In today’s connected financial environment and more so in the digital environment securing information becomes a crucial issue for financial firms and institutions. These organizations process billions of personal, financial, and transactional details annually, all attractive to hackers. Currently, keeping an eye on numerous risks, financial institutions need to adopt comprehensive information security policies that may cover essentially all potential threats. These policies also guarantee people’s compliance with different laws that apply to the industry dealing with data protection.
In this guide, we will explore the essential components of information security policies for financial institutions, why they are critical, and how to implement them effectively. Such technologies will also be discussed alongside the major regulations that financial institutions need to adhere to to conduct business securely.
What are Information Security Policies?
Information security policies are official recommendations for capacitating specific processes, rules, or procedures that organizations implement to minimize the risk of possessing, sharing, accessing, or transmitting various exposures of proprietary information. They support the institution to uphold information confidentiality, integrity and availability hence protecting their information assets.
In financial institutions information security policies play a special role because the processed information is sensitive and requires special protection; this information can be a customer’s financial information and records, his/her Personal Identification Information, and other valuable data that is unique to the business.
Key Objectives of Information Security Policies:
- Confidentiality: They include; Guaranteeing that only individuals who are allowed to access the information get to do so.
- Integrity: The issues of data accuracy and data completeness were also important to be kept under control.
- Availability: Next, to possibly enhance the utility of the information, they need to ensure that the information is available to the approved users whenever required.
Through the development of these policies, risks are minimized, security is improved and full compliance with the law is achieved in financial institutions.
What Should Information Security Policies for Financial Institutions Cover?
Banking and other financial entities are at risk of facing various financial threats coupled with standard-setter requirements on infosec policies. These policies should cover a wide topical area that includes data encryption, and the generation of incident response plans among others. Here are some critical areas that every financial institution’s security policy should cover:
1. Data Encryption and Secure Storage
The information that is processed in financial institutions should have very robust encryption methods used in storing the information and exit and entry encryption systems in place because this information has to move around within networks and the internet. Encryption also helps to guarantee that regardless of data leak it is not easily read by the wrong individuals.
2. Access Control
Essential measures of access control are as follows: They are important to prevent wrong persons from accessing sensitive information. Financial institutions need to have definite RBAC policies that regulate who can access certain kinds of information and when.
3. Incident Response
The incident response plan describes in detail the recommended measures that an organization will need to take in case of an incident. This should include; procedures of how the breach was detected, how the spread was controlled, how data loss was handled, and whether the regulators and customers were informed.
4. Risk Management
Every institution needs to evaluate the possible threats arising from one cybersecurity threat or the other. The suggestion is to conduct regular risk assessments to ensure that institutes uncover weaknesses that might be exploited in the course of doing business.
5. Auditing and Monitoring
Performing system reviews and scanning activities within a given network continuously allows the early identification of security threats. Banks and other major financial organizations should apply financial automation tools that analyze traffic and logs and generate an alert when they spot anomalous activity.
6. Employee Security Awareness
It is surprising but it is evident that human factors continue to act as the root of security problems. Employers in the financial industry must ensure they come up with intensive training programs for their employees to fraternize them with knowledge on how to fight or resist phishing, social engineering, and other cyber-related incidents.
Importance of Information Security in the Financial Sector
The importance of information security is well understood by financial institutions as a requirement across several areas such as the protection of their data as well as meeting regulatory compliance. Here’s why it’s so important:
1. Customer Trust
Customers provide financial institutions with some of the most personal information and the status of their financial health. This trust level is vulnerable to identified security breaches, thus, hampering its reputation and likely to lose customers and get sued. Recommended secure policies assist in the protection of this trust given the need to ensure that data is and remains secure.
2. Regulatory Compliance
The financial sector is set with a variety of cybersecurity regulations. Penalties of noncompliance include penalties, fines, prosecution, suspended license, and overall business and operations shut down. Here, information security policies assist institutions in maintaining compliance because they address those compliance requirements stated by regulatory authorities.
3. Preventing Financial Losses
Cyber threats can lead to direct costs from phishing scams, theft, or ransomware attacks. In addition, the expense of restoring business after a breach, rectifying the problem, and paying fines can be a huge amount. Likely, adopting sound information security policies eliminates such a financial loss.
4. Operational Continuity
Where institutions experience this threat they will have to close their doors for a while so that they can solve some cyber threats hence customers will have to look for other institutions to attend to their needs. Security policies always facilitate the un-interruption of business operations by minimizing the threat detection time and containing it.
Essential Information Security Policies and Processes for Financial Institutions
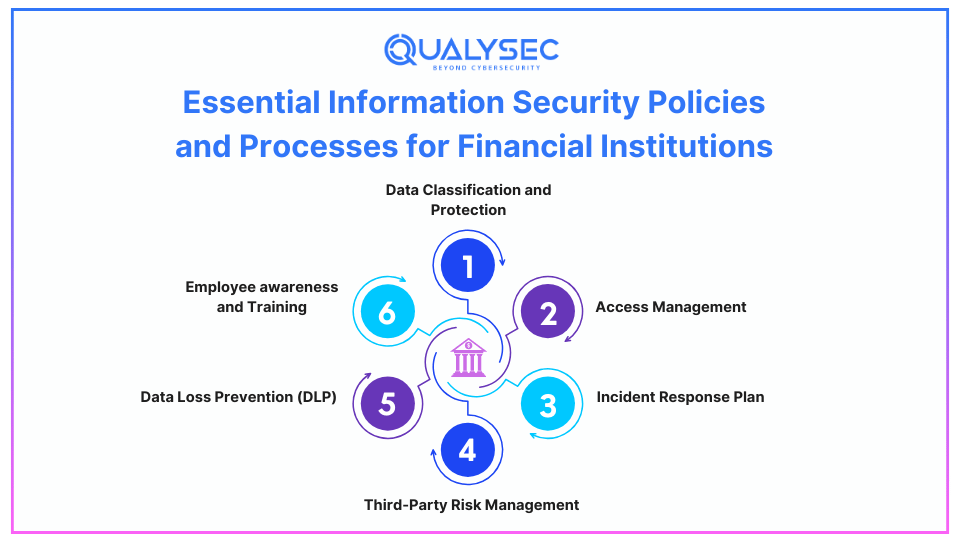
To protect sensitive data and ensure smooth operations, financial institutions need to adopt several key security policies and processes:
1. Data Classification and Protection
Financial institutions deal with different types of information including public information, own information as well as customer information. The protection of information security policies should categorize this data according to the risk level and indicate the required safeguards for each threat level.
- Public Data: Few security measures are necessary for this type of identification system.
- Internal Data: Stored but retrievable for authorized use by employees in the institution.
- Confidential Data: Needs considerable protection and is available for access to individuals or company security personnel only.
2. Access Management
A good access management policy guards against the wrong people accessing the data. The RBAC (Roles Based Access Control) means that no one will be able to view any information beyond the range of duties required of them by the organization. This helps to reduce the dangers of internal leakage of information.
3. Incident Response Plan
Any comprehensive security management should include an incident response plan that should map out what action is to be taken in case of a security breach. This includes:
- Detection: How to identify the breach.
- Containment: Some measures are taken to isolate the breach and minimize damage.
- Eradication: Disarming the threat from the context.
- Recovery: Restoring definite business operations and data.
- Post-Incident Review: Examining cases to identify strategies for managing similar breaches.
4. Third-Party Risk Management
Third parties are commonly used by many financial institutions, and that makes them vulnerable to security risks. Consequently, one needs to develop key policies that dictate how the institution interacts with its third-party vendors and guarantee that they are following the institution’s security policies.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Other policies under DLP make it possible to identify cases where a particular data was transferred to an area outside the institution’s local area network. DLP tools watch over the network for signs of data leakage and will raise the alarm when the data leakage has been found.
6. Employee awareness and Training
Security awareness training for employees is crucial to enable them to notice risks that may cause loss within the firm. This includes; fake emails, care bandits, fake IDs, and awareness of the use of the right passwords and other secure means of identification.
Key Cybersecurity Laws and Regulations for Financial Institutions
Currently, financial institutions are required to follow several legal provisions on cybersecurity that define the approach to the security of information. Some of the most important regulations include:
1. Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
The GLBA calls for financial organizations to tell customers about the sharing of their information in a company, and also for protection measures for the same. It makes it obligatory to establish legal security policies and data protection regimes.
2. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI)
PCI DSS compliance relates to any company that accepts, stores, or forwards credit card information. Since credit card transactions require high-security standards, such institutions have to follow this standard.
3. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
While GDPR serves as a regulation of the EU, any financial organization dealing with the personal information of EU customers cannot avoid it. There are numerous principles of data protection apart from the right to be forgotten and data portability that are required under GDPR.
4. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
The SOX Act regulates the corporation’s governance structure and financial reporting practices and requires that financial institutions put in place control and security features to protect financial information.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Compliance Needs for Financial Institutions
Any financial institution must keep in its focus lists of regulations owing to certain industries. Here are some key areas where compliance is crucial:
- Data Protection: Say for instance you have to make sure that every single piece of data retrieved from customers and transactions is safe and secure as required by law.
- Auditing and Reporting: Audits and detailed accounts have to be done to be able to prove the set regulations of the bodies in question.
- Regular Policy Reviews: It is recommended that financial institutions make periodic adjustments to their existing security policies to reflect the new set of legislation.
Legal consequences of non-compliance include fines and legal proceedings, while business consequences are adverse publicity and losing license to trade.
Technology and Tools for Policy Implementation
To implement and enforce information security policies, financial institutions rely on various technologies and tools:
1. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):
Firewalls and IDS defend specifically at the edge of the network from other networks and the Internet. They scan the network for different activities that are questionable and prevent users from accessing different resources on the network.
2. Encryption Tools
Encryption software guarantees the fact that the data is unreadable to any other person unless they have the decryption key. This is especially important to shield data both in transmission and warehoused in database systems.
3. Multiple Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA security because the program demands that a user proves authenticity in two or more factors before accessing the information. This can be passwords, fingerprints, or anything that is considered to be a personal identification number or PIN.
4. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM Systems)
SIEM systems pull in data from heterogeneous sources in an organization to look for security threats in real-time.
5. Cloud Security Solutions
Because the adoption of the cloud in the financial sector is increasing, cloud security offers the security of data located in the cloud.
Conclusion
Policy and guidelines are critical for financial institutions to secure their data, to be in line with the law requirements, and to retain customers’ confidence. There are many security measures available, auditing, and proper utilization of technology to minimize the impact of cyber threats in the financial institution.
Adopting a proactive approach to security translation not only makes provision for compliance with current industry standards but also creates a productive base for operational reliability and credibility for acceptance by customers.
Financial institutions need to ensure that efforts to enhance and expand security policies are ongoing given changes in risks and the introduction of new opportunities. Focusing on detailed information security policies an institution can safeguard its important data resources and contain any risky security events.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is information security in financial institutions?
A- Integrity in financial institutions covers the means, tools, and measures applied to safeguard any financial data from being leaked, penetrated, or hacked. These include sales data, customers’ information, transaction records as well as other sensitive information. The purpose is to protect data, ensure its authenticity as well as relevance and meet the legal requirements and norms.
Q. How do financial institutions stay compliant with cybersecurity regulations?
A- Financial institutions stay compliant by:
- Applying and enforcing security policies that reflect GAFLA, PCI DSS, GDPR, etc.
- Carrying out internal checks and inspections, and risk analysis frequently to conform to the regulations of the law.
- Notifications to regulatory authorities of any instance of violation of security systems.
- Of special importance is the failure to keep up with augmented legal standards in the sphere of cybersecurity and develop corresponding regulations and policies.
- Encrypting and controlling data access, organizing security awareness training, etc.
Q. What is the list of information security policies for financial institutions?
A- Some essential information security policies for financial institutions include:
1. Data encryption policies
2. Access control policies
3. Incident response plans
4. Risk management protocols
5. Third-party vendor risk management
6. Data loss prevention (DLP) policies
7. Employee security awareness and training
8. Auditing and monitoring policies
These policies work together to provide comprehensive protection against various security threats.
Q. Which technologies help implement security policies?
A- Several technologies help financial institutions implement and enforce security policies, including:
1. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Specific security goals are as follows: Secure the network perimeter against intruder threats.
2. Encryption Tools: This is particularly important to protect sensitive information when transferred within a system or when it is stored in a system.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): A means of increasing security because it requires users to authenticate themselves at least twice.
4. SIEM Systems: Process security data at runtime to look for the possible threats to contain them.
5. Cloud Security Solutions: Secure information that is stored as well as processed in cloud platforms.
6. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: A critical one is to be able to detect and control leakage of information.
If integrated with defined policies these tools are effective in setting up a secure and compliant environment for financial institutions.

















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments