Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals access, store, and manage data. By offering scalable, on-demand resources over the internet, cloud computing has become a key driver of innovation, enabling companies to reduce costs and improve efficiency. However, as cloud adoption grows, so does the need for standardization to ensure security, interoperability, and reliability.
This is where the NIST Cloud Computing Architecture comes into play. Defined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), this framework establishes a common understanding of cloud computing components, service models, and deployment methods, providing a structured approach for organizations to adopt cloud technology securely and efficiently.
This blog will explore the NIST architecture of cloud computing, breaking down its components, service and deployment models, key characteristics, and why it matters for businesses today.
Understanding NIST Cloud Computing Architecture
What is the NIST Definition of Cloud Computing?
NIST defines cloud computing as a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Overview of the NIST Cloud Computing Reference Model
The NIST reference model for cloud computing serves as a blueprint to guide stakeholders—including cloud consumers, providers, and auditors—in understanding how cloud environments function. It outlines key roles, relationships, and standards needed to ensure secure, efficient, and interoperable cloud services. The framework also acts as a common language for discussing and managing cloud computing systems.
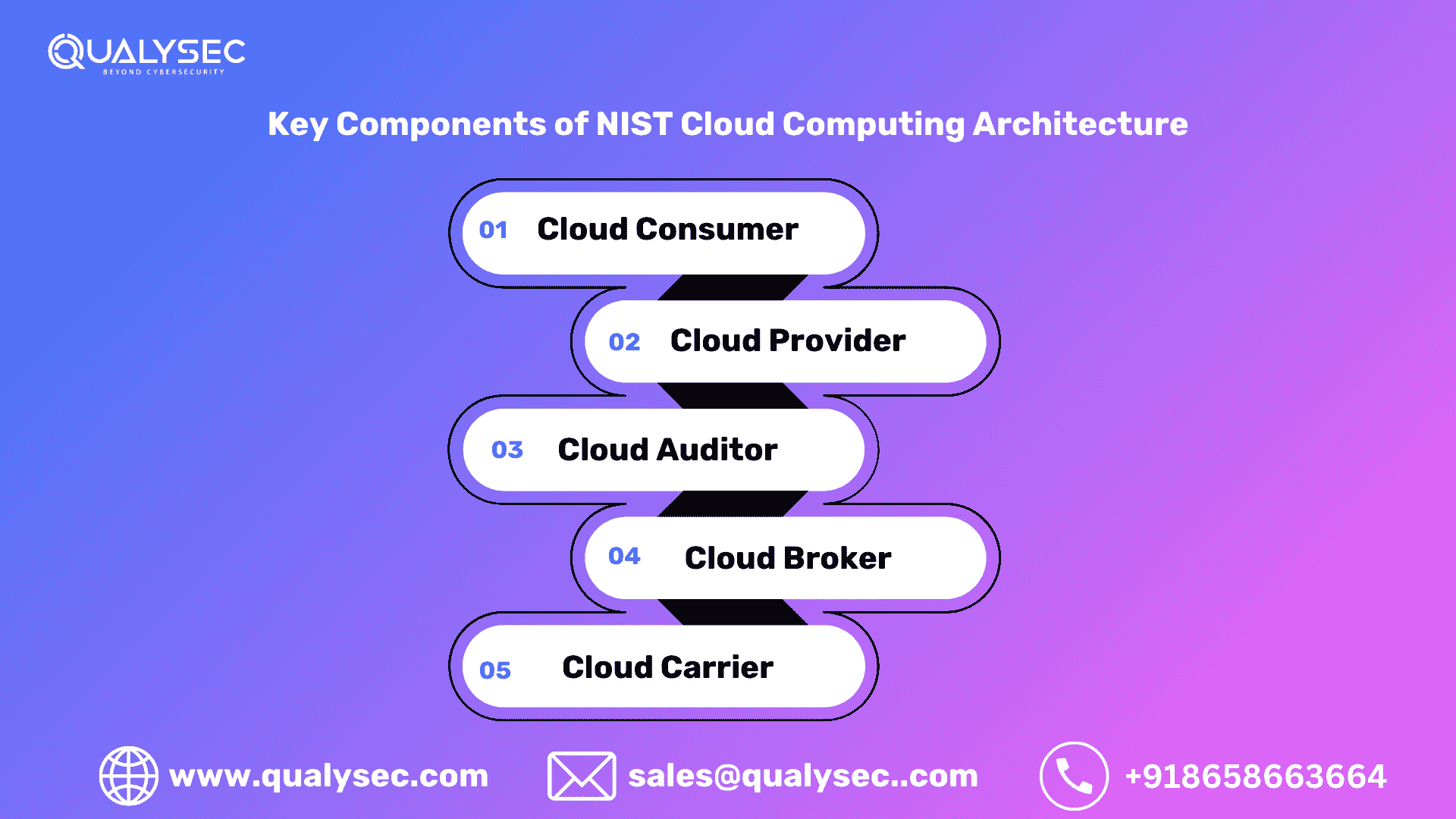
Key Components of NIST Cloud Computing Architecture
At the heart of the NIST model are several key roles and intermediaries that interact within the cloud ecosystem:
1. Cloud Consumer
The cloud consumer refers to individuals or organizations that use cloud services. They acquire capabilities such as storage, computing power, or software from cloud providers. Examples include businesses leveraging Amazon Web Services (AWS) for hosting applications or individuals using Google Drive for file storage.
2. Cloud Provider
Cloud providers are entities like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud that offer cloud services to consumers. They manage and deliver essential resources and services, ensuring availability, security, and performance.
“Also explore: Top 20 Cloud Security Providers of 2025
3. Cloud Auditor
Cloud auditors ensure the compliance, security, and performance of cloud services. They play a critical role in verifying that cloud providers meet regulatory and organizational standards, often performing third-party assessments.
4. Cloud Broker
Cloud brokers manage cloud services across multiple providers. They help consumers optimize their cloud environments by mediating usage, performance, and pricing across public, private, and hybrid clouds.
5. Cloud Carrier
The cloud carrier serves as the intermediary that connects cloud consumers and providers. It includes telecommunications and network providers that facilitate data transfer and communications between users and cloud services.
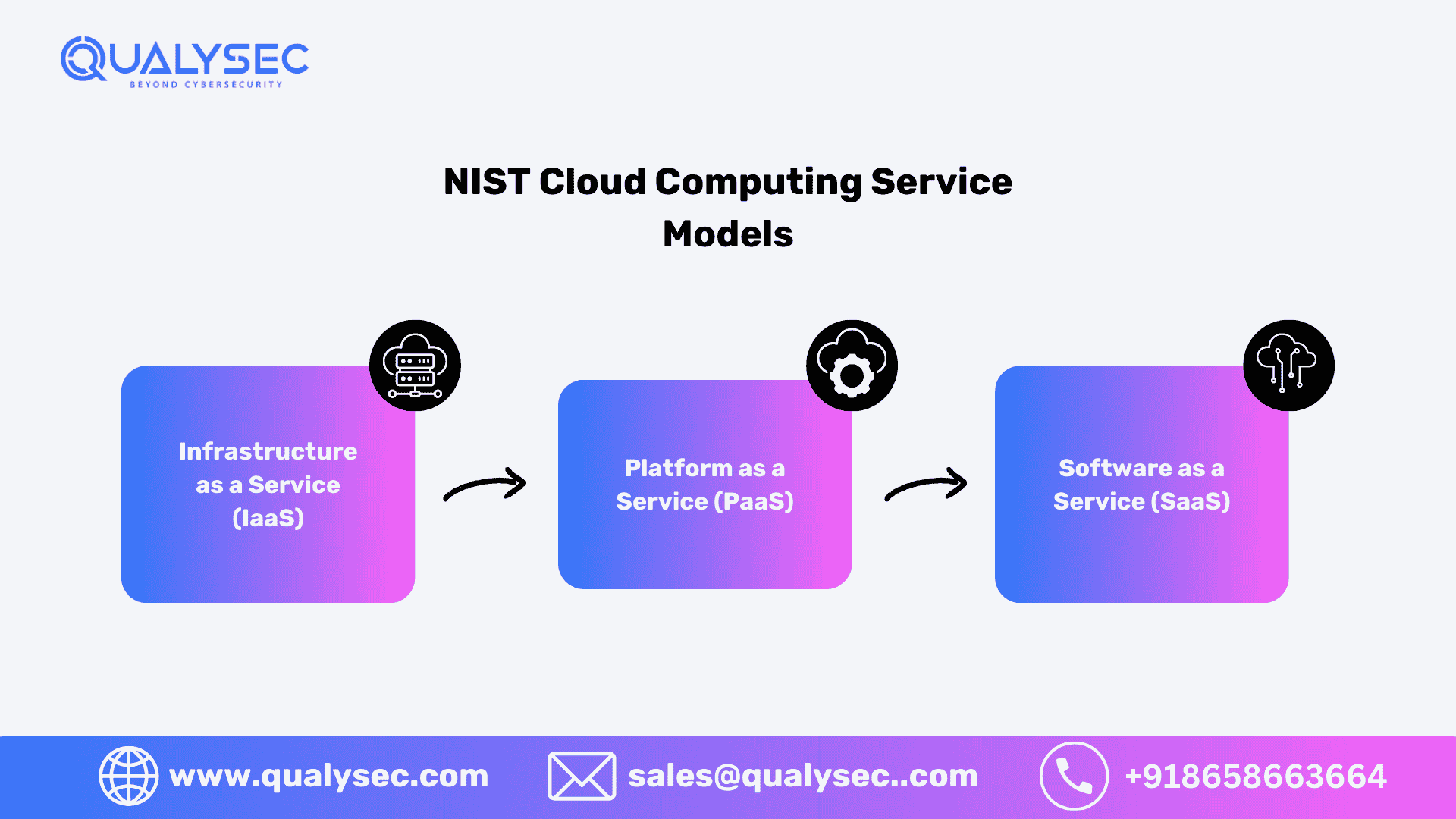
NIST Cloud Computing Service Models
NIST outlines three primary service models, each catering to specific needs and use cases:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can configure virtual machines, storage, and networks while maintaining control over the operating systems and applications. Examples include AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS delivers a complete development and deployment environment, enabling users to build, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. Examples include Microsoft Azure App Services and Google App Engine.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS offers ready-to-use applications hosted in the cloud, accessible via web browsers. Users benefit from minimal upfront costs and seamless updates. Examples include Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Dropbox.
NIST Cloud Deployment Models
Deployment models describe how cloud services are made available to users. NIST identifies four key deployment models:
1. Public Cloud
Public clouds are open for public use and managed by third-party providers. They are highly scalable and cost-effective but may raise privacy and security concerns. Examples include AWS and Microsoft Azure.
2. Private Cloud
Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, offering enhanced security and control. They are often used by enterprises that require strict compliance and data protection.
3. Community Cloud
A community cloud shares infrastructure among a specific group of organizations with similar interests or compliance requirements. Examples include government or healthcare entities sharing resources.
4. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds combine two or more deployment models, such as private and public clouds, to achieve a balance of scalability, security, and cost efficiency.
“Related Content: Read our guide to Cloud Penetration Testing or Cloud Security VAPT service to secure your cloud infrastructure effectively!“
Latest Penetration Testing Report

NIST Cloud Computing Characteristics
NIST outlines five core characteristics that define cloud computing. These elements distinguish cloud services from traditional computing models:
1. On-Demand Self-Service
Users can provision and manage resources like storage and computing power without human intervention from the service provider, offering unmatched flexibility.
2. Broad Network Access
Cloud services are accessible over the internet, allowing users to connect from various devices such as smartphones, laptops, and desktops.
3. Resource Pooling
Resources are shared across multiple users, with providers dynamically allocating resources based on demand. This multi-tenancy model ensures cost-effectiveness and scalability.
4. Rapid Elasticity
Cloud resources can scale up or down seamlessly based on demand, ensuring that businesses have the capacity they need when they need it.
5. Measured Service
Cloud platforms utilize a pay-as-you-go pricing model, allowing users to pay only for resources they use, which promotes efficiency and cost savings.
“Check out our guide on Infrastructure Security in Cloud Computing!
Why NIST Cloud Computing Architecture Matters
The NIST cloud computing architecture represents more than just a theoretical framework; it serves as a critical tool for organizations navigating the complexities of cloud adoption. Here’s why it matters:
1. Establish Clarity and Consistency
One of the biggest challenges organizations face when adopting cloud computing is the lack of standardized language. The NIST framework provides a common terminology and conceptual model, ensuring everyone—from IT teams to C-suite executives—is on the same page. By defining terms like “on-demand self-service” or “community cloud,” it eliminates misunderstandings and creates cohesion across departments.
Think of it as providing a “cloud dictionary” to streamline communication, regardless of the organization’s size or technical expertise.
2. Align Technology with Goals
Implementing cloud computing successfully requires aligning technology with an organization’s business objectives. The NIST architecture emphasizes the importance of choosing the right service and deployment models to support scalability, cost-efficiency, and security.
For example, a healthcare firm handling sensitive patient data might prioritize private or hybrid cloud models to meet stringent compliance standards. Conversely, a startup focused on rapid growth may opt for public cloud services to scale affordably.
3. Allow Smarter Investment Decisions
With its clear breakdown of service and deployment models, the NIST framework empowers businesses to make informed decisions about where and how to invest. Organizations can assess their unique needs and match them with appropriate cloud offerings, ensuring a balanced approach that minimizes waste while maximizing ROI.
For instance, a team requiring high computing power for a limited period—like during product testing—can take advantage of the rapid elasticity offered by IaaS without overspending.
4. Strengthen Cybersecurity
Today’s interconnected world puts cybersecurity at the forefront of every business conversation. The NIST framework highlights the importance of resource and risk monitoring, particularly in hybrid or private environments. It recognizes that cloud adoption often intersects with regulatory compliance requirements (like GDPR or HIPAA), making it a vital foundation for industries handling sensitive data.
Additionally, organizations can use this model to create strategies for privacy, access controls, and data encryption, ensuring their platforms meet best practices.
5. Build Innovation
Cloud computing isn’t just about efficiency—it’s also a springboard for innovation. The NIST architecture, with its flexible service models, enables organizations to experiment with new tools, technologies, and workflows.
For example, businesses can use PaaS to prototype new applications without the overhead of managing infrastructure. This freedom to innovate helps industries ranging from retail to finance push boundaries, explore new business models, and maintain a competitive edge.
Schedule a meeting with our cloud security experts to secure your cloud!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Start Adopting a NIST-Guided Cloud Strategy
NIST’s cloud computing architecture provides a solid foundation for organizations looking to leverage the power of the cloud. By understanding its components, service and deployment models, and core principles, businesses can make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and stay competitive in today’s digital landscape.
If you’re interested in learning more, explore NIST’s official cloud computing publications to gain deeper insights into their guidelines and standards.











































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments