In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats continue to evolve, ensuring robust IT security audits is crucial for organizations. An IT security audit plays a vital role in assessing the effectiveness of security controls, identifying vulnerabilities, and mitigating risks. In this blog, we will explore the importance of IT security audits, the different types of audits, the methodology involved, best practices for conducting audits, and address frequently asked questions (FAQs).
Why Is There a Need for IT Security Audits?
IT security audits are essential for several reasons
- Risk Identification and Mitigation: Audits help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure, enabling proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have regulatory requirements mandating regular IT security audits, ensuring organizations remain compliant with relevant laws and regulations.
- Protection of Confidential Information: Audits assess data protection measures, access controls, encryption practices, and authentication mechanisms, safeguarding sensitive information from breaches.
- Enhanced Incident Response Preparedness: By evaluating incident response plans and procedures, audits identify gaps, allowing organizations to improve their ability to respond effectively to security incidents.
How Often Do You Conduct IT Security Audits?
The frequency of IT security audits depends on various factors such as industry regulations, organizational size, the complexity of IT infrastructure, and the evolving threat landscape.
We advise companies that handle sensitive information and payment or security data to conduct security audits at least twice a year. It is crucial to consider that security audits require time and planning to ensure a seamless process. Typically, audits should be conducted annually or whenever significant changes occur in the IT environment.
IT Security Audit Checklist
comprehensive checklist of key items to be evaluated during an IT security audit. It’s important to note that the specific items may vary based on the unique needs and requirements of each company. However, the following checklist provides a general overview:
- Data Security:
- Verify the implementation of data encryption for both data at rest and in transit using protocols like TLS.
- Assess the effectiveness of access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
- Check for the presence of regular data backups and verify their secure storage to protect against data loss.
- Network Security:
- Verify that firewalls are properly configured and up to date to prevent unauthorized access.
- Conduct checks for open ports and ensure they are secured to minimize potential vulnerabilities.
- Confirm the presence of up-to-date antivirus and malware protection to safeguard against malicious software.
- Application Security:
- Verify that all software applications have the latest patches and security fixes applied to address known vulnerabilities.
- Perform vulnerability scans, including checks for common vulnerabilities like SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Consider conducting penetration tests to gain detailed insights into application vulnerabilities and potential exploitation.
- User Security:
- Verify the strength and effectiveness of password policies in place, including requirements for complexity and regular password changes.
- Ensure that users are trained on best security practices, such as avoiding phishing scams and practicing good password hygiene.
- Regularly review and update user access privileges to prevent unauthorized access and ensure only necessary permissions are granted.
During an IT security audit, it is crucial to thoroughly examine these areas as they represent significant aspects requiring assessment. However, the specific checklist items may vary depending on the organization’s unique requirements and industry standards.
Benefits of IT Security Audit
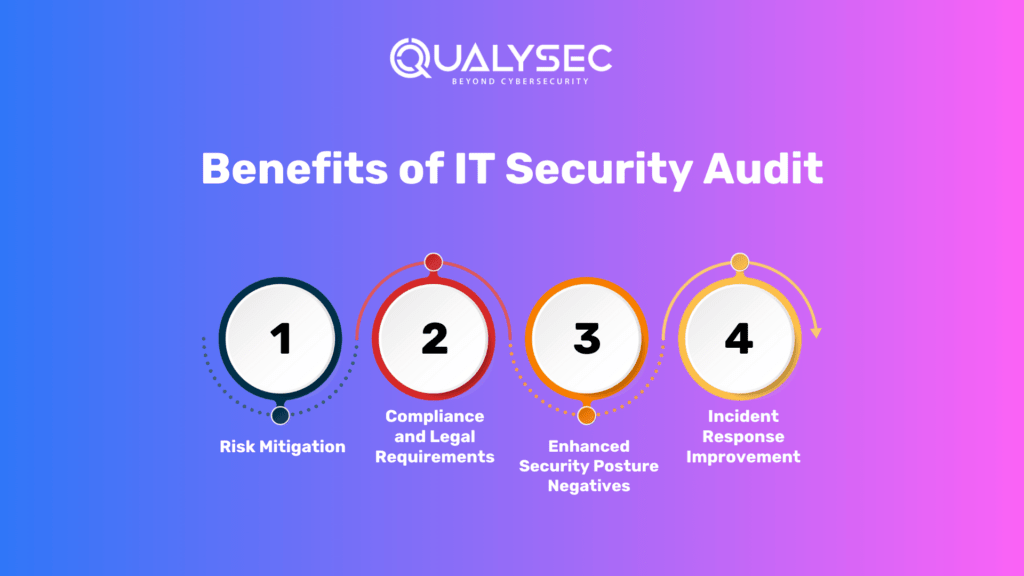
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying vulnerabilities and risks enables organizations to implement appropriate measures to mitigate potential threats.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Audits ensure organizations comply with industry regulations, avoiding penalties and reputational damage.
- Enhanced Security Posture: By evaluating existing controls and implementing improvements, organizations strengthen their overall security defenses.
- Incident Response Improvement: Audits identify gaps in incident response plans, allowing organizations to enhance their response capabilities.
Methodology for Conducting an IT Security Audit
- Define Audit Scope: Clearly define the scope of the audit, including the systems, networks, applications, and data to be assessed. Consider industry regulations, compliance requirements, and the organization’s specific security concerns.
- Gather Information: Collect relevant documentation, such as security policies, procedures, network diagrams, and system configurations. Conduct interviews with key personnel to gain an understanding of existing security controls and practices.
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and vulnerabilities by conducting a risk assessment. Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk to prioritize mitigation efforts.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Perform a comprehensive vulnerability assessment using automated scanning tools and manual techniques to identify vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications.
- Controls Evaluation: Assess the effectiveness of existing security controls, including access controls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and incident response procedures. Verify compliance with industry standards and best practices.
- Gap Analysis: Compare the organization’s current security posture with industry standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices. Identify gaps and areas requiring improvement.
- Reporting: Prepare a detailed audit report summarizing findings, including identified risks, vulnerabilities, and recommendations for improvement. Prioritize recommendations based on risk levels and potential impact.
- Remediation: Work with relevant stakeholders to address identified vulnerabilities and implement recommended security enhancements. Develop a remediation plan with clear responsibilities and timelines.
- Follow-up and Continuous Monitoring: Conduct follow-up assessments to ensure that identified vulnerabilities have been addressed and security controls have been implemented effectively. Implement continuous monitoring processes to detect and respond to emerging threats.
How to Conduct an IT Security Audit for Your Business?
- Define the Audit Objectives: Determine the specific goals and objectives of the audit based on industry regulations, organizational requirements, and security concerns.
- Select the Right Audit Team: Assemble a qualified team with expertise in IT security, risk assessment, compliance, and audit methodologies.
- Plan and Prepare: Develop an audit plan, gather relevant documentation, and define the scope of the audit.
- Conduct the Audit: Perform risk assessments, vulnerability scans, control evaluations, and gap analysis. Document findings and recommendations.
- Prepare the Audit Report: Summarise the audit findings, including identified risks, vulnerabilities, and recommended actions. Prioritise recommendations based on risk levels.
- Implement Remediation Efforts: Work with relevant stakeholders to address identified vulnerabilities and implement recommended security enhancements.
- Follow-Up and Continuous Monitoring: Conduct follow-up assessments to ensure that identified vulnerabilities have been addressed and monitor ongoing compliance and security status.
Qualysec, The Best Among IT Security Audit Service Providers
Qualysec is a leading provider of Cybersecurity and compliance management solutions. Their platform allows companies to conduct continuous monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and compliance management across their entire IT infrastructure with the help of AI.
Qualysec follows a comprehensive methodology that combines manual and automated testing techniques and AI to ensure maximum coverage of vulnerabilities. They also provide detailed reports that include a prioritized list of vulnerabilities, along with recommendations for remediation.
They work closely with organizations to understand their unique needs.
Qualysec offers various services which include:
- Web App Pentesting
- Mobile App Pentesting
- API Pentesting
- Cloud Security Pentesting
- IoT Device Pentesting
- AI /ML Pen-testing
The methodologies offered by Qualysec for IT Security Audit are particularly beneficial for businesses that must adhere to industry rules or prove their dedication to security to clients and partners. So, by opting for Qualysec as a reliable service provider, businesses can ensure the safety of their web applications.
Hence, choose Qualysec for a comprehensive and reliable vulnerability scanning report. Also, their penetration testing guide will help you make informed decisions and understand the various factors that impact the cost. Hence, protect your assets and enhance your security posture by choosing us.
Key Features
- Over 3,000 tests to detect and root out all types of vulnerabilities.
- Capable of detecting business logic errors and gaps in security.
- Ensures zero false positives through manual pen testing.
- Compliance-specific scans for SOC2, HIPAA, ISO27001, and other relevant standards.
- Provides in-call remediation assistance from security experts
Conclusion
IT security audits are vital for organizations to assess and enhance their security posture. By conducting regular audits, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and protect sensitive information. Following a systematic methodology, utilizing best practices, and considering industry standards, organizations can conduct effective IT security audits and strengthen their overall security defenses. Implementing the necessary remediation efforts based on audit findings allows organizations to proactively protect their digital assets and mitigate potential threats.
There are several types of Pen testing Solutions one might need, and vulnerability scanners, including network scanners, host scanners, application scanners, cloud scanners, and wireless scanners. Each with its own set of benefits and use cases. Additionally, both internal and external vulnerability scanners are necessary. These cover all devices and systems that are accessible from within and outside of an organization’s network. We are always ready to help, talk to our Experts and fill out your requirements.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: Can I conduct an IT security audit internally, or should I hire an external auditor?
A: We recommend involving external auditors, especially for larger organizations or when regulatory compliance is a concern. External auditors bring impartiality and expertise to the audit process.
Q2: What are the typical costs associated with an IT security audit?
A: The costs of an IT security audit can vary depending on factors such as the size of the organization, the sophistication of the IT infrastructure, and the scope of the audit. It is advisable to obtain quotes from reputable audit firms or consultants.
Q3: How long does an IT security audit take?
A: The duration of an IT security audit depends on various factors, including the size and complexity of the organization’s IT environment and the scope of the audit. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Q4: What happens if vulnerabilities are identified during an IT security audit?
A: If you identify vulnerabilities, it is important to address them promptly. Prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of the vulnerabilities and their potential impact on your organization’s security.
































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments