With cyber threats becoming increasingly complex and frequent, organizations are investing more in understanding their vulnerabilities. Two common methods for evaluating the strength of an organization’s cybersecurity are penetration testing (pentesting) and cybersecurity audits. But what are these processes, and how do they differ? This guide will discuss Pen Testing vs Cybersecurity Audit, highlighting the key distinctions between pentesting and cybersecurity audits to help you determine which approach or combination of both is the best fit for your organization’s needs.
What is Pentesting?
Pentesting, short for penetration testing, is a simulated cyberattack on your systems. Its primary goal is to uncover vulnerabilities by mimicking the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of real-world attackers.
This is often performed by ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, who identify and exploit weaknesses to demonstrate how a threat actor might breach your systems.
Examples of issues a pentesting session may uncover include:
- Unpatched software vulnerabilities
- Misconfigured firewalls
- Weak passwords and exposed credentials
Types of Pentesting
Pentests come in various forms, depending on the scope and objective. Here are the most common types:
- Network Pentesting – Targets vulnerabilities in a company’s network infrastructure, such as routers, servers, or firewalls.
- Web Application Pentesting – Focuses on identifying exploits in web-based applications, including injection attacks and session management flaws.
- Wireless Pentesting – Examines vulnerabilities in a company’s wireless infrastructure, such as open Wi-Fi networks or outdated encryption protocols.
- Cloud Penetration Testing – Evaluates security risks in cloud environments by testing misconfigurations, access controls, and data leaks.
- Mobile Application Penetration Testing – Identifies security flaws in iOS and Android apps, including insecure data storage, weak authentication, and API vulnerabilities.
- API Penetration Testing – Focuses on API security by testing authentication, authorization, and data exposure risks in applications and integrations.
Goals of Pentesting
The primary aim of pentesting is to answer this question: “Can your defenses stand up to a real cyberattack?” By identifying vulnerabilities before attackers do, organizations can take immediate action to strengthen their systems.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

What is a Cybersecurity Audit?
A cybersecurity audit, on the other hand, is a comprehensive evaluation of your company’s cybersecurity processes, policies, and compliance measures. The audit provides a broader view of the organization’s security practices, ensuring alignment with industry frameworks and standards, such as ISO 27001 or NIST.
Unlike a pentest, which is adversarial, audits focus on assessment and evaluation.
Components of a Cybersecurity Audit
A robust cybersecurity audit typically includes three key components:
- Policy Review – Examines existing security policies, such as data protection plans and access control measures.
- Compliance Checks – Ensures that an organization meets regulatory and legal requirements, like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
- Risk Assessments – Evaluate potential threats to critical assets to prioritize investments in security measures.
For example, instead of simulating an attack, an audit might assess whether an organization has written incident response plans and if employees are trained to follow them.
Goals of a Cybersecurity Audit
The primary goal of an audit is to evaluate the overall health of your cybersecurity program and measure your organization’s compliance with industry standards. Think of it as a routine health check for your digital security.
Key Differences Between Pen Testing Vs Cybersecurity Audit
Understanding the differences between pentesting and cybersecurity audits is crucial in choosing the right strategy for your organization. Below are the key distinctions:
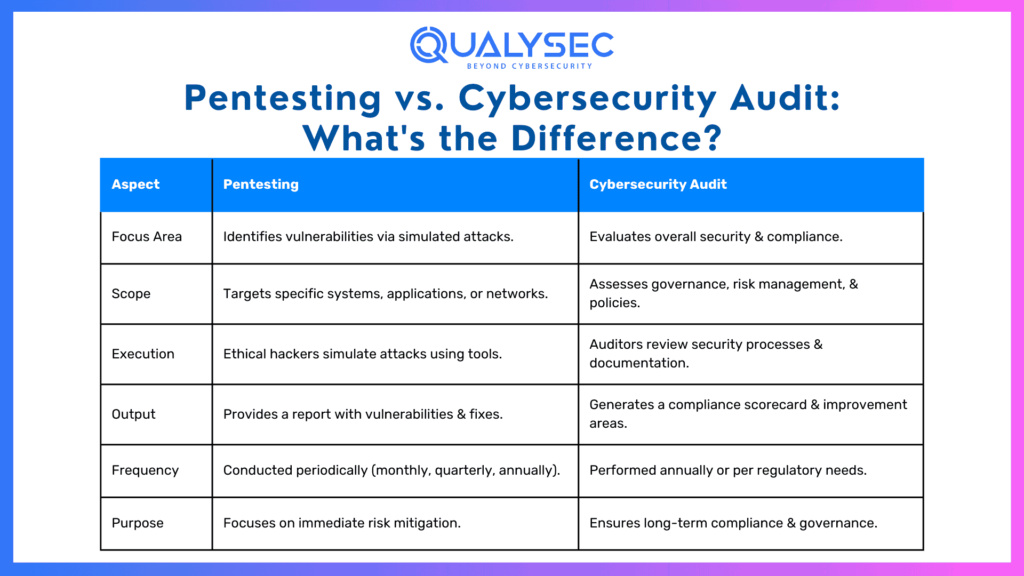
1. Focus Area
The primary distinction starts with what each approach focuses on.
Pentesting:
- Focuses specifically on uncovering vulnerabilities in systems or networks.
- Simulates attacks to identify potential points of exploitation by hackers.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- Evaluate the organization’s overall security framework, including people, processes, and technology.
- Ensures compliance with security and regulatory standards.
If your business has concerns about specific digital assets, pentesting is the go-to. For a higher-level evaluation of security policies and practices, prioritize a cybersecurity audit.
2. Scope
The scope determines how detailed or comprehensive each approach is.
Pentesting:
- A narrow, technical focus that targets specific systems, applications, or networks.
- Ideal for organizations that recently launched new software, expanded their network, or handled a breach.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- A broader examination encompassing the organization’s entire security environment.
- Looks at governance, risk management practices, user behavior, and how physical security integrates with digital defenses.
While pentesting dives into the “how” of breaches, cybersecurity audits answer the “why.”
3. Execution
How each method is executed reveals another critical difference.
Pentesting:
- Conducted by ethical hackers who simulate attacks to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Testers use a mix of automated tools and manual techniques to mimic real-world scenarios.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- Systematically executed by certified auditors who examine security processes, policies, and controls.
- Includes reviewing documentation, interviewing employees, and analyzing infrastructure compliance.
The hands-on, technical approach of pentesting contrasts sharply with the procedural evaluation of an audit.
4. Output
Both generate reports, but the type of output you’ll receive varies.
Pentesting:
- Delivers a detailed report highlighting vulnerabilities, ranked by severity.
- Includes actionable remediation steps to strengthen defenses.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- Provides a comprehensive compliance scorecard with insights into how the organization aligns with frameworks like NIST or ISO.
- Suggest areas for improvement to meet or maintain certification standards.
While pentests aim to fix immediate risks, audits provide a big-picture perspective on your security program.
“Also, read our guide to Compliance Security Audit!”
5. Frequency
When and how often these activities occur also differs.
Pentesting:
- Typically performed periodically, based on security needs or after significant changes (e.g., launching new software or recovering from a breach).
- Can occur monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- Usually conducted once a year or to meet certification and compliance deadlines.
- May also occur post-security incidents or when preparing for regulatory inspections.
This means pentests are much more adaptable, while cybersecurity audits follow a more structured calendar.
6. Purpose
Finally, the overarching purpose and goals of each strategy set them apart.
Pentesting:
- Aims to improve defenses against attacks by identifying exploitable weaknesses.
- Focuses on immediate security risks.
Cybersecurity Audit:
- Ensures long-term alignment with industry standards and benchmarks.
- Concentrates on sustainability and compliance.
Together, these approaches complement each other, building a more robust security posture.
Do You Need a Pentest, an Audit, or Both?
The choice between pen testing Vs cybersecurity audit depends on your organization’s goals. Here’s a quick breakdown:
When to Choose Pentesting?
- You need to test the effectiveness of your current defenses.
- You’re rolling out new systems or software.
- You suspect vulnerabilities after a security incident.
When to Choose a Cybersecurity Audit?
- You need to meet compliance or regulatory requirements.
- You want a comprehensive understanding of your overall cybersecurity framework.
- You will be presenting the audit results to stakeholders or regulators.
For maximum protection, many organizations opt for a combination of both. The insights from an audit can guide long-term security strategy, while pentesting provides immediate feedback on specific vulnerabilities.
The Business Case for Prioritizing Cybersecurity Investments
Investing in cybersecurity measures like pentesting and audits isn’t just a tech upgrade—it’s a business imperative. Organizations that neglect their cybersecurity often lose customers, revenue, and their reputation following breaches.
Prevention is always better than a cure. Proactively addressing vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance shows your clients and partners that you take security seriously.
Next Steps for a More Secure Organization
Both pentesting and cybersecurity audits are essential tools for modern businesses navigating a world filled with digital threats. Selecting the right approach—or combining both—depends on your specific needs, goals, and resources.
If you’re serious about protecting your data and strengthening your organization against cyber threats, now’s the time to take action.
Want Professional Help?
Get in touch with our cybersecurity experts to discuss a custom plan that includes pentesting, audits, or both. Let’s build a stronger, more secure future together.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments