Scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness have posed SaaS in front of the business operation face. It allows organizations to deploy applications efficiently, streamlines workflows, and enhances collaboration without the management of complex IT infrastructure. However, there are a set of SaaS security risks like data breaches, insecure APIs, compliance issues, and insider threats exposing sensitive data to cybercriminals. Ignorance of these risks is vital for maintaining security.
All precautionary measures like encryption, MFA, security audit regularly, compliance, and risk minimization. IAM shall be done strictly. All third-party integration needs to be monitored. Strong plans need to formulate a response to the incident of cybersecurity. Since human error has remained one of the primary reasons for breaching attacks in many incidents. Employees need to be equipped with cyber security awareness.
This protects the SaaS security software and makes it easier for the company to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data using active security measures. Monitoring it incessantly, following compliance rules, and training the staff always gives a safe assurance about a guaranteed SaaS environment in this digital world.
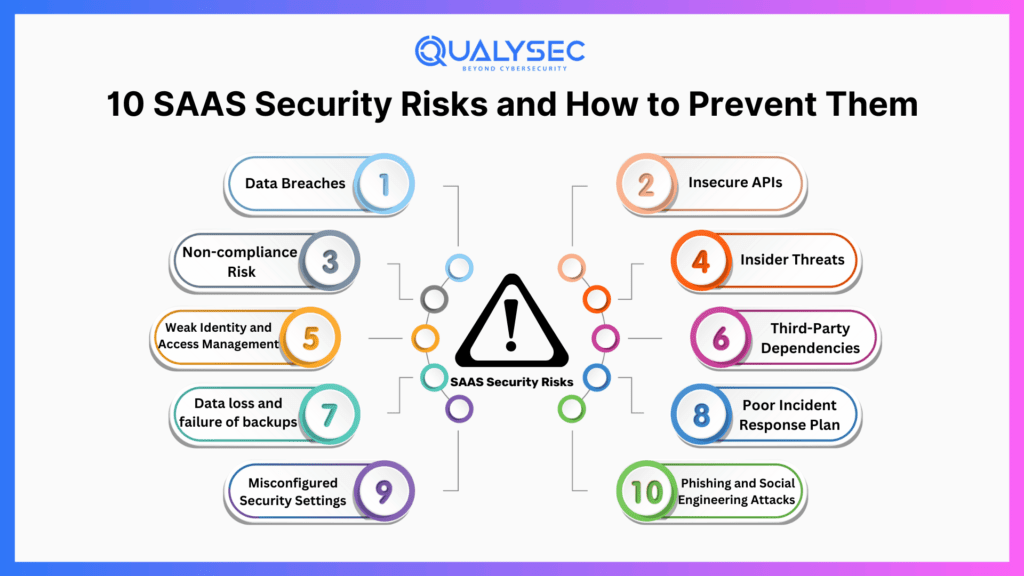
1. Data Breaches
Risk:
SaaS security platforms hold a lot of sensitive data, which is why cybercriminals are eyeing them as a prime target. A breach can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. For example, in 2021, a large SaaS provider suffered a breach that exposed the personal data of millions of users, resulting in costly lawsuits and regulatory fines. It may also lead to loss of customer trust, thereby reducing sales and long-term brand damage.
Prevention
- Use of good encryption: Encrypt data that is rest and transit so that its access is strictly prohibited to unauthorized people. Use standards like AES-256 or better.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Passwords should just be one of the verification factors that must be included. This significantly lowers the chances of being compromised by credentials.
- Regular Security Audits: Penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, and code review need to be performed to find out the vulnerabilities before they are exploited for security breaches.
- Data Minimization: Data needs to be stored only as long as necessary to minimize exposure in case of a breach.
- Access Control Policies: Implement strong access control and monitor who accesses the sensitive data.
2. Insecure APIs
Risk:
Most SaaS applications are developed to communicate using APIs. A poorly protected API can serve as the entrance through which an attacker will enter your application. In 2018, one of the most famous fitness tracking apps exposed thousands of users’ private data due to an insecure API. These people could track where other people live and other private information.
Prevention
- Authentication & Authorization: Implement OAuth 2.0, API keys, and token-based authentication to ensure that only authorized users can access the APIs.
- Penetration Testing: Execute periodic API security scanning to catch vulnerabilities and mitigate them before the hackers can take advantage of them same.
- Rate Limiting: Implement request throttling and rate limiting to help prevent DoS attacks, and brute-force, among other attacks.
- API Gateway Security: Employ gateways in real-time enforcement of security policies as well as usage monitoring and anomalies
3. Non-compliance Risk
Risk
Security SaaS providers haven’t been putting the industry’s regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2, so they are faced with legal and monetary penalties. If companies are found not to have followed the laws, they would be fined, for example, Google was fined $57 million by GDPR. However, non-adherence may even result in accessing data restrictions and loss of business opportunities.
Prevention
- Select Measured Vendors: Your SaaS security vendors should follow the relevant industry standards, and they should have any of the below-mentioned certifications such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
- Automation of Compliance: Use compliance automation tools to check and monitor regulatory compliance
- Internal and third-party audits to abide by the relevant data protection acts.
- Data Residency and Retention Policies: Clearly state where your data is held and ensure compliance with regional data protection laws.
4. Insider Threats
Risk:
Employees or third-party vendors who have access to the SaaS based platform can sometimes do it unwittingly or for other malicious purposes. In 2019, there was an incident at a huge tech firm whose employee who was upset made available some very critical company information which led to a loss in reputation and money.
Prevention:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grant the employees minimum access necessary to perform the task.
- Background Checks: Run background checks on the employees and the vendors before they are allowed access to sensitive systems
- Activity Monitoring: Monitor activities such as downloading or modifying data and alert for an action on such data
- Session Timeouts: Automatically time-out inactive accounts from logging on the system.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

5. Weak Identity and Access Management
Risk:
Bad IAM practices open the gateway for unauthorized access and theft of credentials; it is surprising to note that a 2020 report accounted for 61% of breaches due to stolen credentials.
Prevention
- Strong Password Policy: Difficult and unique passwords; in addition, passwords are changed from time to time.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Reduction of password fatigue and reuse through secure authentication of several applications.
- Access Logging: Access activities are tracked with detailed logs to detect and investigate security-related incidents.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Implementation of PAM solutions to regulate sensitive system access and restrain user-privileged activity.
6. Third-Party Dependencies
Risk:
Because many SaaS security companies‘ offerings are going to be reliant on third-party services with known vulnerabilities, if those same services are not security-hardened, thousands of businesses had secrets laid bare before one vulnerable vendor supply chain attack in 2020. Businesses’ third-party providers will most likely have multiple different security steps every time that they work with, and probably expose businesses completely out of one’s control.
Prevention
- Vendor Security Assessment: Third-party security controls should be evaluated before integration to ensure they meet your organization’s standards.
- Security Audits: Third-party services should be reviewed periodically for compliance with your security policies and best practices.
- Access Control: Third-party access should be restricted to only those data and systems that need to be accessed.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Monitor third-party risks, vulnerabilities, and changes in the third-party security posture of third-party companies to avoid a supply chain attack.
7. Data loss and failure of backups
Risks:
A good backup policy is what may mean the difference between life and death for businesses against the loss of critical data resulting from accidental deletion, ransomware, or collapse of a SaaS provider. For instance, a health provider loses the records of patients due to the failure to have a proper backup policy which leads to non-compliance and loss of confidence. Besides, organizations risk experiencing serious operational disruption if there is no proper procedure for data recovery.
Prevention
- Automated Backups: Schedule redundant backups across multiple locations to prevent data loss.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Regularly test the procedures for data restoration to ensure rapid and reliable recovery in case of emergency.
- Retention Policies: Define clear retention and recovery policies for data to adhere to regulations and the continuity of business.
- Immutable Backups: Backups of data are in a way they cannot be altered or deleted, prevent ransomware attacks, and give integrity to data.
8. Poor Incident Response Plan
Risk:
Many organizations have not planned any incident response processes well, so the damage aggravates and costs skyrocket. In 2017, a global enterprise lost $300 million due to an unprepared incident response strategy. Without the predefined response process, businesses would not be in a position to handle the situation and attackers take advantage to their fullest extent.
Prevention:
- Comprehensive Plan: Overall response plan to a security incident, which would ensure a very short response.
- Training of Employees: Organizing security incidence handling workshops and tabletop exercises to prime teams for real incidents in the field.
- Incident Response Simulations: Recurrent incident responses where readiness will be tested and response time improved.
- Integrate Threat Feeds: Utilize feeds from known threat intelligence sources to proactively identify potential attacks before they gain precedence.
9. Misconfigured Security Settings
Risk:
Default security settings in SaaS application management are low, and hence, organizations are exposed to cyber threats. In 2019, the misconfiguration of a cloud storage bucket led to the exposure of 100 million records. Typically these occur when settings are missed while deploying or the person lacks knowledge regarding what makes the sensitive data vulnerable to be accessed by unknown people.
Prevention:
- Security Reviews: Review and configure security settings by best practices and organizational needs as often as possible.
- Enable Security Features: Activate most central security features, such as logging, encryption, and access controls, which eliminate most of the vulnerabilities.
- Regular Security Assessment: Review the configurations and fill the patch gaps using appropriate configuration settings.
- Zero Trust Security Model: Implement a zero-trust security model in which all sources request access, and verification is carried out.
10. Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Risk:
Phishing e-mails and social engineering attacks have been common techniques used by attackers to steal credentials and access sensitive systems. Phishing attacks characterized the 2016 election interference, where data leaks occurred through major phishing attacks. Such attacks exploit human vulnerabilities, which sometimes bypass technical controls and access sensitive systems.
Prevention
- Staff Training: Train employees on the identification and reporting of phishing attacks to prevent or minimize the possibility of stolen credentials.
- Email Security Solutions: Anti-phishing filters and tools, such as Microsoft Defender or Proofpoint, that block malicious emails before they reach employees.
- Authentication Protocols: DMARC, SPF, and DKIM can be used in securing email communications and against email spoofing, which makes phishing campaigns less effective.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Conclusion
Though there are plenty of benefits to SaaS security in cloud computing, like cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of use, all these bring inherent security concerns to the fore, which must be proactively addressed. If this is not done, it results in data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage for companies as more and more cyber threats are documented against SaaS platforms.
All of these risks have to be prevented, and a multi-layered security approach should be carried out by the organization. Encryptions along with the security of data would be required with the criteria in line with numerous industries and stringent access controls in such a manner that no one unauthorized person would be allowed. Cybersecurity training for all employees will be as essential since most phishing and social engineering attacks occur when employees do not realize that the attack has started. It then requires an effective incident response mechanism in which proper steps have to be outlined within an organization, allowing it to respond quickly.
Continuous monitoring and security audits must be conducted regularly so that vulnerabilities can be found and dealt with before the exploitation of that risk. In addition, proactive measures like advanced threat detection, securing APIs, and endpoint protection give an added layer of robust defense against every kind of emerging threat.
The overall security posture in the SaaS cyber security companies is a result of technology, a clear policy base, and very informed employees. Meanwhile, prioritizing cybersecurity will provide organizations with much-needed protection over sensitive data while maintaining compliance as well as a relationship of trust with customers. Organizations will remain prepared for the complexities of the digital landscape with more confident steps; their business will be safeguarded with reputation. The cyber-world presents challenges that never change but continue. It, therefore, follows that it becomes paramount to move forward with an incessant change like threats.

















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments