment methods, such as digital wallets, contactless payments, purchase now, pay later, and other local options. These new payment systems raise significant data privacy concerns for enterprises. And the method you use to safeguard data for one solution may differ.
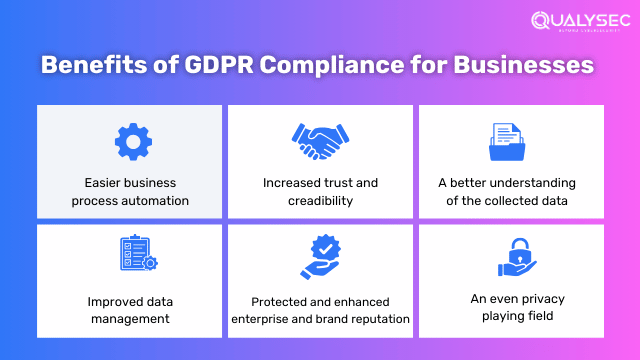
The Advantages of Following GDPR Compliance for Businesses
While GDPR compliance may appear to be an onerous endeavor for organizations, there are various perks and opportunities:
- Enhanced consumer trust: GDPR compliance fosters trust and credibility among customers by demonstrating a commitment to preserving their privacy rights.
- Competitive advantage: GDPR compliance can help firms differentiate from non-compliant rivals, particularly when dealing with EU clients.
- Streamlined data processes: The GDPR pushes organizations to rethink their data operations by introducing tools like data mapping, permission management, and privacy impact assessments. This can increase productivity, improve data governance, and reduce data breaches.
- Improved data security: GDPR compliance requires organizations to take strong measures to protect personal data from breaches or unauthorized access, strengthening overall data security procedures
15 GDPR Compliance Requirements for Businesses to Know About
Some essential concepts form the basis of GDPR compliance requirements, which establish rules for the right processing and management of personal data and ensure that personal data is treated lawfully and equitably. The following are the primary GDPR principles every business should know:
1. Purpose Limitation
The GDPR limits the use of data for particular activities. According to the GDPR compliance, data is only “collected for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes” under this purpose constraint.
The purposes for processing data must be explicitly defined. Furthermore, they must be explicitly stated to persons via a privacy notice. Finally, you must strictly adhere to them, restricting data processing to the objectives specified.
2. Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
When processing personal data, you should have a valid basis for doing so. GDPR refers to this principle as lawfulness. Reasons for processing data may include:
-
- The user has permitted you to do so.
- You must do it to fulfill a contract.
- It is required to meet a legal responsibility.
- To preserve the vital interests of a natural person.
- It is a public work completed in the public interest.
You can demonstrate that you have a legitimate interest not outweighed by the data subject’s rights and interests.
Fairness, as defined in the GDPR compliance, is synonymous with lawfulness. It means you should refrain from intentionally withholding information about what or why you collect data. Furthermore, fairness means that you will not mishandle or abuse the information you acquire.
Transparency is intimately related to fairness. Transparency is being transparent, open, and honest with data subjects about who you are, why, and how you process their data. By following it, you demonstrate fairness to your data subjects.
3. Data Minimization
Only obtain the minimum quantity of data required to fulfill your objectives. This is the GDPR’s concept of data minimization. For example, to acquire subscribers for your email newsletter, you should request the information required to distribute the emails. Avoid collecting personal information such as phone numbers or home addresses that aren’t directly relevant to your objective.
4. Accuracy
It is up to you to ensure the accuracy of the information you gather and keep. Set up checks and balances to fix, amend, or delete inaccurate or incomplete data that arrives. Schedule periodic audits to ensure the cleanliness of stored data.
5. Integrity and Confidentiality
The GDPR compliance requires you to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of the data you gather, protecting it from internal and external threats. This requires foresight and deliberate diligence. Furthermore, data must be protected from illegal processing and accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
6. Accountability
GDPR authorities understand that an entity might claim to be following all of the requirements while not doing so. That’s why they need accountability: You must have suitable methods and records in place to demonstrate your compliance with the data processing principles. Supervisory agencies might request this evidence at any moment. Documentation is essential here. It generates an audit trail you and the authorities may use to show accountability.
7. Storage Constraint
According to the GDPR, you must explain how much time you store each piece of data. Setting data retention periods is an excellent way to satisfy this storage limitation requirement. In addition, set a time limit after which you will anonymize any data you are not actively utilizing.
8. Data Breach Notification
The GDPR compliance requirements explicitly define deadlines for rapid notification of data breaches. As the responsible authority, data controllers or data protection officers shall notify DPA (Data Protection Authorities) in the relevant EU state of the breach as soon as they become aware and no later than 72 hours after the event. DPAs can then launch investigations and order corrective actions. In the event of a high-risk breach, data subjects should be promptly notified.
9. International Data Transfers
Any data transmission outside the European Union is considered an international data transfer and must meet specific regulations. The European Union will issue an ‘adequacy judgment’ for the nation that receives the data after assessing the robustness of its data protection laws and protections. Contractual clauses or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) isssue in instances when adequacy determinations are not applicable.
10. Cooperation with Supervisory Authorities
Cooperation with supervisory authorities is crucial to GDPR, emphasizing the need to collaborate with data protection regulations. Organizations should be prepared to give information and help to supervisory authorities when needed. Furthermore, this cooperation includes responding to questions, accessing relevant records, and reporting to authorities about data breaches within 72 hours. Cooperation allows authorities to efficiently monitor compliance and enforce GDPR compliance requirements. Timely and honest contact with regulatory agencies is critical for demonstrating commitment to data protection and addressing difficulties.
11. Consent
According to the (General Data Protection Regulation) GDPR compliance in cyber security, consent indicates that a person has been granted permission for their personal information to be collected, processed, and disclosed. Furthermore, this consent must be freely provided, specific, and informed, and the individual must have indicated their approval by clicking buttons or checking boxes. Consent regards as one of the legitimate bases and business utilize in limited circumstances.
12. Record of Processing Activities
Records of processing operations are extensive documentation kept by Data Controllers such as a GDPR compliance service provider and Processors to describe subject categories, data retention periods, security measures, and any international data transfers. Maintaining these documents is a critical component of GDPR accountability and transparency. In addition, they give a comprehensive picture of an organization’s data processing operations, allowing supervisory authorities and Data Subjects to understand how to handle Personal data.
If you want to learn about how documentation works, click below to download a sample report that can help your business achieve GDPR compliance.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Challenges in GDPR Compliance Regulations
Examine the issues that blockchain, AI, and face recognition pose to GDPR compliance. Here are the challenges in achieving GDPR compliance regulation:
1. AI’s Opacity
It is challenging to guarantee that AI, which has great capabilities, conforms with GDPR. GDPR requires openness, but AI can draw erroneous conclusions. It isn’t easy to understand why an intelligent computer operates the way it does.
2. Face Recognition and Privacy
Facial recognition technology necessitates a delicate balance between privacy and innovation since it raises concerns about consent, profiling, and the legal use of biometric data.
3. Blockchain’s Immutability
While blockchain assures data integrity, its immutability complicates GDPR’s “right to erasure” due to the difficulty of erasing data without jeopardizing the technology’s integrity.
4. Cross-border Data Transfers
Because developing technologies are global, cross-border data transfers must be carefully considered in light of GDPR’s limits on moving personal data outside the EEA.
5. Lack of legal precedents
The dynamic nature of technology creates a gap in legal frameworks, with questions about how GDPR compliance relates to specific AI algorithms, face recognition, and blockchain implementations, necessitating a balance between innovation and compliance.
How Qualysec Help with Achieving GDPR Compliance?
GDPR compliance is rigorous and thorough. Companies spend a significant amount of effort dealing with ambiguity and mistranslation. However, non-fulfillment leads to reduced market access and missed economic prospects. That’s perhaps why 27% of firms have paid more than half a million dollars to comply with GDPR.
However, the number did not need to be that large. The most effective approach to achieve GDPR compliance is utilizing GDPR consulting companies such as Qualysec Technologies. We are the leading process-based penetration testing company that has helped businesses achieve GDPR with our hybrid approach to testing.
Qualysec follows this approach to combine manual effort and automated testing to find accurate results and zero false positives. We follow industry best practices and methodologies NIST 800 to create a comprehensive, developer-friendly report.
With our third-party pentest report, your business can easily achieve GDPR compliance requirements and others such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, ISO 27001, etc. To get professional help, contact us today or visit Qualysec Technologies.
Conclusion
The GDPR compliance requirements have not only changed the way organizations function but have also emphasized the need for personal data protection. Compliance with GDPR is critical for businesses seeking to establish consumer trust, maintain a competitive edge, and improve data security policies.
Furthermore, by adhering to the regulation’s fundamental principles and taking the prescribed actions, companies may negotiate the intricacies of GDPR, reducing risks and establishing themselves as responsible guardians of personal data in today’s digital era.
Embracing GDPR compliance is a legal requirement and a chance for businesses to grow and build a better, more secure data environment for everyone. For professional help, reach out to us for better achievement.
FAQ:
1. Does GDPR apply to private companies?
GDPR primarily governs data processing activities involving solely EU citizens’ and residents’ data conducted by any public or private entity globally. Furthermore, there are two exceptions to GDPR. If you gather personal data solely for personal reasons or to invite people to family activities, GDPR does not apply to you.
2. Why is GDPR important for cyber security?
The GDPR mandates that personal data be processed securely using suitable technological and organizational methods. The Regulation does not require precise cyber security measures; rather, it expects you to take ‘appropriate’ action.
3. What is the difference between GDPR and PDPA in India?
The DPDPA does not apply to personal data made publicly available by the data principals or in response to a legal necessity. No-action gaps: The DPDPA only applies to “digital personal data,” but the GDPR applies to all personal data, whether digital or not.
4. Which Business Needs GDPR COMPLIANCE?
Any firm that keeps or processes personal information on EU people within EU states must comply with the GDPR, even if it does not have a corporate presence in the EU. Companies obliged to comply must meet specific requirements, which include A presence in one of the European Union countries.

















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments