Cloud computing has revolutionized business operations, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. But as organizations move their critical workloads to the cloud, securing the underlying infrastructure becomes more important than ever. This is where infrastructure security in cloud computing comes into play.
Whether you’re a developer managing cloud-hosted applications, an IT manager overseeing a hybrid environment or a business leader looking to protect sensitive data, understanding infrastructure security is key to maintaining trust, continuity, and compliance in the cloud. This blog will break down what infrastructure security means in cloud computing, why it matters, and how you can implement best practices.
What Is Infrastructure Security in Cloud Computing?
Infrastructure security in cloud computing refers to the measures and strategies put in place to protect the foundational systems of your cloud environment. These systems include the hardware, software, networking components, and virtualization layers that enable cloud services.
Unlike traditional on-premises data centers, cloud infrastructures often exist on shared physical servers hosted by third-party providers (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud). While providers ensure the physical security of their data centers, users are responsible for securing their cloud configurations, workloads, and applications.
Infrastructure security involves addressing threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, malware, service disruptions, and insider attacks.
Key components of infrastructure security in cloud environments include:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Network Security (firewalls, VPNs, and monitoring)
- Data Encryption (in transit and at rest)
- Compliance and Auditing Tools
Now that we have defined infrastructure security, let’s explore why it is so important.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Why Is Infrastructure Security Vital in the Cloud?
Security issues in the cloud aren’t hypothetical. Below are some reasons why protecting infrastructure is mission-critical for any business moving to or relying on cloud services:
1. Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) adhere to the shared responsibility model, meaning security duties are split between the provider and the customer. The provider ensures the security of the cloud (e.g., physical servers and storage), while customers are responsible for securing what they host in the cloud (e.g., apps, data, configurations). Lacking comprehensive infrastructure security practices puts your part of the model at risk.
2. Cloud’s Massive Attack Surface
The flexibility of cloud environments makes them attractive to attackers. Misconfigured servers, outdated software, and exposed APIs (application programming interfaces) can introduce vulnerabilities. For example, IBM’s 2022 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index reports that cloud misconfigurations caused over 15% of all data breaches, which is a stark reminder that vigilance is key.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Organizations in heavily regulated industries (e.g., healthcare, finance) often handle sensitive data subject to legal requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Poor infrastructure security practices could result in non-compliance fines and reputational damage.
Infrastructure security forms the backbone of maintaining all three pillars of cybersecurity – confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) – in the cloud.
Best Practices for Securing Your Cloud Infrastructure
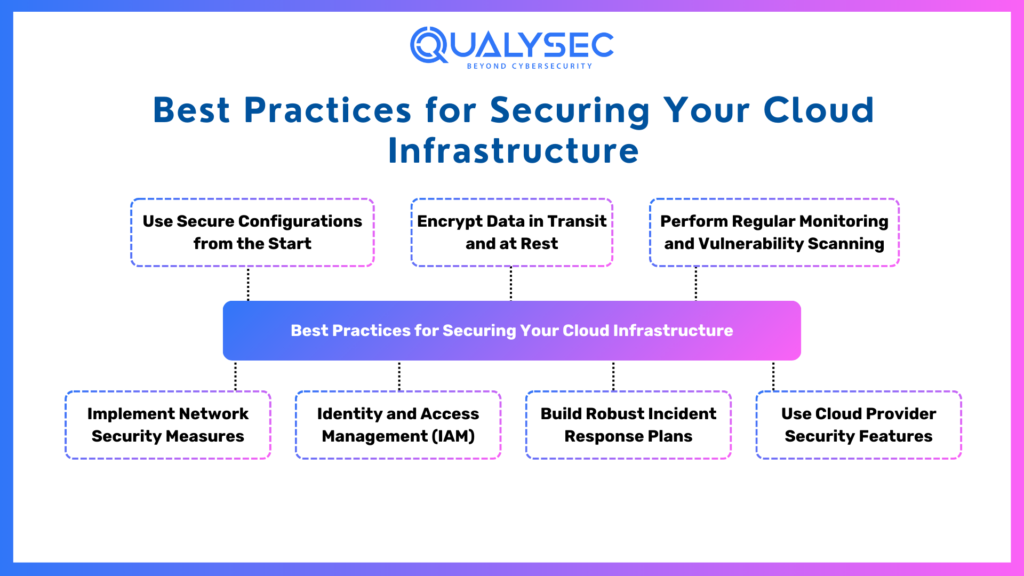
A robust Cloud computing security plan involves proactive planning, reliable monitoring, and effective tools. Below are 7 significant practices to help secure your cloud-based environments.
1. Use Secure Configurations from the Start
When implementing any cloud infrastructure, it’s critical to start with a strong foundation. Misconfigurations are a leading cause of vulnerabilities in the cloud.
Tips for Secure Configurations:
- Always follow cloud service providers’ (CSP) configuration guides.
- Automate configurations using infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation.
- Conduct regular configuration reviews to adjust as needed.
A simple oversight in setup, such as leaving storage buckets public, can expose sensitive data to external threats. Addressing configurations early minimizes risks later.
2. Implement Network Security Measures
The network layer is a common entry point for attackers, making cloud network security an essential aspect of cloud infrastructure protection.
Strategies for Network Security:
- Use firewalls: Employ cloud-native firewalls like AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) or Azure Firewall to block malicious traffic.
- Enable virtual private clouds (VPCs): Isolate workloads in unique network environments.
- Implement load balancers: Prevent traffic overloads and provide redundancy.
- Restrict inbound traffic: Use access control lists (ACL) and network segmentation to limit unnecessary access.
A well-protected cloud network blocks potential intrusions before they reach critical workloads.
3. Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest
Encryption serves as a critical defense mechanism in cloud environments, protecting data from unauthorized access—even if intercepted by attackers.
Encryption Best Practices Include:
- Use SSL/TLS protocols for data in transit.
- Employ cloud-native encryption services (e.g., AWS Key Management Service, Azure Key Vault).
- Store sensitive data only when necessary, and delete obsolete data promptly.
Encrypting both your active (in-transit) and stored (at-rest) data ensures an additional layer of security against breaches.
4. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Proper identity and access management are critical to ensure that the right individuals have access to the right resources—and nothing more.
IAM Practices to Deploy:
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users.
- Follow a least privilege rule, granting users only the access necessary to perform their tasks.
- Rotate credentials and secure API keys using centralized tools.
Organizations that neglect IAM practices inadvertently increase their risk of insider threats or unauthorized access.
5. Perform Regular Monitoring and Vulnerability Scanning
Ongoing monitoring of your cloud infrastructure security is key to identifying vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Tools and Practices for Optimal Monitoring:
- Implement cloud-native monitoring tools, such as AWS CloudWatch or Azure Monitor.
- Perform regular vulnerability assessments with tools like Tenable, Qualys, or Nessus.
- Use a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution to detect anomalous activities across integrated systems.
Through constant vigilance, businesses can act on potential threats in real-time before they escalate into significant breaches.
6. Build Robust Incident Response Plans
Even with the strongest preventive measures, incidents may still occur. A well-prepared response ensures your organization can act swiftly to minimize damage.
Key Elements of an Incident Response Plan:
- Define the roles and responsibilities of team members during incidents.
- Create system backups for quick restoration.
- Test and refine the incident response processes through simulated events.
Proactive planning enables businesses to recover faster, reducing financial and reputational damages during cyber incidents.
7. Use Cloud Provider Security Features
Major cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide built-in security tools and recommendations for your specific environment. Utilizing these security solutions ensures maximum compatibility.
Examples of Cloud Native Security Services:
- AWS Shield Advanced: Protects against DDoS attacks.
- Google Cloud Armor: Safeguards applications from targeted attacks.
- Azure Security Center: A centralized hub for security management and advanced threat protection.
Partnering with your cloud provider’s native tools can significantly enhance your security posture.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Strengthen Cloud Ecosystems Through Infrastructure Security!
Cloud computing’s flexibility and scalability are immense, but without secure infrastructure, your organization is vulnerable to cyberattacks. By prioritizing configuration controls, network protection, and regular monitoring, businesses can create safer cloud environments tailored to their needs.
However, the complexity of infrastructure security can be daunting, especially for businesses managing hybrid or multi-cloud setups. Using tools and expertise from trusted cloud service providers is an excellent way to stay safe.
Protect your business, and your data, and ensure compliance with QualySec to improve your infrastructure security in cloud computing today.

















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments