In the contemporary world where cyber threats are dynamic, businesses should persistently be alert in their cybersecurity. While organizations previously conducted penetration testing annually or semi-annually, these measures fall short against today’s more sophisticated attacks. This is where Continuous Penetration Testing comes into play. This proactive and ongoing process enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities that hackers can easily exploit.
In this blog post, we will discuss what continuous penetration testing is, how it works, the procedure involved, and the advantages it offers your organization.
What Is Continuous Penetration Testing?
Continuous Penetration Testing is an automated form of Penetration Testing by which security testers probe a company’s system continuously to establish a realistic level of exposure. While typical testing is an annual activity, continuous pentesting runs constantly, therefore keeping your systems effective in defending against modern threats.
Another advantage of this continuous testing is that it reveals fragile areas, so they can be secured before an attacker takes advantage and exploits them.
How does Continuous Penetration Testing work?
Continuous penetration testing combines automation and human input and involves imitating a cyber attacker on a system. This testing recurrently assesses your website, application, or network for vulnerabilities.
Here’s how the process typically works:
1. Automated Monitoring: There are constantly running self-test tools that automatically scan your system looking for opportunities where your strengths could be exploited, weaknesses, or possible improvement.
2. Real-Time Alerts: For any form of vulnerability that is found, the system then produces alert notifications to your team in real time.
3. Human Oversight: Though automation automates most of the process, cybersecurity experts analyze complicated threats that the tool cannot detect, making security comprehensive.
4. Remediation Recommendations: Once the flaws are identified, the system generates reports with all information about them and advice on how to resolve these problems.
5. Follow-up Testing: After the problems are identified engine confirms the removal of the malicious activities Follow-up testing confirms that the openings are sealed.
Continuous Penetration Testing vs. Traditional Penetration Testing
Both continuous and traditional penetration testing exist to discover the weaknesses, although there are differences between the two.
| Feature | Traditional Penetration Testing | Continuous Penetration Testing |
| Frequency | Once or twice a year | Regular and Continuous |
| Detection speed | Delayed detection | Subscription-based on going cost |
| Automation | Limited | Heavily automated with human oversight |
| Cost | One time high cost | Subscription based on going cost |
| Effectiveness | Reactive | Proactive and preventive |
Why Do You Need Continuous Penetration Testing?
In the current threat environment, new risks appear every day and attack every day. The long periods between traditional tests can leave businesses open for attacks. Continuous penetration testing offers several advantages:
- Proactive Security: This is because all the loopholes are identified, and solutions to all the problems are implemented as soon as they are discovered.
- Compliance with Regulations: Several businesses cannot afford a lapse of days without monitoring their security systems due to regulatory compliance in these industries like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Improved Risk Management: The frequency of reports can help companies handle their cybersecurity risks better when they have up-to-date information on security status.
- Cost-Effective in the Long Run: However, traditional penetration testing may appear to be cheaper when it comes to the initial cost of investment, but the consequences of an undetected breach can be significantly more costly than carrying out the tests constantly.
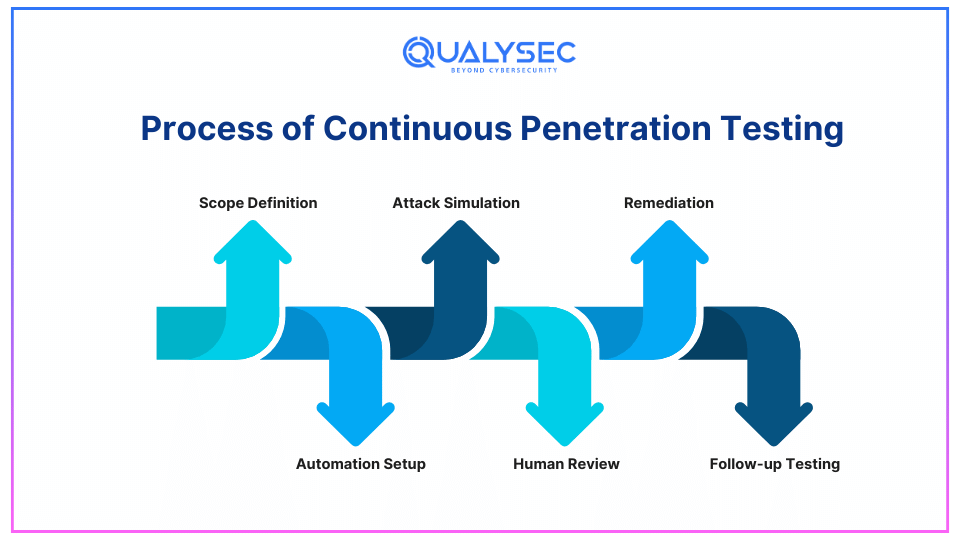
Process of Continuous Penetration Testing
The methodology and process of continuous penetration testing involves several key steps:
1. Scope Definition
Determine the inputs, outputs, and controls of your system or applications that will be tested. This entails a website, mobile application, server, network, API, or database.
2. Automation Setup
There are automated tools applied for its constant scanning of the system for existing vulnerabilities. This comprises network discovery, port operation, or being able to define vulnerabilities in the code.
3. Attack Simulation
Some of the attack simulations include; the SQL injection attack, Cross-site scripting attack, and phishing attack. It aims at searching for weak points and checking your system’s reaction to them.
4. Human Review
When vulnerabilities are found through continuous security testing, these are flagged and checked by security engineers; the engineers also recommend ways to control or eradicate such vulnerabilities. In such cases, some vulnerabilities might be more complex and require more scrutiny than the automated tool can deliver.
5. Remediation
When gaps become identifiable, your IT or cybersecurity staff respond to the issue. Continual penetration testing tools may also offer solutions to patch or document vulnerabilities as well.
6. Follow-up Testing
When vulnerabilities are addressed additional testing is performed to verify that the problems are rectified and that no new vulnerabilities exist.
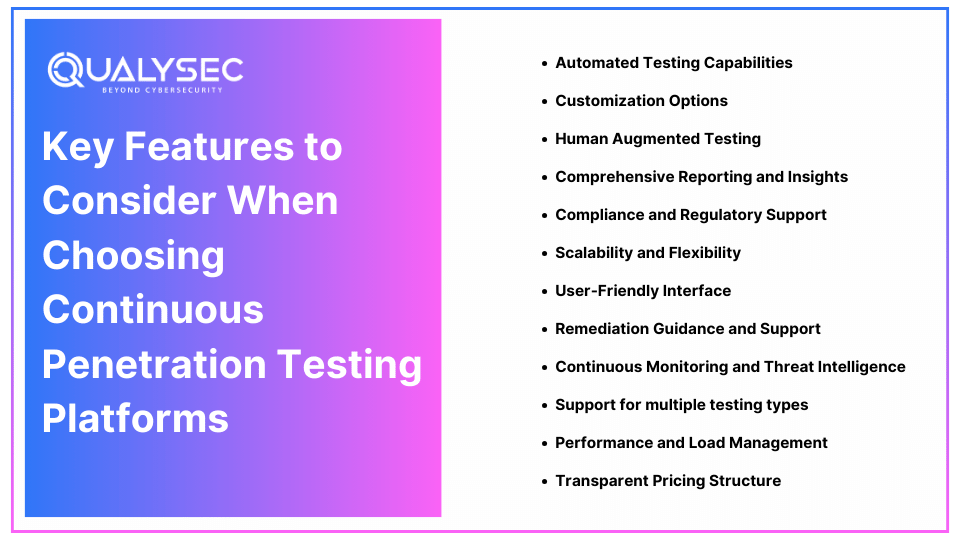
Important Features to Consider When Choosing Continuous Penetration Testing Platforms
Selecting a continuous pentesting platform is one of the most important decisions that organizations pursuing good cybersecurity should make. As the number of choices remains rather vast, it is critical and feasible to choose the option that would be relevant to your business, your security requirements, as well as your capabilities. The following outlines attributes you should consider when searching for continuous penetration testing platforms.
1. Automated Testing Capabilities
Real-Time Vulnerability Detection: Ongoing penetration testing platforms should be able to provide a constant scan to identify the existing vulnerabilities. This helps to make sure that the security is always up to date without needing manual updates.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: Other platforms that employ the use of Artificial intelligence and machine learning can be able to identify new threat patterns making the test regimen shorter and more precise. As mentioned earlier, there is another advantage, AI-generated automation could also discover latent threats.
2. Customization Options
Customizable Scans: In an effective platform for scanning, there should be an ability to set up the scans depending on the organization’s need and it should enable scanning on applications, networks, or servers.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This feature makes it possible for organizations to control who can work on specific documents or be allowed to manage specific features of the platform, for instance only allowed testers should be allowed to work on testing data files.
3. Human Augmented Testing
Manual Review and Analysis: Automated environments should be complemented by human control designed to review the outcomes of the tests and spot more intricate weaknesses. Even the platforms, that offer both automated and manual testing, give out a better evaluation.
Access to Expert Analysts: Some of the platforms allow the user to get in touch with certified cybersecurity experts who explain the details of particular openings suggest how to address them, and/or help when an emergency occurs.
4. Comprehensive Reporting and Insights
Real-Time Alerts: It may take a while before they are categorized as critical, so seek platforms that send out instant notifications of critical vulnerabilities. This feature means that different teams can deal with problems right away, thereby reducing the risks brought by weaknesses.
Detailed Reporting: This involves; An effective information management platform offering detailed information and comprehensive reports on identified vulnerabilities, their severity, and probable solutions.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

5. Compliance and Regulatory Support
Compliance Templates: Select those services that have common test procedures and check compliance with the norms of GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. It saves a lot of time on compliance checks and provides confidence that your systems align with industry standards.
Audit Trails: Those platforms that provide rich and complete audit trails help one track the actions initiated by the user as well as by the system. It is relevant bearing in mind it helps in dealing with compliance issues and identification of cases of improper access.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalable Testing: Organizational growth requires that your organization or company should also grow and this must include strong security testing measures. It may also be capable of handling larger systems, more applications, additional user traffic and hence, should be scalable enough to grow with your business.
By including continuous security testing, you can ensure that your security framework stays effective and flexible as your organization grows.
Flexible Integration Options: Those that can be easily integrated with current tools ranging from project management tools, DevOps tools, or even CICD tools make it easier to work and run efficiently.
7. User-Friendly Interface
Ease of Use: The management of the platform should be easy which may involve a comprehensive and simple graphical user interface that ordinary users can comprehend and manipulate the operations of the platform. A less complex design makes it possible to spend less time on recruitment and training of the workforce.
Clear Visualization of Vulnerabilities: Visualization of vulnerability data in the forms of graphs, charts, and networks assists teams in comprehending problems and in the right prioritization of those issues.
8. Remediation Guidance and Support
Actionable Recommendations: A good platform needs to give precise information on how each vulnerability can be addressed. This guidance is most valuable for teams that lack specific expertise in the cybersecurity field.
Automated Remediation Workflows: Some service providers, already provide a form of automated workflows that can minimize handling time to remediate these issues. Interestingly, most of these workflows can be easily integrated into your existing workflow, if you have one.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Threat Intelligence Integration: Some offers include threat intelligence feeds that feed the system daily with the known vulnerable ones to enhance security threats.
Continuous Monitoring: Computing platforms on the other hand have features that allow constant monitoring for threats, and any weakness is detected as soon as it is present, which offers better security than with scheduled or periodic scans.
10. Support for multiple testing types
Diverse Testing Approaches: A solution, that involves network testing, application testing, and API testing, ensures full-spectrum safety for various digital assets.
Support for External and Internal Testing: External and internal testing makes sure that different sections of the program are scrutinized for any given blind spot from internal users and other attacks from external users.
11. Performance and Load Management
Minimal System Disruption: Platforms should be able to run default test cases without interfering with the normal execution of your applications or networks which is crucial in business.
Load Testing Capabilities: Some also provide load testing to get to know how your systems work when there’s heavy traffic or load, whether they are still secure or not.
12. Transparent Pricing Structure
Subscription vs. Pay-Per-Use: It is advisable to look for a model that covers the pricing when you are developing it. There is a need for continual testing, in which case subscription models would be most appropriate while there is the need for testing only a few times probably due to a specific project, the pay-per-use would be suitable.
No Hidden Costs: Go with the pricing that is as clear as possible to not find yourself having to pay extra for a feature, extra scans, or extra users.
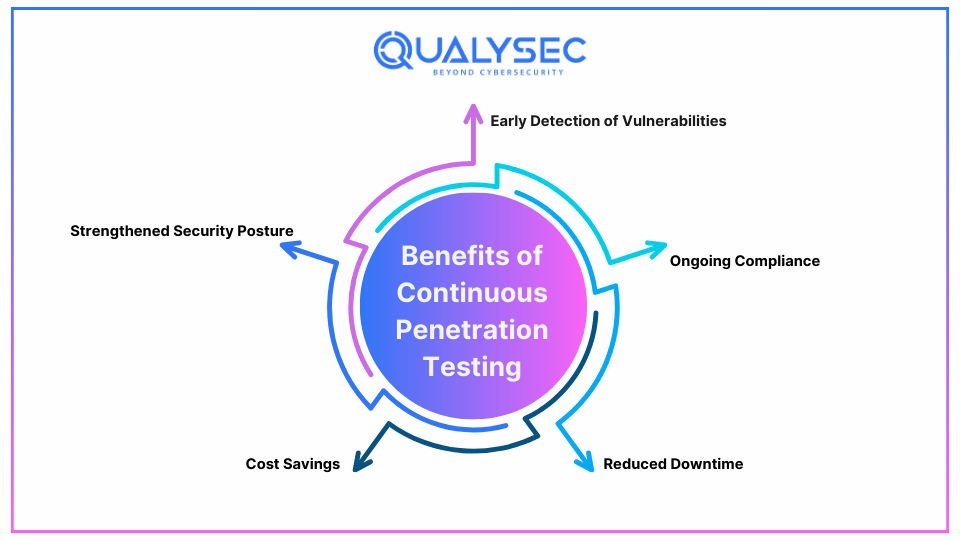
Top 5 Benefits of Continuous Penetration Testing
Continuous penetration testing offers several significant benefits for businesses:
1. Early Detection of Vulnerabilities
It reveals that the system is still open to some weaknesses through testing them before the hackers take the opportunity to exploit them. Thereby reducing cases of leakage, loss-making, and compromising the reputation of your business organization.
2. Ongoing Compliance
Some sectors like the financial or the healthcare sector require continuous security evaluations. Ongoing penetration testing keeps businesses on the right side of the law to data protection and the resulting penalty.
3. Reduced Downtime
Ongoing testing points out the weak links in the process and minimizes the chances of a major event resulting in a systems outage or disruption of business.
4. Cost Savings
Although continuous penetration testing may come bundled with a monthly or yearly subscription fee, it is cheaper in the long run. The expenses that arise from a breach of data, its loss in sales, the time for legal issues, and the erosion of customer trust are much more than the cost of constant security testing.
5. Strengthened Security Posture
When penetration testing is done continuously, an organization is always in a position to check its security health at any one time. This helps you be in a position to address given weaknesses in good time and also remain well-fortified to combat cyber threats.
How Can Qualysec Help?
Here at Qualysec, we are experts in delivering the most superior services such as continuous pentesting. Our team of certified ethical hackers means you get the highest level of security protection through the use of sophisticated automated tools for regular scans of your systems’ weaknesses.
- Comprehensive Testing: That is why we offer regularly scheduled penetration testing of websites, mobile applications, APIs, and networks.
- Real-Time Alerts: We offer real-time alerting of identified risks so that your team can react accordingly.
- Expert Analysis: Automated tools are used hand in hand with the manual testing done by our cybersecurity professionals and, therefore, provide end-to-end coverage.
- Custom Solutions: Our penetration testing services are fully scalable depending on your business needs whether a small business or a large business entity.
Complimenting this, with Qualysec, you are able to leave the responsibility of monitoring your systems to us while you relax knowing that your systems are fully protected at all times.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Conclusion
Different organizations consistently use penetration testing as a key aspect of enforcing strong security measures. Since its monitoring is real-time with proactive identification and constant enhancement of security, it affords absolute protection from cyber threats. In today’s constantly evolving threat environment, continuous penetration testing lets your business maintain high ground against potential attackers.
Whether you need assistance in improving, adjusting, or establishing Penetration Testing procedures, Qualysec provides you with the ideal Penetration Testing services for your organization’s protection against malicious threats.
Watch our Recent Webinar: Why Penetration Testing is Important For Business
FAQ
Q. Why is it important to continuously conduct penetration testing for a strong security system?
It is important to know that the threats that are prevalent in the cyber world are becoming more and more complex. Ongoing penetration testing checks for vulnerabilities in a network and then works to fix these issues before they create an exploitable weakness in software.
Q. What is the cost of continuous penetration testing?
The cost of such testing can therefore vary with the extent of the test required and the complexity of the testing as well. The best form of continuous penetration testing will often come in a subscription form to provide constant vigilance as opposed to a single fixed fee.
Q. How often should you perform penetration testing?
To validate critical systems and applications, organizations should perform testing continuously. For other systems that are not so sensitive, testing at least on a quarterly or semi-annual basis makes it possible to address the vulnerabilities with a certain degree of frequency.






















![Top 20 Network Security Companies in USA [2025 Updated List]](https://qualysec.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Top-20-Network-Security-Companies-in-USA-2025-Updated-List-scaled.jpg)































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments