Thanks to handheld devices, professionals can currently conduct business and interact from virtually any location. However, there is a cost to that ease. The increasing number of mobile devices has coincided with increased safety concerns and a rise in Mobile Security Threats..
Criminals know that mobile devices, such as cell phones, tablets, and the ChromeOS platform components, offer a fantastic route for spreading viruses, phishing messages, and fraudulent transactions.
To safeguard businesses from possible cyberattacks, companies must know how malicious individuals approach mobile devices, adopt established risk-mitigation techniques, and implement efficient security measures.
What Are Mobile Security Threats?
Threats to security on mobile devices might include fraudulent web pages and applications, spyware, fraud, phishing schemes, and more. They are designed to infiltrate a network, steal data, interfere with communication, and exploit flaws in remote endpoints. Mobile device security aims to safeguard sensitive information such as login credentials, banking information, corporate data, and other private data kept on the device you are using. Internet criminals are prevented from accessing your data by employing safety software, login credentials, and cryptography.
Top 10 Mobile Security Threats and Prevention
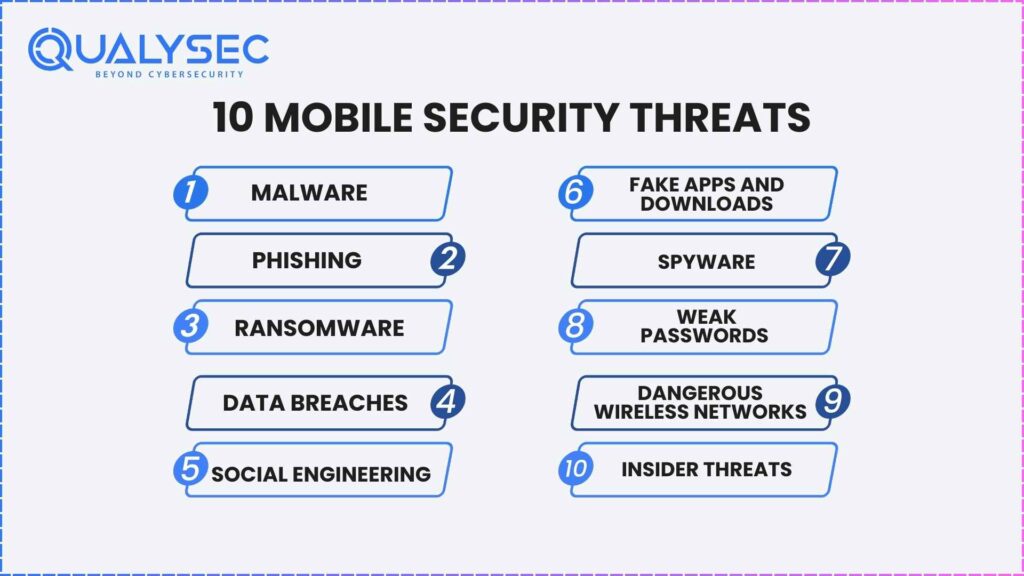
1. Malware
- Risk: malicious applications intended to damage hardware or acquire information.
- Preventive measures: Avoid installing programs via unknown sources, upgrade the machine’s systems and programs often, and use trustworthy anti-virus programs.
2. Phishing
- Risk: fraudulent emails or communications that fool recipients into disclosing private data.
- Preventive measures: Avoid giving private data to unidentified parties, be cautious of dubious files and hyperlinks, and confirm the authenticity of sites before inputting sensitive data.
Read More: Mobile Security Testing: Why Your App Must Have It Before Shipping.
3. Ransomware
- Risk: A malicious software that encodes all data on its way and wants ransom for its release!
- Preventive measures: update the OS and antivirus software, do not click on suspicious links, and consider backing up your files regularly.
4. Data breaches
- Risk: Data breaches involving unauthorised access to delicate information exists on a device.
- Preventive measures: Set strong passwords, especially ones that differ for each account. Enable two-factor authentication. If interested, use a VPN when using Wi-Fi at a public place!
5. Social engineering
- Risk: These scheming strategies pretend to be a user or force a user into unconsciously letting out information or performing actions they otherwise wouldn’t have done.
- Preventive measures: Never give out your personal details, be cautious of unknown/unsuspected information requests, and look out for any probable cons.
6. Fake Apps and Downloads
- Risk: Malware disguised as legitimate software.
- Preventive measures: Installing applications should be done only from reliable sources, such as official app stores, checking for application approvals before installing, and being alert to cons.
Read more: What is Mobile Application Security Testing?
7. Spyware
- Risk: Malware that surreptitiously records an individual’s equipment actions.
- Preventive measures include using a reliable security program, exercising caution when installing apps from unknown sites, and routinely checking the authorizations of programs.
8. Weak Passwords
- Risk: The login credentials that are simple to figure out or enable unwanted database access.
- Preventive measures: Create solid, one-of-a-kind credentials for every user account and think about generating and safely storing them with an encrypted password generator.
Read our recent guide on Mobile Application Penetration Testing.
9. Dangerous Wireless Networks
- Risk: Insecure wireless connections that put consumers at risk of spying and additional threats.
- Preventive measures include avoiding free Wi-Fi areas, using a VPN, and exercising caution when disclosing sensitive data over unsecured connections.
10. Insider Threats
- Risk: These threats are presented by people working for a company who could have access to private information and could abuse it.
- Preventive measures: Put in place robust accessibility and identification systems, keep an eye on worker behaviour, and inform staff members on potential cybersecurity risks.
Explore: Top 10 Mobile App Security Companies in 2025 to Protect Your Apps from Cyber Threats.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Conclusion
Mobile phones are used in daily operations and the utilisation of the business for which one works. Smartphones and tablets may access, change, and distribute private information, whether provided by the organization or maintained by employees. Because of this, the business must protect mobile devices just as carefully as it does workstations and computers.
Challenges to the security of mobile devices are growing in quantity and changing in depth. Consumers need to be aware of typical sources of attack and ready for the next wave of illegal actions to safeguard their mobile devices and information.
A strong online safety system should offer complete protection beyond PCs and workstations to safeguard mobile devices, Internet of Things devices, and other connected internet devices.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
FAQs:
Why is mobile security important?
Due to the accessibility of corporate and social networking applications, mobile devices have become an essential element of daily life and are now used by workers as portable PCs. Mobile devices must thus be secured to prevent them from being used to risk personal data.
What is a mobile security threat?
Threats to the security of mobile devices may involve harmful mobile applications and websites, malware, theft of information, social engineering scams, and beyond. They are made to break into a network, steal information, disrupt interactions, and take advantage of weaknesses in distant endpoints.


























![Top 20 Network Security Companies in USA [2025 Updated List]](https://qualysec.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Top-20-Network-Security-Companies-in-USA-2025-Updated-List-scaled.jpg)































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments