Global e-commerce is on the rise and more companies are stepping into Web 2.0 at an ever-increasing rate. However, with the advancement in technology and usage of the internet, more business firms and organizations are likely to be attacked by cyber threats. Online E-commerce websites are especially vulnerable to cyber-attacks because they process a vast amount of information about the clients, their payment methods, and the company itself.
You might be thinking how can E-commerce websites be protected against vulnerabilities of cyber attacks, this is where E-Commerce penetration testing comes into play. E-commerce penetration testing is a procedure that aims at determining the weaknesses of online businesses and fixing them to prevent hackers from finding and exploiting them. It is an important measure that needs to be taken to ensure the protection of online businesses.
In this guide, we are going to explore what e-commerce penetration testing consists of, why it is crucial, the steps to e-commerce penetration testing, the tools applied, and how companies can protect their online properties from cyber threats.
What is E-commerce Penetration Testing?
E-commerce penetration testing also referred to as pen testing is a procedure that assesses the readiness of an e-commerce system in facing actual attacks from hackers. This involves looking for weaknesses within the system as well as probing for susceptibilities in the system to determine its security strength. In other words, it’s the plan to detect vulnerabilities and address them before they can be targeted by hackers.
In a pen test, hackers otherwise known as pen-testers, carry out attacks that are typical to test the security of the e-commerce platform. They employ different methods and approaches to attempt to penetrate the system, pinpoint weaknesses, and then report it to the business. This testing encompasses web applications, servers, databases, and networks thus covering all the aspects of e-commerce systems.
Importance of E-commerce Penetration Testing
Websites involved in selling goods and services are especially attractive to hackers because such sites store valuable and often sensitive information, such as customers’ credit card information and transaction history. The implications of security breaches may include heavy monetary losses, damage to the company image, and legal penalties. This is why e-commerce penetration testing is required.
Here are a few reasons why businesses need to prioritize pen testing services:
1. Protecting customer data: These cyber attacks therefore result in the leakage of customer information such as names, addresses, and payment profiles. Pen testing assists in revealing those weaknesses that may lead to such breaches.
2. Maintaining trust and reputation: Customers have to feel secure that their information will not be compromised the moment they place an order for their products. Any security incident removes that trust and customers and greatly harms the brand.
3. Complying with regulations: In many spheres, particularly those working with information, certain requirements concerning security must be fulfilled, for example, PCI DSS in a sphere of payments. These regulations are strictly adhered to through the use of penetration testing done frequently.
4. Preventing financial loss: Cyberattacks can result in stolen funds, fraud, and costly legal battles. Pen testing reduces the risk of such losses by identifying and mitigating security flaws.
E-commerce websites are high-value targets due to the wealth of sensitive information they process, such as credit card data, personal customer details, and transaction history. A security breach could lead to significant financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences. This is why e-commerce penetration testing is vital.
Key Vulnerabilities in E-commerce Systems
As with any other technological platform, e-commerce platforms have various security risks as they are quite complex and deal with a lot of sensitive data. Some of the most common vulnerabilities in e-commerce systems include:
1. SQL Injection (SQLi)
SQL injection is a type of attack that involves the insertion of malicious code into the input fields of any database connection. This causes the vulnerability of the database to hackers whereby they gain access to the data that is crucial for the customers such as user names, passwords, and payment details among others.
2. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS vulnerabilities allow the attacker to insert the piece of code into the page which would be viewed by other users. This may result in the capture of session cookies, and personal details or even perform other unauthorized actions in the name of the user like for instance making unwanted transactions.
3. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
CSRF is a process whereby the attacker takes advantage of users and makes them perform actions on an e-commerce platform without their knowledge. For instance, a logged-in user may modify his profile information or purchase a product, just by clicking on a link they didn’t know was malicious.
4. Insecure Payment Gateways
Another weakness that has been noted about payment gateways is that if they are not protected adequately, they pose a risk to a firm’s financial data including credit card information. Weak payment gateways are potential areas of concern for attackers who aim at intercepting payments and other sensitive data during online transactions.
5. Weak Authentication Mechanisms
Lack of strong passwords and no implementation of two-factor authentication makes it easier for the attacker to penetrate the accounts of the users. Password reuse and other weak password habits enhance this risk, chiefly if the implementation of static or reversible cryptographic hash functions is done incorrectly.
6. Session Hijacking
External session hijacking or man-in-the-middle attack is one where attackers can capture the user’s session token and use it to gain access to the session. This vulnerability can stem from poor session management or weak encryption or no encryption at all.
7. Unsecured APIs
Most e-commerce platforms integrate with Third-party APIs for such services as payment processing, shipping, and inventory management. It means if these APIs are not secured they can simply become the weak entry points for the attacker to infiltrate into the system.
8. Inadequate Data Encryption
When passing through the internet, if the data such as payment information or personal customer information is not encrypted well, they are vulnerable to being hacked by cyber criminals.
9. Vulnerabilities in Third-Party Plugins
There are always multiple plugins or extensions that help the e-commerce site to provide added functionality like the shopping cart or payment gateway. These plugins can pose a threat to the website especially if they are outdated or they possess built-in vulnerabilities.
10. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
A DoS or Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack involves flooding an e-commerce platform with traffic and thus restricting the platform’s access to genuine users. Although not necessarily concerning the data of customers directly, such attacks are likely to lead to heavy losses related to the time the business is unable to operate.
Through e-commerce penetration testing, these vulnerabilities are effectively managed and minimized hence lowering the attack risk and maximizing customer confidence in online shopping.
| Also Read – Top 10 Web Application Vulnerabilities |
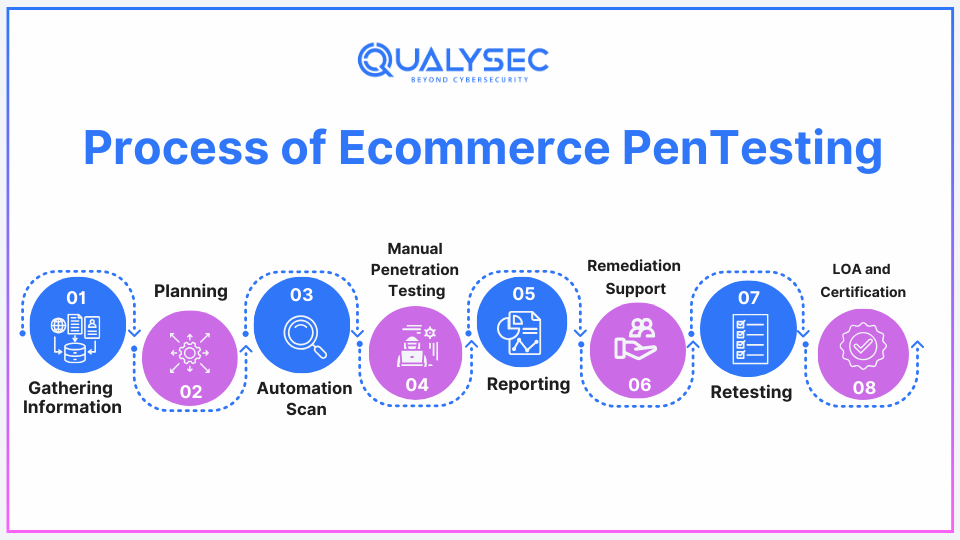
Process of E-commerce Penetration Testing

E-commerce penetration testing is quite systematic and organized so that the assessment of the entire e-commerce system is done systematically. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the typical pen-testing process:
1. Information Gathering
Pen testing specialists start with data gathering concerning the target system. This involves a determination of the e-commerce platform used, technology structure, network, and web applications. It becomes the intention of the tester to understand how the system works and thereby identify possible points of vulnerability that a hacker would use in attacking the system.
2. Planning
The testing plan is made based on the information that has been gathered. This involves identification of the areas to test which involves coming up with the criteria of the test such as whether to test the system, applications, or the networks. The testers also tell what kinds of vulnerabilities they will look for, and which kind of attacks they will employ.
3. Automated Vulnerability Scans
Automated vulnerability scanners are used to scan the system for generic weaknesses in the systems, the application, firmware, and other components such as those which are outdated software, old patches, and wrong configuration of the system. These scanners offer a general view of the risks involved, in the case of a business.
4. Manual Penetration Testing
Even though automatic scans are helpful, they cannot identify all the potential issues. This is where manual testing comes in. Manual testing is the process of testing the software or application manually by an individual or a team of testers by inputs and usage instead of by automatic test cases or scripts. Ethical hackers seek to take advantage of the loopholes that might not have been identified by automated tools and these are among others; SQL injections XSS, and CSRF.
5. Reporting
Once these tests are done, the penetration testers provide a comprehensive report on the weaknesses found and their implications as well as the methods used to exploit them. This report also has recommendations on how to rectify the problems that have been highlighted.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

6. Remediation
Once the vulnerabilities have been identified, the business needs to address them. This may be done by fixing vulnerable points in software, rectifying improper settings, and upgrading security measures such as user identification and encryption among others.
7. Retest
The process involves repeating a similar set of tests after the vulnerabilities have been addressed in an attempt to confirm that more of them have not been created in the process.
8. LOA and Security Certificate
After the retesting is done and the system has been declared secure, the organization is given the Letter of Attestation (LOA) also referred to as a security certificate which testifies that the given e-commerce platform has successfully gone through the penetration testing.
E-commerce Penetration Testing Tools

To discover vulnerabilities, various tools are used in e-commerce penetration testing to help evaluate system security. Some popular tools include:
- BurpSuite is an all-in-one application for Web application penetration testing and performs its checks both automatically and manually to reveal security vulnerabilities.
- The OWASP Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) is one of the most popular and widely used tools in the modern world that detects vulnerabilities in any web application.
- NetSparker is a tool that is effective in analyzing web applications for different vulnerabilities like; SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- Nikto is a tool for scanning web server settings, either Apache or NGINX open source, that can point to the existence of problems like outdated software.
- Metasploit is a strong tool for penetration testing that can be used to duplicate actual IT assaults and analyze the vulnerability of the system.
Best Practices for E-commerce Penetration Testing
To ensure a thorough and effective pen test, businesses should follow these best practices:
1. Regular Testing: Regular penetration tests should be conducted with the retest after critical updates or changes concerning the e-commerce system.
2. Use a Combination of Tools and Manual Testing: Although there are various automated testing tools, which can detect well-known weaknesses the testing should be carried out manually to detect severe problems.
3. Focus on High-Risk Areas: Security features such as payment gateways, customer data storage, and authentication mechanisms are additional elements that need more attention.
4. Prioritize Remediation: Once such areas have been identified in the organizations, they must be addressed according to the risks that they pose to the business.
5. Ensure Compliance: Make sure that pen testing is compliant with regulations that apply to the tested environment for instance PCI DSS for payments.
Conclusion
E-commerce businesses are prime targets for cyberattacks, but with the proper security measures, they can protect themselves and their customers from potential threats. E-commerce penetration testing is a critical step in securing online platforms, helping to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. By conducting regular pen tests, using the right tools, and following best practices, businesses can build trust with their customers and protect their valuable assets.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
FAQ
Q. What are the different types of testing in e-commerce?
A. Different types of testing in e-commerce include: Different types of testing in e-commerce include:
- Functional Testing: Makes sure that the different elements designed in the e-commerce platform work in the right way, such as product searches, payments, and orders.
- Performance Testing: Tests how the e-commerce site would be when put under different loads to determine whether it can handle a large traffic volume without freezing or crashing.
- Security Testing: Concentrates on finding the loopholes in the system that have to be covered against hacker attacks.
- Usability Testing: Evaluate the usability of the website so that consumers can be able to perform their transactions conveniently.
Q. How Qualysec Can Help with E-commerce Penetration Testing?
A. Qualysec is a specialized cybersecurity company focusing on the e-commerce penetration testing business. The people in the team are ethical hacking professionals who are equipped with sophisticated gadgets and approaches including hacking exercises that can imitate live real-life e-commerce attacks to uncover gaps and flaws in the e-commerce platforms. In addition to the scanning services, Qualysec offers reports and advice for the remediation of security risks and protection from cyber threats.
Q. What is the Cost of E-commerce Penetration Testing?
A. Evaluating the cost of e-commerce penetration testing may differ from one e-commerce platform to another based on its size and sophistication level, testing coverage, and tools used. As with most services, the cost of getting a penetration test done ranges from $3,000 to $30,000 for large-scale testing.
Some of the aspects that may affect the cost include the number of systems, web applications, and/or networks to be tested. However, the investment is a worthy one, especially given the possibility of avoiding data loss and other security threats.

































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments