Penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities in a target system or network and is essentially a simulated cyber attack with several stages. The process starts with defining the scope and goals and collecting information on the target. These steps form the foundation of the Phases Of Penetration Testing, ensuring a structured approach to identifying and mitigating security risks.
This brings about the asset-mapping stage, which outlines discovering systems, networks, and applications in the target environment. Once the assets are mapped, vulnerability analysis discovers any potential weaknesses. These are subsequently exploited during and after exploitation to determine the probable impact.
Lastly, during the reporting phase, the specialist summarizes the vulnerabilities discovered, gives the remediation steps, and recommends a rescan interval to verify the efficacy of the countermeasures taken. Let us discuss the 7 Phases Of Penetration Testing in this blog.
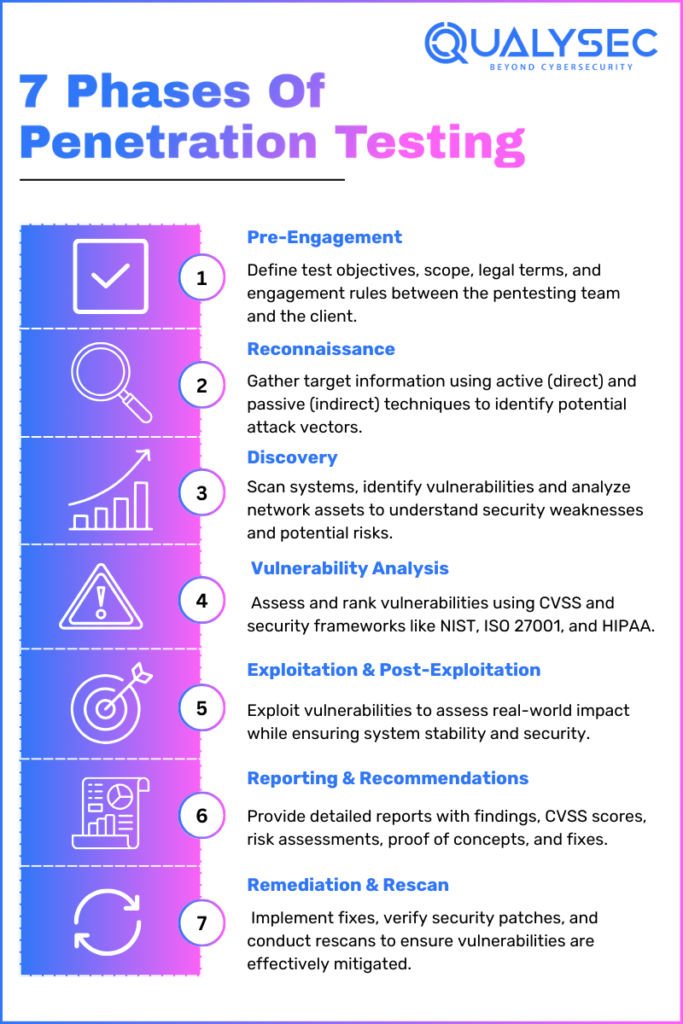
7 Steps and Phases of Penetration Testing
- Pre-Engagement
- Reconnaissance
- Discovery
- Vulnerability Analysis
- Exploitation and Post-Exploitation
- Reporting and Recommendations
- Remediation and Rescan
Penetration Testing Phase I: Pre-Engagement Phase
Here, the security expert examines the test’s logistics and rules of engagement. The VAPT providers and the target organization engage in dialogue about the exercise’s legal aspects.
- Define the objectives of the test: The penetration testing team and the customer work together to define precise objectives for the test that match the organization’s specific security needs.
- Define the scope of the test: The customer and the service provider agree on the systems, networks, and applications to be tested. They also specify off-limits areas or systems, which inform both parties what to anticipate from the testing process. This agreement contains the rules of engagement.
- Discussed legal and contractual implications: They then touch upon legal aspects, including possible liabilities and necessary authorizations for the testing procedure.
Penetration Testing Phase II: Reconnaissance
The pentester requires access to information regarding the target to mimic a cyber attack on an application or a network, and they obtain this information during the reconnaissance phase.
Regardless of whether a hacker wishes to attack a whole network or a single web application, they must be aware of as much as they can about it. The scoping that has been performed in the earlier phase assists the pentester in focusing the survey to make the test more efficient.
Mapping is also a part of the recon operation during a web app simulated attack. This step enables the attacker to look at all the application components in a single location and comprehend how they work.
Two types of reconnaissance exist:
1. Active Reconnaissance
The pen testers interact with the target system directly to harvest information in active recon. This is a more direct method of reconnaissance, though one that is considerably more intrusive as the attacker interacts with the system.
2. Passive Reconnaissance
In this technique, the intruder doesn’t interact with the target system and uses various passive approaches instead to obtain information. They attempt to spy on network traffic and track OS or internet footprinting.
Penetration Testing Phase III: Discovery
The discovery step consists of collecting data about the target network and determining vulnerabilities. It can be split into two parts:
1. Further Information Gathering
Pentesters collect more details regarding the target network using methods such as DNS interrogation, InterNIC questions, and network sniffing in order to determine hostnames and IP data. During an in-house test, the tester finds data such as names and shares by using NetBIOS enumeration and banner grabbing.
2. Vulnerability Scanning
Pentesters run the application or operating system against known vulnerabilities. They can execute automated scans, which check the system with a database of vulnerabilities, or manual scans, which excel at discovering new and concealed vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing Phase IV: Vulnerability Analysis
On security scanning, multiple sources of threats are identified, which are then examined by pen testers to ascertain underlying vulnerabilities and rank them on the basis of the risk posed to the system. A routine process must be followed to inspect the vulnerabilities on the basis of severity and risk, which VAPT vendors accomplish.
- CVSS: Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a popular semi-quantitative rating system for the severity of vulnerabilities. Each vulnerability receives a numerical value, with severity corresponding to the value. The score is used to prioritize the remediation of vulnerabilities, the last step in penetration testing.
- Assessment Standards: Vulnerabilities are generally evaluated based on different security and risk assessment standards, including the Risk Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), ISO 27001, and HIPAA.
The exploitation stage is designed to create access to a system in a simulated attack via the discovered vulnerabilities. The pentester discovers an entry point and then searches for assets that are accessible.
Penetration Testing Phase V: Exploitation and Post-Exploitation
The exploitation step seeks to gain access to a system in the emulated attack using the discovered vulnerabilities. The pentester identifies an entry point and subsequently seeks assets that can be accessed.
The pen testers need to be extremely cautious of the target’s functionality while performing this test and ensure that there is no damage to the workflow.
The Post-Exploitation Phase
Once the pentester has gained access to a vulnerability and located an entry point into the system, the next task is to ascertain the value of the entry point. The questions to ask are:
- How much access does the entry point provide?
- How simple is it to keep access?
- How long might it be before the breach is detected?
- What is the level of damage that the vulnerability can inflict?
The exploitation and post-exploitation stages assist the tester in acquiring access, finding sensitive information, determining communication channels, etc. They can also take advantage of the relationship between multiple systems within the network and enlarge the breach.
Agreed rules of engagement in the pre-engagement phase dictate how much a pentester can exploit a particular vulnerability.
Penetration Testing Phase VI: Reporting and Recommendations
All the above penetration testing activities lead to this stage, where a VAPT is produced and presented to the client. The pen testers then give an in-depth description of the vulnerabilities, including:
- Description of the vulnerabilities.
- Ratings based on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
- Severity and vulnerability impact.
- Risk assessment report.
- Video POCs.
- Fixing recommendations for the vulnerabilities.
The quality of your VAPT report will decide how fast and effectively you will replicate and eliminate the vulnerabilities from your system.
Penetration Testing Phase VII: Remediation and Rescan
The VAPT report includes step-by-step guidance on how to remedy the vulnerabilities. Your developers can implement those guidelines to plug the loopholes in your app security.
A perfect remediation phase includes the following steps:
- Vulnerabilities are reported along with step-by-step remediation steps.
- Security engineers offer video-based support.
- Developers hop on a call to go over the remediation process when necessary.
- After fixing the vulnerabilities, the VAPT firm should provide rescans to determine unattended security loopholes.
Timeline for the Phases of Penetration Testing
The initial six phases of penetration testing, ranging from reconnaissance to the generation of a VAPT report, would take about ten days. The duration may differ slightly based on the test’s scope.
The timeline for the remediation phase is contingent upon the speed at which your development team will be able to implement the fixes suggested by the pen testing team. Nevertheless, there is always a specified period to take advantage of the free rescan a VAPT company provides.
Post-Pentest Rescans
Once the vulnerabilities are discovered and remediated, the VAPT firm suggests periodic rescans of your application. In case no additional vulnerabilities are discovered in the rescans, the VAPT firm may also issue a certificate to utilize for regulatory compliances like ISO, SOC2, and HIPAA.
Run periodic automated scans to maintain the security of your system. You also need to scan each time you update your application or program to confirm that the new releases do not have vulnerabilities.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Top 3 Tools for Different Phases of Penetration Testing
1. Qualysec
Key Features:
- Platform: Cloud
- Pentest Capability: Ongoing auto-scans combined with manual tests
- Accuracy: No false positives
- Compliance: PCI-DSS, HIPAA, ISO27001, and SOC2
- Expert Remediation: Available
- Integration: Slack, Jira, GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, and many others
- Price: From $1000 to $5000/yr
The Qualysec Pentest Platform is a comprehensive pen-testing tool that spans the gap between AI-driven automated vulnerability scanning and penetrating manual pen-testing. Our platform allows for intensive security audits aligned with OWASP TOP 10 and SANS 25 standards, with our scanner performing 9300+ tests.
While our expert-tested automated scans deliver zero false positives, our penetration tests by security professionals assist in uncovering sophisticated vulnerabilities—such as payment gateway breaches and business logic flaws—that tend to fall through automated checks.
We offer functionality such as scan-behind-login pages and reports that can be tailored to the level of detail needed for individuals from various hierarchies. Following the testing process, clients are offered several free rescans to confirm the fix, in addition to a publicly verifiable Pentest certificate.
2. Kali Linux (Open-Source)
Key Features:
Target: Physical and online systems, networks, and applications
- Pentest Capabilities: No Limit Scans for post-exploitation, exploitation, privilege escalation, vulnerability scanning
- Compliance: N/A as it’s open-source
- Integrations: 600+ pen testing tools such as John the Ripper, Wireshark, Nmap
- Expert Remediation: No
- Accuracy: False positives are possible
- Price: Open-source OS
- Kali Linux is an operating system that has been developed for penetration testing and security auditing. Its extensive platform, which comes pre-installed with over 600 tools, offers a full solution to security professionals to perform effective vulnerability assessments.
From reconnaissance to post-exploitation analysis, Kali provides the tools and functionality required to address the whole range of penetration testing activities. This powerful OS enables security professionals to explore in-depth system weaknesses and exploit probable vulnerabilities.
Though its robust collection of tools and customization possibilities ensure it’s popular among veterans, it is critical to acknowledge that Kali Linux demands proficiency with Linux commands as well as a steep learning curve for beginners.
3. Burp Suite Professional
Key Features:
- Platform: Windows, macOS, Linux
- Pentest Capability: Manual and automated scans for web applications
- Accuracy: False positives are possible
- Compliance: PCI-DSS, OWASP Top 10, HIPAA, and GDPR
- Expert Remediation: No
- Integration: Slack, Jira, Jenkins, GitLab, and many more
- Price: $449/yr/user
Burp Suite Professional is a top web application security testing platform with a global reputation for its toolset. They validate quick vulnerability discovery through manual and automated testing methods.
Burp Suite offers seamless integration with third-party tools in a productive testing environment. Although typically robust, certain users have also experienced unstable crashes and socket connection issues with the tool.
In addition, while Burp Suite successfully detects vulnerabilities, it fails to point out sensitive information leakage, including personal and financial data exposures.
Conclusion
Penetration testing involves seven crucial steps to assist in the discovery and minimization of the vulnerabilities within the system or network being examined. These steps define the Phases Of Penetration Testing, providing a structured way to spot security weaknesses.
Several Types Of Penetration Testing can be used by security experts to understand an organization’s security posture through pre-engagement, reconnaissance, discovery, vulnerability analysis, exploitation, reporting, and remediation.
Manual testing is crucial for the discovery of sophisticated vulnerabilities; nevertheless, automated scanning supplemented with manual testing enhances the efficiency and speed of the process.
We have pitted the best three pen testing tools that you can utilize to secure your overall security. Select a suitable pen-testing provider for your purposes.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
FAQs
1. What is the Penetration Testing timeline?
Web app penetration testing is done in 7-10 days. The vulnerabilities begin appearing in Qualysec’s pen test dashboard on the third day so that you can head start in remediating them. The timeline could be different based on the scope of the pentest.
2. How much does Pentesting for a Web App cost?
Web app Pentesting is $99 to $399 per month to conduct web application penetration testing, depending on your plan of choice.
3. Do you receive rescans once the vulnerabilities are remediated?
Yes, based on your plan, you receive 2-3 rescans. You can apply the rescans within 30 days of completion of the initial scan, even after a bug is patched.






















![Top 20 Network Security Companies in USA [2025 Updated List]](https://qualysec.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Top-20-Network-Security-Companies-in-USA-2025-Updated-List-scaled.jpg)































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments