In an era where the digital landscape is constantly expanding, the role of cyber security compliance audit in ensuring regulatory compliance has become paramount. The evolving threat landscape and the increasing cyber-attacks underscore the critical need for businesses to fortify their defenses.
This blog delves into the intricate connection between cybersecurity audits and regulatory compliance, shedding light on these audits’ pivotal role in safeguarding organizations. We’ll also cover the benefits, challenges, and best practices. So, keep reading!
Understanding Cyber Security Compliance
Any business that works with data, which is the majority of them, or has an internet-connected edge must prioritize cybersecurity. Accessing and transferring data from one location to another exposes enterprises to possible intrusions.
At its foundation, cyber security compliance is conforming to norms and regulatory obligations established by an agency, law, or authoritative group. Organizations further must accomplish compliance by using risk-based controls to ensure information confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA).
Information must be safeguarded when it is kept, processed, integrated, or transported. Cyber security compliance audits are a huge concern for businesses since industry standards and obligations often overlap, causing confusion and additional labor.
Importance of Cybersecurity Compliance: Why Does it Matter?
No firm is immune to cyberattacks; thus, adhering to cybersecurity standards and laws is critical. It may significantly impact an organization’s capacity to succeed, run smoothly, and adhere to security policies.
Cybersecurity policies are critical to ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of digital platforms. They offer a disciplined strategy for managing possible risks and protecting against cyber-attacks. Furthermore, compliance with these standards protects firms from legal penalties, improves their reputation, and fosters consumer trust.
Here are the reasons why IT security compliance matters:
- Ensures businesses comply with data protection laws, avoiding legal repercussions.
- Maintains customer trust by safeguarding sensitive information and preventing damage to brand reputation.
- Mitigates the financial impact of data breaches, avoiding hefty fines and recovery costs.
- Demonstrates commitment to cybersecurity, fostering competitive advantage in the market.
- Guarantees the protection of personal and sensitive data, aligning with privacy regulations.
- Identifies and addresses vulnerabilities, minimizing the risk of cyber threats and attacks.
- Aligns with specific industry regulations, ensuring adherence to sector-specific cybersecurity standards.
- Safeguards against disruptions, maintaining seamless business operations.
- Enhances customer confidence in digital transactions and interactions.
- Meets international cybersecurity standards, facilitating entry into global markets.
Are you a business looking for services that can help in achieving compliance requirements? We at Qualysec offer the best process-based penetration testing solutions. Consult our security experts for Free today!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Types of Cyber Security Compliance
It is critical to understand what main cybersecurity rules exist and to determine the appropriate cybersecurity policy for your sector. The following are some prevalent policies that affect cybersecurity and data professionals equally. These assist your firm in being compliant, depending on your industry and the places where you do business.
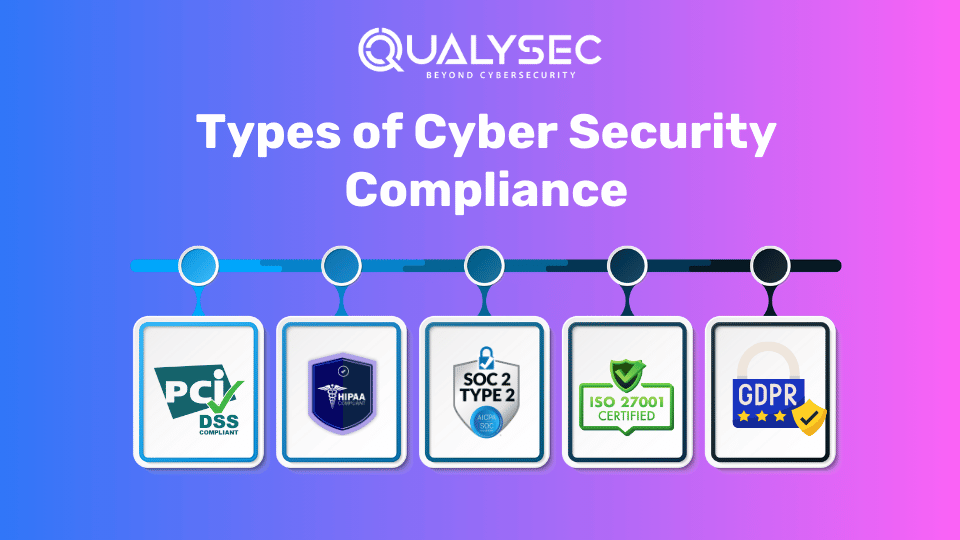
PCI DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) sets regulatory guidelines for enterprises to guarantee that credit card information is safe. To be compliant, organizations further must confirm their compliance every year. All criteria put forth to secure cardholder data are based on these six principles:
- Create and manage a secure network.
- Protect cardholder data.
- Maintain a vulnerability-management program.
- Implement tight access controls.
- Regularly monitor and test networks.
- Maintain an information security policy.
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, or HIPAA, is a law that protects the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of PHI. Furthermore, HIPAA is commonly used in healthcare contexts, including:
- Healthcare providers
- Health Care Clearinghouses
- Health Care Plans
- Business experts who often handle PHI
- The entities mentioned above must comply with HIPPA and adhere to its privacy rules.
SOC 2
System and Organization Control 2 (SOC 2) provides rules for handling client records based on five trust service principles:
- Safety
- Availability
- Process integrity
- Secrecy
- Privacy
SOC 2 reports are unique to the institution that produces them, and each organization creates its controls to comply with one or more of the trust criteria. While SOC 2 compliance is not mandatory, it is critical in safeguarding data for software as a service (SaaS) and cloud computing providers.
GDPR
GDPR is the General Data Protection Regulation established by the European Union (EU) in 2018. The GDPR establishes requirements for firms that collect data or target persons in the EU, even if they are based outside the EU or its member states. The GDPR has seven principles, including:
- Lawfulness
- Accuracy
- Data minimization
- Fairness and transparency.
- Purpose limitation
- Storage constraint.
- Integrity, secrecy, and security
- Accountability
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a standard that outlines a set of best practices and processes that businesses may use to manage information security risks and protect sensitive data. Furthermore, the standard requires enterprises to develop and apply a process for identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks. Furthermore, it requires enterprises to implement several security protocols to mitigate these threats.
Also read: Demystifying ISO 27001 Penetration Testing
What is a Cyber Security Compliance Audit ?
A Cyber security Compliance Audit systematically examines an organization’s adherence to established cybersecurity standards, regulations, and policies. Furthermore, this audit assesses the effectiveness of the organization’s security measures, policies, and procedures to ensure they align with industry-specific and regulatory cybersecurity requirements.
The goal is to verify that the organization’s security practices adequately protect sensitive data, mitigate cyber threats, and maintain compliance with relevant laws and industry standards. The audit typically includes evaluating aspects such as data protection protocols, access controls, incident response plans, and overall cybersecurity infrastructure to identify any gaps or areas of improvement in compliance.
The Role of Cyber Security Compliance Audit
The Impact on Businesses
In the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, regulations play a pivotal role in shaping how businesses handle sensitive information and safeguard their digital assets. Governments and industry bodies worldwide have established a framework of rules and standards to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Furthermore, understanding the impact of these regulations is crucial for businesses to navigate the intricate web of compliance requirements:
1. Legal Implications
The regulatory landscape in cybersecurity encompasses many laws that dictate how organizations handle and protect data. From the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, non-compliance can lead to severe legal consequences, including hefty fines and legal actions.
2. Reputation Damage
Beyond legal repercussions, failing to comply with cybersecurity regulations can damage a company’s reputation. News of a data breach or non-compliance can erode customer trust, resulting in business loss and tarnishing the brand image. Furthermore, maintaining a positive reputation is integral for sustained success in today’s interconnected world.
3. Economic Impact
Non-compliance can have significant economic ramifications. Fines and legal expenses aside, recovering from a cyber-attack or data breach can be astronomical. Furthermore, this includes the expenses incurred in resolving the incident, compensating affected parties, and implementing measures to prevent future occurrences.
Consequences of Non-Compliance in the Cybersecurity
The consequences of failing to adhere to cybersecurity regulations extend far beyond financial penalties. Businesses further face a range of challenges that can cripple operations and compromise their competitive edge.
1. Data Breaches
Non-compliance increases the likelihood of data breaches, exposing sensitive information to unauthorized entities. Furthermore, this puts customer data at risk and can lead to intellectual property theft, jeopardizing a company’s proprietary information.
2. Legal Action
Regulatory bodies are empowered to take legal action against organizations that neglect cybersecurity mandates. Furthermore, legal consequences may include fines, sanctions, and even temporary or permanent bans on conducting certain business activities.
3. Operational Disruptions
The fallout from non-compliance can disrupt day-to-day operations. Furthermore, regulatory investigations, legal proceedings, and efforts to rectify security vulnerabilities can divert resources and attention away from core business activities.
The Need for a Proactive Compliance Strategy
Organizations must adopt a proactive compliance strategy to navigate the complex web of cybersecurity regulations and mitigate the associated risks. More than waiting until a breach occurs or reacting only after non-compliance is identified is required in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
1. Risk Assessment
Conducting regular risk assessments allows organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities and assess their exposure to cyber threats. Furthermore, this proactive approach enables the development of strategies to address and mitigate identified risks.
2. Continuous Monitoring
Rather than viewing compliance as a one-time task, organizations should embrace continuous monitoring of their cybersecurity posture. This involves regularly assessing and updating security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats and regulatory changes.
Also Read: How to Choose the Best Cybersecurity Audit Company
How Do Cybersecurity Audits Ensure Adherence to Regulatory Requirements?
In the complex cybersecurity landscape, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements is a multifaceted challenge that demands strategic planning and rigorous implementation. Furthermore, cybersecurity audits emerge as a critical tool in bridging the gap between regulatory mandates and effective organizational security. This section explores how cybersecurity audits play a fundamental role in ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
1. Comprehensive Evaluation of Security Measures
Cybersecurity audits thoroughly examine an organization’s security infrastructure, policies, and procedures. Furthermore, this comprehensive evaluation ensures that every aspect of the cybersecurity framework aligns with the specific requirements laid out by relevant regulations. This process includes scrutinizing access controls, data encryption practices, and incident response plans.
2. Identification and Mitigation of Vulnerabilities
One of the primary objectives of cybersecurity audits is to identify vulnerabilities within an organization’s systems and networks. Furthermore, by conducting regular audits, businesses can proactively discover weaknesses that malicious actors could exploit. Addressing these vulnerabilities on time enhances security and ensures compliance with regulations that mandate robust protective measures.
3. Validation of Data Protection and Privacy Measures
Many cybersecurity regulations focus on the protection of sensitive data and user privacy. Cybersecurity audits delve into the measures in place to secure and safeguard such information. Furthermore, this includes assessing data storage practices, encryption methods, and protocols for handling personally identifiable information (PII). By validating these measures, audits contribute to cybersecurity regulatory compliance in GDPR and HIPAA.
4. Documentation and Record-Keeping
Regulatory bodies often require organizations to maintain detailed records of their cybersecurity activities. Furthermore, audits ensure that proper documentation is in place, covering security policies, incident response plans, and training programs. This meticulous record-keeping not only aids in demonstrating compliance but also serves as a valuable resource for continuous improvement.
5. Alignment with Industry Standards
Cybersecurity audits are designed to meet regulatory requirements and align with industry best practices and standards. Adhering to widely recognized standards, such as ISO 27001 or NIST Cybersecurity Framework, not only enhances the overall security posture but also positions the organization favorably in terms of cybersecurity regulatory compliance.
6. Continuous Improvement through Feedback
Cybersecurity audits provide a feedback loop that enables organizations to continuously improve security measures. By identifying areas for enhancement and addressing gaps, businesses can iteratively strengthen their cybersecurity posture, ensuring sustained compliance with evolving regulatory landscapes.
Cyber security compliance audit serve as a bridge between regulatory requirements and effective security practices. Furthermore, through their comprehensive penetration testing, identification of vulnerabilities, validation of data protection measures, meticulous documentation/ reporting, alignment with industry standards, and continuous improvement initiatives, audits play a crucial role in ensuring organizations meet and exceed the cybersecurity expectations set by regulatory bodies.
Key Components of Cybersecurity Audits
Here are the key aspects of cybersecurity audits that every business should know:
1. Foundation of Security
- Risk assessment forms the foundation of a cybersecurity audit, identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Enables organizations to prioritize security efforts based on the risk associated with various assets.
2. Proactive Mitigation:
- Guides proactive risk management strategies, allowing organizations to preemptively address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Minimizes the likelihood of security incidents and ensures a robust defense against emerging threats.
3. Identifying Weaknesses:
- Involves systematic testing to identify weaknesses in network infrastructure and systems.
- Pinpoints potential entry points for attackers, helping organizations fortify their defenses.
4. Continuous Improvement:
- Ongoing vulnerability assessments contribute to continuous improvement by adapting security measures to evolving threats.
- Ensures that the organization’s cybersecurity posture remains resilient against emerging vulnerabilities.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensures data protection measures align with relevant regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or other industry-specific standards.
- Demonstrates commitment to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining legal compliance.
6. Privacy by Design:
- Integrates privacy considerations into the development and implementation of systems, enhancing overall data protection.
- Fosters a culture of privacy awareness and responsibility throughout the organization.
7. Simulating Real-World Scenarios:
- Involves the simulation of security incidents to test the effectiveness of incident response plans.
- Identifies strengths and weaknesses, allowing organizations to refine their strategies for handling security breaches.
8. Continuous Training:
- Incorporates lessons learned from simulations into ongoing training programs for incident response teams.
- Enhances the organization’s readiness to effectively respond to and mitigate the impact of cyber incidents.
Overcoming the Cybersecurity Compliance Challenges
Cybersecurity compliance brings challenges for companies and industries. Here are a few challenges businesses should know about:
1. Address Common Issues
- Implement effective communication strategies to convey the importance of cybersecurity compliance throughout the organization.
- Foster a culture of shared responsibility for maintaining a secure digital environment.
A pentest report can help businesses in addressing and achieving regulatory compliance. Here’s a glance at a comprehensive pentest report.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

2. Mitigate Resource Constraints and Budgetary Challenges
- Identify and prioritize cybersecurity measures with the highest impact on risk reduction.
- Maximize the effectiveness of available resources by focusing on critical areas of vulnerability.
- Explore cost-effective cybersecurity solutions and technologies without compromising on effectiveness.
- Leverage open-source tools, collaborations, and strategic partnerships to enhance cybersecurity capabilities.
3. Adapt to the Evolving Cyber Threats
- Integrate threat intelligence sources to stay informed about emerging cyber threats.
- Enable organizations to adopt security measures in real-time to counter evolving threats.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify and address new vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Establish a proactive approach to cybersecurity by staying ahead of the evolving threat landscape.
Best Practices of Cyber Security Compliance Audit: 7 Things to Consider
To execute an effective cybersecurity audit, businesses should follow some procedures. Below are some of the best practices:
1. Establish a Robust Cyber Security Framework
- Develop and enforce comprehensive cybersecurity policies tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
- Establish a clear framework for security practices, ensuring consistency across the organization.
2. Regularly Update and Review
- Regularly update the cybersecurity framework to reflect regulations, technologies, and threat landscape changes.
- Conduct periodic reviews to ensure ongoing relevance and effectiveness.
3. Simulate Phishing Exercises
- Conducts simulated phishing exercises to test employees’ ability to recognize and avoid phishing attempts.
- Reinforces the importance of cybersecurity awareness in preventing social engineering attacks.
4. Collaborate with Third-Party Experts
- Engage third-party cybersecurity experts to provide an unbiased and external perspective on security measures.
- Benefits from external auditors’ specialized knowledge and experience in identifying potential blind spots.
5. Perform Comprehensive Assessments
- Collaborates with third-party experts to conduct in-depth assessments covering various aspects of cybersecurity.
- Ensures a comprehensive audit, addressing potential vulnerabilities that might be overlooked internally by a cyber security audit company.
6. Implement Next-Generation Security Solutions
- Adopt advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and behavioral analytics for proactive threat detection.
- Enhance the organization’s ability to identify and respond to sophisticated cyber threats in real-time.
7. Implement Continuous Monitoring Systems
- Implement continuous monitoring systems that provide real-time insights into the organization’s cybersecurity posture.
- Enable swift responses to emerging threats and enhance overall incident response capabilities.
How Can Qualysec Help Achieve Regulatory Compliance for Business?
Qualysec is pivotal in helping businesses achieve regulatory compliance through its comprehensive and innovative penetration testing solutions. Leveraging cutting-edge technologies, we offer a suite of services designed to address the diverse and evolving landscape of regulatory requirements.
We conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential compliance gaps within an organization. Furthermore, this proactive approach enables businesses to understand their vulnerabilities and implement targeted measures to meet regulatory standards.
We further provide robust cybersecurity audit services to safeguard sensitive data and ensure adherence to data protection regulations. This includes encryption protocols, secure access controls, and real-time monitoring to detect and mitigate potential threats.
Furthermore, we facilitate the implementation of industry-specific compliance frameworks, ensuring businesses align with regulations such as ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Our solutions’ continuous monitoring and reporting capabilities empower businesses to maintain compliance over time.
Furthermore, regular security audits and assessments streamline the process, offering a proactive stance toward compliance management. Our comprehensive pentest report guarantees businesses achieve cybersecurity regulatory compliance with thorough penetration testing.
Contact us to safeguard your applications and achieve regulatory compliance requirements.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Compliance through Vigilant Auditing
In cyber security compliance audit, emerge as indispensable guardians of organizational integrity. These audits protect against legal repercussions and reputational damage by rigorously examining and fortifying security measures.
Furthermore, the insights gained from assessing vulnerabilities, data protection, and incident response plans ensure alignment with regulations and foster a proactive cybersecurity stance. In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses must recognize the pivotal role of cybersecurity audits, embracing them as continuous guardians of compliance to navigate the intricate web of cybersecurity regulations successfully.
FAQs
1. What is a compliance audit in cyber security?
A Cyber security compliance audit is a systematic assessment to ensure an organization adheres to established security regulations, standards, and policies. It examines whether security measures align with legal requirements, industry standards, and internal policies, helping organizations identify and rectify gaps to maintain a secure and compliant posture.
2. What is the role of security risk audit compliance?
The role of security risk audit compliance is to assess and manage the risks associated with an organization’s cybersecurity practices. It involves evaluating vulnerabilities, potential threats, and the effectiveness of security measures. Identifying and addressing risks ensures that security practices align with regulatory requirements and industry standards, minimizing the likelihood of security incidents.
3. How often should a Cybersecurity Audit be performed?
The frequency of cybersecurity audits depends on factors like industry regulations, organizational changes, and the evolving threat landscape. Generally, conducting an audit annually is common. However, industries with sensitive data or those facing rapid technological changes may opt for more frequent audits to ensure continuous compliance and effective risk management.
4. What is the purpose of cybersecurity audit and compliance?
A Cyber security audit and compliance aims to verify that an organization’s security measures align with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies. It protects sensitive data, mitigates cyber threats, and maintains a secure environment. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, audits contribute to the overall resilience and compliance of the organization.
5. What is the difference between IT audit and IT compliance?
IT audit evaluates the effectiveness of an organization’s information technology systems and processes. It assesses controls, identifies risks, and ensures efficient IT operations. On the other hand, IT compliance involves adhering to specific laws, regulations, and standards applicable to the IT domain. While IT audits contribute to compliance, compliance extends beyond audits to encompass regulatory adherence and policy alignment.
















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments