Cloud data security is the practice of protecting data and other digital information stored in the cloud from data breaches, unauthorized access, and insider threats. With more than 60% of enterprise data stored in the cloud, businesses need to understand that cloud data security is crucial to avoid data theft, reputation damage, financial loss, and compliance risks.
Organizations often use a combination of cloud, multi-cloud, on-premises, and hybrid infrastructure. This means they store huge amounts of sensitive data in multiple locations. As a result, organizations often fail to realize where their confidential data is kept, who uses it, and whether it is protected. This is why, cybercriminals have turned to the cloud, to steal highly valuable corporate and personally identifiable information (PII).
In this blog, you’ll learn about cloud data security, common security risks associated with cloud data, and steps organizations can take to protect their sensitive data.
What is Cloud Data Security?
Cloud data security refers to the strategies and techniques that protect the data stored in a cloud environment. Simply put, cloud data security protects the data that is at rest or moving (in transit) from unauthorized access, theft, security threats, and corruption. Data security policies should be a priority for organizations using cloud services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure.
Cloud Data Security includes:
- Identifying and classifying structured and unstructured data
- Establishing and monitoring access management controls at both the file and field levels
- Detecting data storage locations
- Data transmission flows
- Encryption configurations
Read more: Cloud application penetration testing
Why Companies Need Cloud Data Security?
Today, we are in the age of big data, where companies are generating, collecting, and storing vast amounts of data each second. This includes everything, from highly sensitive business or customer data to less sensitive marketing and behavioral analytics.
The growing volumes of data need to be accessed, managed, and analyzed properly. This is why, organizations are adopting multiple cloud services to make their operations agile and support remote or hybrid workforces.
The traditional network perimeter is rapidly disappearing, making the security teams rethink their strategies for securing cloud data. With data and applications now operating outside traditional data centers and more employees working remotely, companies must find effective ways to protect data and control access as it moves across multiple environments.
Core Principles of Cloud Data Security
Cloud data security policies follow the same three principles of information security and data governance. These principles are:
- Data Confidentiality: Only authorized individuals or processes can access or modify the data. This means you need to ensure the data is kept private and secure.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that data is accurate, authentic, and reliable. This involves implementing policies or measures to prevent data tampering or deletion.
- Data Availability: While organizations want to avoid unauthorized access, data still needs to be accessible and available to authorized people whenever needed. As a result, you’ll need to maintain continuous uptime and ensure system, networks, and devices operate smoothly.
These three broad pillars – Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability – often referred to as the “CIA Triad” represent the core concepts essential for robust and effective security infrastructure in any organization. Any attack, vulnerability, or security incident is likely to compromise one or more of these principles. Therefore, security professionals use this framework to assess potential risks to an organization’s data assets.
Benefits of Cloud Data Security
Along with protecting sensitive data, cloud data security also benefits companies in many ways, like:
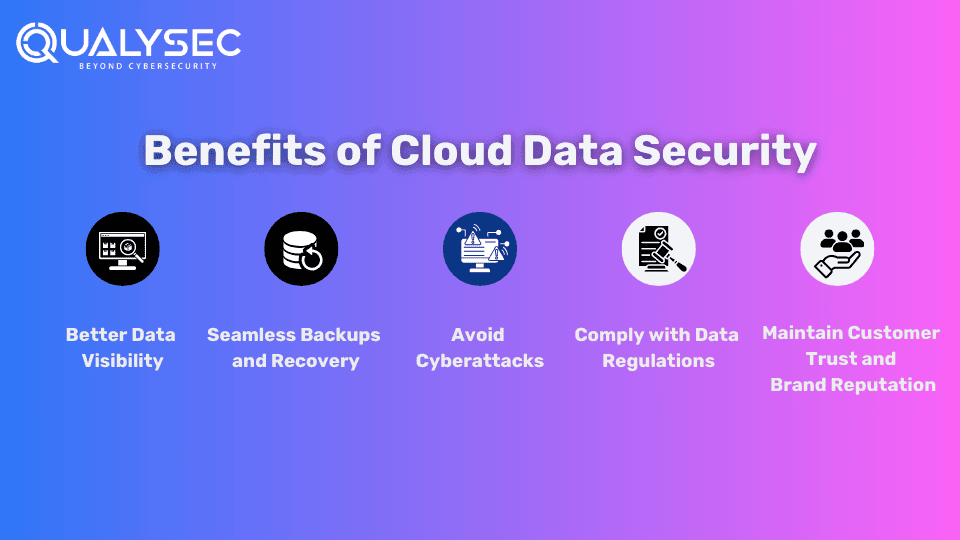
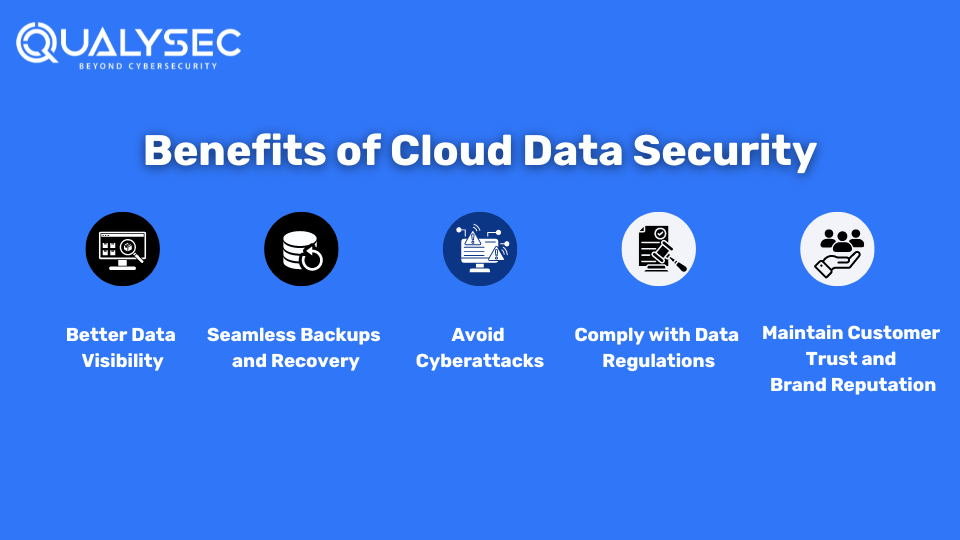
1. Better Data Visibility
Strong cloud data security protocols allow you to maintain visibility into the cloud’s inner workings. This includes the data assets you have and their locations, the users of your cloud services, and the types of data they are accessing.
2. Seamless Backups and Recovery
Cloud data security provides various solutions and features to automate and standardize backups. This helps relieve your teams from monitoring manual backups and troubleshooting problems. Additionally, cloud-based disaster recovery allows you to restore and recover data and applications within minutes.
3. Avoid Cyberattacks
Cloud data security measures reduce the success rate of cyberattacks. For example, implementing data access controls makes it hard for attackers to access sensitive data. Additionally, other data control measures like “encryption” make the data unreadable even if they find a way to breach.
4. Comply with Data Regulations
Not complying with data privacy and protection laws leads to costly fines and legal problems. For example, if a company violates the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), it can be fined up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual revenue. Different regions and industries have different data laws like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and HIPPA. Cloud data security measures like penetration testing help you comply with these regulations.
5. Maintain Customer Trust and Brand Reputation
72% of business leaders believe that reputation is the bigger driver of business performance than any other factor. Every data breach that hits the headlines hampers the company’s brand reputation. Additionally, if you can’t show people that you can protect their data, they won’t want to buy from you. Therefore, cloud data security is essential if you want to preserve your brand reputation and attract loyal customers.
Cloud Data Security Challenges
As data and applications move away from the central data center and traditional security measures, the risk of exposure becomes high. While many core aspects of on-premises data security remain, they need to be adjusted for the cloud environment.
Common data protection challenges in the cloud or hybrid environment include:
- Lack of Visibility: Companies often don’t know where their data and applications are located and what assets are in their inventory.
- Less Control: As data and applications are hosted on third-party cloud infrastructure, companies have less control over how data is accessed and shared.
- Shared Responsibility Confusion: Both companies and cloud service providers share cloud security responsibilities. This often leads to confusion about who is responsible for what duties.
- Inconsistent Protection: Many businesses are now using multi-cloud and hybrid cloud services for their businesses. However, different cloud providers offer different levels of protection, which can be inconsistent for the company.
- Changing Cybersecurity Threats: Cloud databases and storage are ideal targets for cybercriminals, especially because companies are still in the understanding phase of cloud data handling and management.
- Strict Compliance Requirements: Organizations are always under pressure to comply with strict data protection and privacy regulations. This requires implementing security policies across multiple environments, which demonstrates you have strong data governance.
- Distributed Data Storage Challenges: Storing data on international servers can offer benefits such as lower latency and increased flexibility. However, it may also raise data sovereignty issues, which might not be a problem if you were operating in your own data center.
- Shadow Data: As engineering teams use cloud database technologies, they often duplicate the data. Because many tools fail to detect this data, organizations are left with this shadow data, which can lead to a data breach.
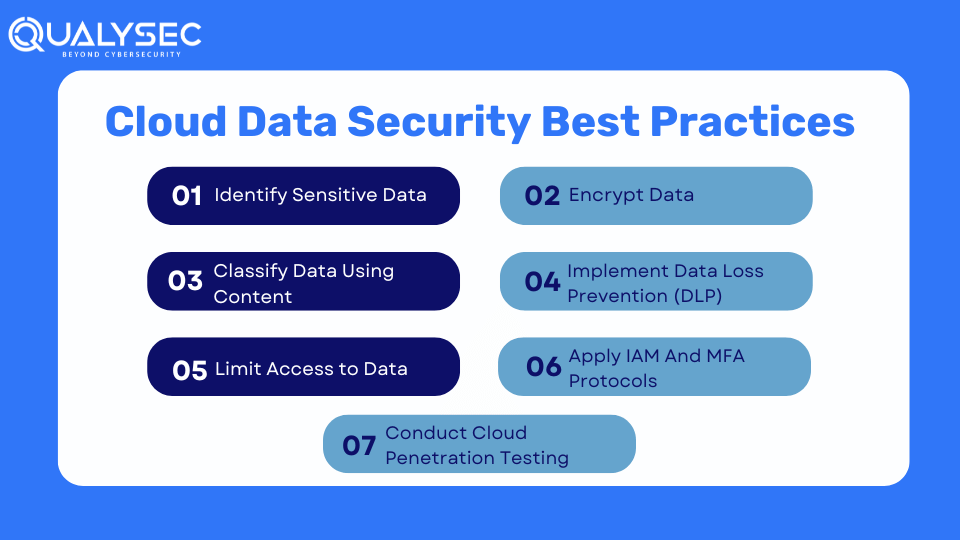
Cloud Data Security Best Practices
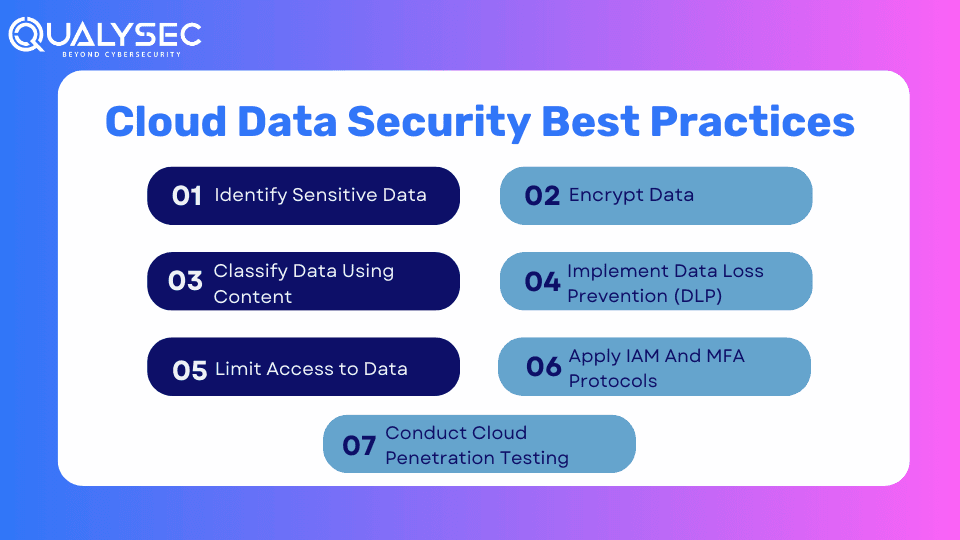
By following these practices, you can secure sensitive data in your cloud environments.
1. Identify Sensitive Data
Before you try to secure cloud data, you need to identify the sensitive information within your organization and where it is located. To achieve visibility into critical data and assess static data risk, you need to identify and classify both structured and unstructured sensitive data across:
- Public cloud platforms, including storage like S3 buckets, RDS, and EFS
- Virtualization environments
- Data analytics platforms
- Databases as a Service
- Shadow data
2. Classify Data Using Context
Once you know where your sensitive data is located, you need to classify them according to:
- Type
- Sensitivity level
- Governing regulation
The classification process should involve how the data is transferred within the organization, who uses it, and how they use it.
3. Limit Access to Data
Once all data has been identified and classified, you can then set user access permissions. Access should be limited to as minimum as possible, granting each user the least amount of access required to fulfill their job responsibilities. You can use a combination of:
- Role-based Access Controls (RBAC): Assigning permission to someone based on their role in the organization, such as their job function or department.
- Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC): Incorporate permissions based on content, such as user device security, geographic location, or time of day.
4. Encrypt Data
Almost all compliance regulations mandate organizations to encrypt data both at rest and in transit. Encryption makes data unreadable unless the user has the decryption key. Even if someone gains unauthorized access to the data, they won’t be able to read it.
5. Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
When cloud users collaborate, there’s a risk of data leakage or loss. It means that someone shared data outside the organization without permission.
Data loss may occur due to:
- Accidental sharing during collaboration
- Cybercriminals compromising systems and networks to steal data
- Malicious insiders downloading information
To avoid these risks, you should implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions that detect real-time data risk across multi-cloud environments. DLP solutions monitor data as it travels between clouds and applications.
6. Apply IAM And MFA Protocols
Organizations should implement identity and access management (IAM) frameworks and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to restrict access to sensitive cloud data. IAM allows IT administrators to grant access to specific users to certain data, while MFA ensures that only users who can complete a specific verification process can access the data itself.
7. Conduct Cloud Penetration Testing
This is probably the best way to secure your cloud data and other assets in the cloud. Cloud penetration testing is where cybersecurity experts (or ethical hackers) simulate real attacks on the cloud environment to find vulnerabilities. They help organizations know where the security flaws lie and how to address them. By fixing the security flaws, organizations can protect their sensitive data in the cloud.
Want to see how a cloud penetration testing report helps with improving cloud data security? Click here to download a real report now!
Conclusion
May be in different forms, but cloud computing is going to be used by businesses for years to come. With organizations storing and moving sensitive data in the cloud, it has become a prime target for cybercriminals. Strong cloud data security is important to prevent data theft, ensure compliance, avoid cyberattacks, maintain brand reputation, and build customer trust.
As one of the most effective cloud data protection strategies, companies should proactively choose penetration testing.
Qualysec Technologies is the leading provider of cloud penetration testing, where we follow the rare yet most effective process-based pentest methodology. If you are worried about your cloud data and its safety, just click here and talk to one of our security experts!
FAQs
Q: What is data security in cloud security?
A: Cloud data security protects sensitive data stored and moving in and out of the cloud from unauthorized access, data theft, and insider threats.
Q: How do you secure data in the cloud?
A: Follow these practices to secure your data in the cloud:
- Identify Sensitive Data
- Limit Access to Data
- Conduct Cloud Penetration Testing
- Encrypt Data
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Apply IAM And MFA Protocols
Q: How does cloud data security work?
A: cloud data security mainly focuses on implementing strategies and technologies together to protect data, support regulatory compliance, and provide control over access, authentication, and privacy for users and devices.
Q: Why protect data in the cloud?
A: Organizations should protect data in the cloud to:
- Secure sensitive information from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Comply with data privacy rules like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001.
- Build customer trust by demonstrating commitment towards data security.
- Avoid financial and reputational damage.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments