In this blog, we will define healthcare device pentesting, discuss the cyber dangers that medical devices face, and how a medical device penetration test may assist in enhancing security. If you’re in charge of medical device security, you should be aware of the threats they face and how to defend them.
Hospitals and other healthcare-related institutions are becoming more linked than ever before, thanks to the proliferation of electronic medical record systems and the rising usage of network-enabled medical equipment. While this growing interconnection frequently leads to advances in both the quality and efficiency of patient care, it is not without certain potential security risks.
Many medical devices are exceedingly expensive to upgrade or replace, and such legacy systems are frequently found in healthcare institutions. Furthermore, many medical devices were designed with patient safety and life-saving as the primary purposes of the equipment, with little attention historically made to the security of these devices.
These trends are supported by recent FDA guidelines (discussed below) as well as several security investigations that reveal significant security flaws in medical equipment. Furthermore, such networked-enabled medical equipment within hospitals or patients is frequently not implemented with security in mind, adding to the ease of penetration.
With the proliferation of botnets and other malware targeting IoT devices, secure medical device deployments are more important than ever. Let’s see how medical device security testing services can help.
Why is Healthcare Device Security Gaining Importance?
Cybersecurity has progressed from a footnote to a front-page headline in the medical device industry. These worries originate from an increasingly integrated medical device environment. Previously, medical devices were mostly independent systems. Now, medical equipment constantly connects with other hospital/clinical systems, PCs, and mobile devices via the Internet.
Because of this interconnectedness, medical device producers face new dangers, weaknesses, and obstacles. Although regulatory agencies such as the FDA compliance in device pen testing have implemented more stringent cybersecurity standards and laws, these guidelines are insufficient to assure patient safety.
What’s the Main Reason? Why is Healthcare the Prime Target?
With its enormous store of data and frequently obsolete technologies, the healthcare industry stands out as an appealing target for hackers. Healthcare records, which are brimming with a rich combination of personal and medical data, are at the center of this appeal, providing a jackpot for malevolent actors looking to exploit this information for financial gain or other criminal goals.
The fact that many healthcare facilities still rely on obsolete legacy systems exacerbates this risk. Because these old infrastructures lack current security measures, they serve as simple access points for attackers. Furthermore, the extensive and complicated networks of healthcare operations, typified by a plethora of interconnected equipment purchased from many manufacturers, complicate security methods.
Each gadget provides a possible weak link in the system, making it more vulnerable to breaches. To summarize, the combination of rich data, outdated systems, and sophisticated networks makes healthcare an ideal and profitable target for cyber assaults.
What are the Major Cyber Threats in Healthcare Device Security?
According to a healthcare cybersecurity assessment report, healthcare data breaches cost the sector $5.6 billion per year. As we mentioned above attackers target the healthcare business because it has a wealth of information, private data, and financial information such as credit card numbers, bank account numbers, and information on medical research and innovation. The following are some of the dangers to the healthcare industry:
1. Breach of Information
When compared to other businesses, the healthcare industry experiences a disproportionately high number of data breaches. In 2020, the average number of data breaches in the healthcare sector per day was 1.76. HIPAA imposes stringent criteria for safeguarding health records and other sensitive information from unauthorized access, but many healthcare organizations fail to execute its security procedures. Such cybersecurity weaknesses provide access opportunities for cyber attackers, threatening the protection of healthcare data despite efforts to limit these occurrences through penetration testing frameworks for medical devices such as HIPAA.
2. DDoS Exploits
A distributed denial-of-service attack is a flood of bogus connection requests directed at a specific server, causing it to go down. Multiple endpoints and IoT devices are forcibly recruited into a botnet via malware infection to engage in this coordinated attack during this attack. The advantage of DDoS assaults is that they may cause the same disruption without compromising a network, making them easier to deploy on a much larger scale. Because of the speed and destruction that these attacks may cause, they have adopted the ransom model. DDoS attackers may now take a healthcare institution offline and only stop the attack if a specified ransom is paid.
3. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is the technique of inserting dangerous links into seemingly harmless emails. According to vulnerability assessment for healthcare devices, email phishing is the most prevalent sort of phishing. Phishing emails can appear quite convincing, and they frequently make use of a well-known medical condition to encourage link clicks. Some advanced threat actors write phishing emails as answers in an existing email thread to increase authenticity and reduce suspicion. When a link in an email scam is clicked, users are sent to a bogus web page that looks like the login screen for known internal software. Once these credentials are supplied, fraudsters utilize them almost immediately to obtain access to healthcare systems.
4. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
When an attacker intercepts communication between two parties, this is known as a Man-in-the-Middle attack. If medical equipment is not properly set up or if the attacker has physical access to the device, this can occur. Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks can result in data breaches and service outages. MITM attacks are among the most serious cyber dangers connected with both public and private Wi-Fi networks. A Man-in-the-Middle assault on a hospital in the United States in 2016 resulted in the loss of patient data.
What is Healthcare Device Pentesting?
Healthcare Device Pentesting, also known as Healthcare Device Penetration Testing, is the systematic method of analyzing medical equipment security using simulated cyber-attacks. These evaluations seek to uncover vulnerabilities and flaws in devices that might be exploited by hostile actors, such as insulin pumps, pacemakers, or medical imaging equipment.
The goal of security testing is to improve medical equipment’s overall cybersecurity posture by ensuring they fulfill severe security requirements and regulations. Security specialists examine the device’s resilience to possible cyber risks, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and manipulation of medical capabilities, by undertaking controlled and ethical hacking efforts.
The ultimate aim is to preserve patient safety, secure sensitive medical data, and avoid potentially life-threatening circumstances caused by hacked equipment. Medical device security testing services are critical in tackling the expanding environment of cybersecurity threats in the healthcare business and encouraging the development of safe and resilient medical technology.
A medical device penetration test can also assist you in meeting regulatory requirements such as the following:
- The Security Rule of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued cybersecurity recommendations for medical equipment.
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-53 medical device security controls.
Are you a medical device manufacturer and worrying about the security of your devices? Be at peace with a FREE CONSULTATION CALL with the INDUSTRY EXPERTS of Cybersecurity.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Why Should Businesses Invest in Medical Device Security Testing Services?
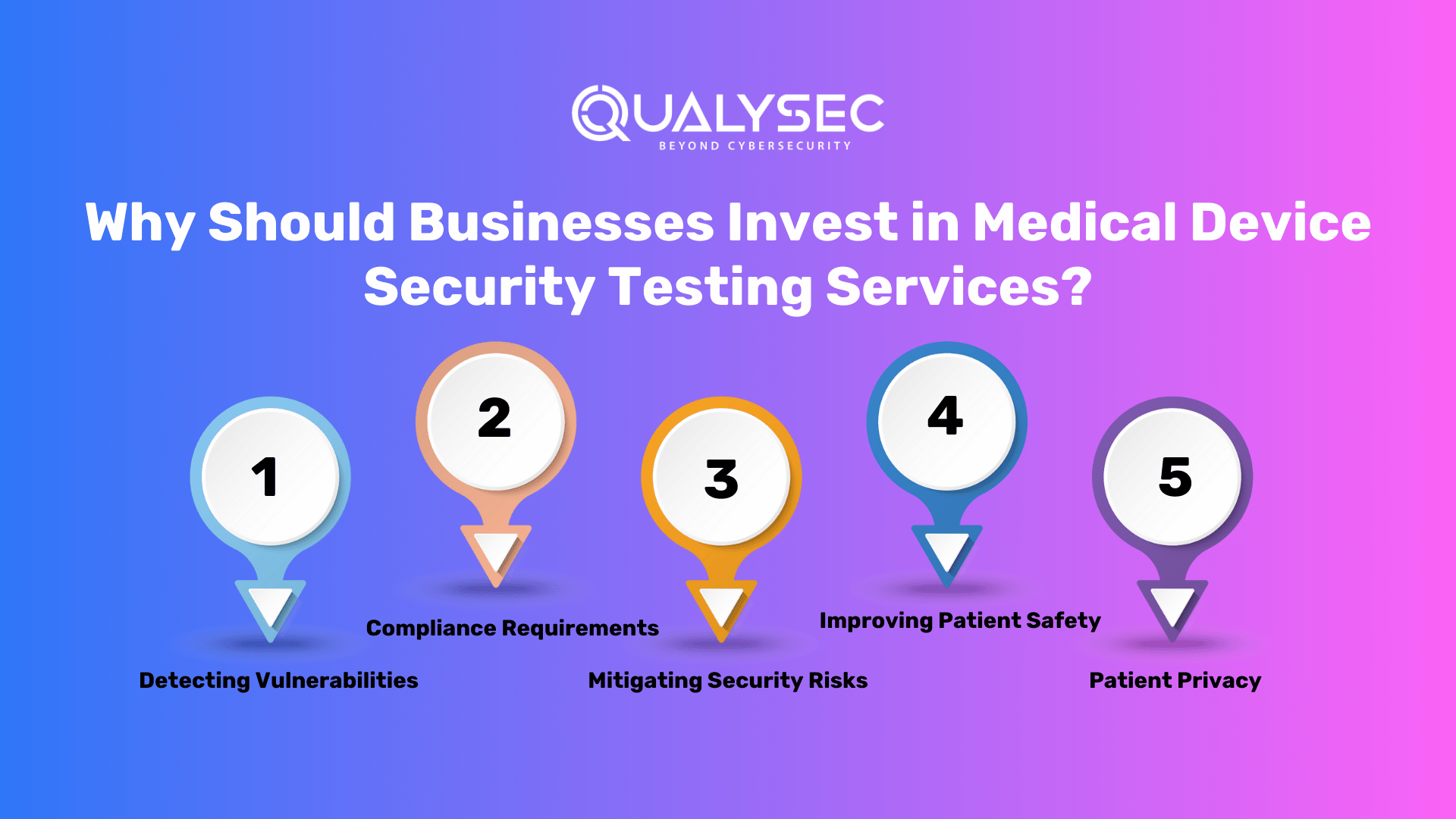
The importance of penetration testing cannot be overstated in the healthcare industry, where the consequences of a security breach can be devastating. Penetration testing frameworks for medical devices help businesses keep one step ahead of cyber attackers by imitating the mentality of a prospective attacker.
1. Detecting Vulnerabilities
Pentesting helps healthcare organizations detect and repair vulnerabilities before hostile actors attack them. This method enables the discovery of trends and fundamental causes, allowing future network vulnerabilities to be avoided. It is possible to identify key parameters such as remediation time, NIST ratings on found vulnerabilities, vulnerability classification, and vulnerability locations throughout the network.
2. Compliance Requirements
It is vital in healthcare to ensure compliance with stringent regulations like as HIPAA. Pentesting has grown into a proactive tool, helping businesses to upgrade their security posture to meet these criteria. Vulnerability assessments for healthcare devices are found and remedied through extensive testing, reducing the risk of data breaches, avoiding legal ramifications, and maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical healthcare information.
3. Mitigating Security Risks
Once vulnerabilities are discovered through penetration testing, healthcare companies may make proactive efforts to reduce these risks. This might include installing security updates, tightening access limits, encrypting critical data, or increasing network security. Organizations may greatly minimize the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber risks by fixing security flaws.
4. Improving Patient Safety
Many medical equipment is network-connected, and their effective operation is crucial for patient safety. By finding and fixing security flaws, penetration testing helps to protect the integrity and dependability of these devices. Organizations may reduce the risk of device failures, illegal access, or tampering that could jeopardize patient safety by safeguarding healthcare equipment with medical device security testing services.
5. Patient Privacy
Healthcare equipment frequently handles sensitive patient information, such as personal and medical data. By detecting and managing potential security issues, penetration testing helps to protect patient privacy. Protecting this information is critical not just for regulatory compliance, but also for retaining patient confidence and ensuring the confidentiality of their health-related data.
How is Healthcare Device Pentesting Performed?
Pen testers act as motivated adversaries to mimic assaults. They usually follow a plan that involves the following steps:
Obtaining Information:
The first stage in penetration testing is gathering as much information as possible. This includes a two-pronged approach: using easily accessible information from your end, as well as several ways and tools to get technical and functional insights. Understanding user roles, permissions, and data flows is critical for designing an effective testing strategy.
Planning
The penetration testing firm begins by carefully defining the objectives and goals. They delve extensively into the technical and functional complexities of the device. This extensive study allows testers to customize their testing methods to target specific vulnerabilities and threats in the application.
A healthcare IoT vulnerability management plan is created, outlining the scope, methodology, and testing criteria. The company provides a high-level checklist to aid in the testing process. They collect and prepare the required files and testing equipment. This method includes defining testing criteria and checking script availability to provide a smooth and successful evaluation.
Auto Tool Scan
An automated and invasive scan is done to seek vulnerabilities on the application’s surface level using tools. Furthermore, as a precautionary measure, the testers utilize this scan to proactively identify and correct surface-level vulnerabilities in the staging environment. This technique allows thorough inspection as well as rapid repair, boosting the application’s security posture.
Manual Testing:
During this step, the healthcare device penetration testing services provider conducts a thorough examination of the IoMT device. The objective is to find flaws both within and outside of the IoMT device. During deep manual testing, testers actively interact with equipment to uncover nuanced flaws that automated procedures may miss. Testers simulate real-world scenarios, study user interfaces, and assess device compatibility to uncover potential vulnerabilities and usability concerns. This manual testing technique is crucial for increasing overall device quality and contributing to a more robust and secure device ecosystem.
Reporting:
The testing team carefully investigates and categorizes detected vulnerabilities in a detailed report. In addition, a senior consultant performs a high-level penetration test and evaluates the complete report. This report also supports developers in fixing detected vulnerabilities by giving information such as:
- Vulnerability Name
- Likelihood, Impact, and Severity.
- Description
- Consequence Instances (URL/Place)
- Reproducible Steps and Proof of Concept (POC)
- CWE No.
- Reference
For a detailed and comprehensive tour of the study, we have provided our penetration test report here. Click below to download!
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Remediation:
A testing company provides a consultation call to ensure that the development team does not experience any issues throughout the repair procedure. Pentesting specialists recommend direct participation to assist developers in responding to security issues. This method also ensures that the development team receives professional help, allowing for the smooth and rapid resolution of vulnerabilities.
Retesting:
Following the development team’s risk reduction, the critical stage of retesting is accomplished during this phase. The healthcare device penetration testing services do a thorough examination to determine the efficiency of the offered fixation. The following are included in the final report:
- Discoveries throughout history
- Situation of Evaluation
- Screenshots
LOA and Certification:
The testing company creates a Letter of Attestation that is supported by evidence gathered during penetration testing and security assessments, such as:
- Confirmation of the level of security
- Securing stakeholders
- Compliance
Furthermore, the testing company will provide you with a Security Certificate, which will improve your capacity to represent a secure workplace, create confidence, and satisfy the demands of many stakeholders in today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity scenario.
Did you know?
This healthcare device pentesting certificate can be shown publicly to convince consumers and stakeholders that your medical device is secure!
Also Read: All about IoT device security testing
What Challenges Are Faced During Vulnerability Assessment for Healthcare Devices?
The following factors contribute to the complexity of protecting medical devices:
- Unpatched IoT devices: IoT healthcare devices are frequently designed with utility in mind rather than security. Healthcare device pentesting professionals are not educated in device security and would be unable to determine whether an IoT device needs to be patched.
- Increasing the number of linked devices: The attack surface grows dramatically when IoT, IoMT, OT, and linked devices interact. Any security team will find it difficult to secure them.
- The complication of mobile devices: When moving assets across rooms, it’s simple to lose track of them. The movement of IV pumps and ultrasound devices, for example, makes acquiring a complete view difficult.
- The disadvantage of durability: IoMT devices are also intended to be long-lasting. Their endurance can be a disadvantage since hospitals may continue to utilize these legacy technologies even after the manufacturer has stopped producing or releasing updates for them, leaving them vulnerable to attackers.
- Software incompatibility: Because IoMT devices often do not support external software, applying patches and safeguarding them via standard endpoint agents is difficult.
- Lack of Context: Security solutions do not grasp the context or behavior of medical IoT devices automatically.
- Lack of Network Segmentation: This is most crucially; a lack of effective network segmentation makes it difficult to protect the numerous IoT and mobile app security in healthcare devices business.
How FDA Compliance in Device Pen Testing Will Help Healthcare Device Manufacturers?
Earlier this year in September, the FDA compliance in device pen testing rolled out new guidelines for medical device manufacturers to pentest their devices before launching them. The FDA supports the creation and implementation of a “Secure Product Development Framework,” or “SPDF.”
This is a set of actions that reduce the quantity and severity of vulnerabilities in goods throughout their lifespan. The SPDF is intended to be the central structure for managing cybersecurity risk, and it focuses on three key elements:
- Risk management in security
- Architecture of security
- Cybersecurity evaluation
The FDA is requesting an SBOM (Software Bill of Materials), which is a comprehensive inventory of all software components used in a medical device, including those created by the manufacturer and those created by third parties. An SBOM assists device manufacturers and users in detecting potential security vulnerabilities promptly, hence easing risk management operations.
The FDA recommends that verification and validation include appropriate testing of the medical device system’s cybersecurity by the manufacturer, as well as the manufacturer’s inputs and outputs, if relevant. The premarket submission should contain security testing documentation, as well as any associated findings or assessments.
Read More: Read the Guidelines on Medical Device Security
QualySec: Your Helping Hand for Healthcare Device Pentesting
As digital technology and connected devices grow more common, so does the need for a robust monitoring and security system. Healthcare organizations can contact QualySec Technologies to scan their devices, networks, and web and mobile app security in healthcare devices for inherent and new threats or vulnerabilities.
In addition, we provide specific security solutions for your medical device via process-based penetration testing. A one-of-a-kind process that employs a Hybrid testing strategy and a professional team with extensive testing expertise to ensure that the app meets the industry’s highest standards.
In addition, our healthcare cybersecurity assessments and pentesting services include a full range of automated vulnerability scanning and deep manual testing using in-house and commercial tools. We actively assist firms in successfully negotiating difficult regulatory compliance settings such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, and NIST-800.
We assist developers in resolving vulnerabilities by delivering comprehensive and developer-friendly pentesting findings. Furthermore, this report includes all of the insights, beginning with the location of the discovered vulnerabilities and ending with a reference on how to resolve them, i.e., you get a detailed step-by-step report on how to resolve a vulnerability.
We’ve successfully served 20+ countries through a network of 100+ partners, and we’re proud to boast a ZERO-DATA-BREACH Record. Contact QualySec right away for unrivaled healthcare security for your device and business.
Conclusion
A cyberattack on any of your medical equipment might have major ramifications for patients, such as interruptions in care and even data loss. As a result, it is critical to take the necessary precautions to protect your medical devices from cyberattacks.
Healthcare device pentesting is an important step in maintaining the availability, confidentiality, and accessibility of your medical equipment, and it should be done regularly. If you need assistance securing your device, please contact us.
FAQs- Frequently Asked Questions
What is healthcare device penetration testing, and why is it crucial?
The systematic process of examining and evaluating the security of healthcare systems and networks is healthcare device pentesting. This proactive strategy helps discover weaknesses, secure patient data, and assure regulatory compliance by simulating real-world cyber assaults.
How often should healthcare organizations conduct device penetration tests?
Device penetration tests should be performed regularly, at least once a year, and more frequently based on risk assessments, changes in the technological environment, and legal requirements. Regular testing aids in the timely identification and remediation of vulnerabilities.
What are the regulatory considerations for healthcare device penetration testing?
Compliance with HIPAA, FDA guidelines, and appropriate standards are among the regulatory issues for healthcare device penetration testing. Healthcare professionals must get patient permission, safeguard patient data, and follow legal and ethical norms. To establish a secure and compliant testing procedure, collaboration with manufacturers should align with regulatory standards.
How can healthcare providers collaborate with manufacturers during penetration testing?
By establishing clear communication channels, and exchanging important network facts and settings, healthcare providers engage with manufacturers. This collaborative approach guarantees that manufacturers can examine vulnerabilities without interfering with healthcare operations, establishing a safe and cooperative atmosphere conducive to improving overall system resilience.
What steps should be taken if vulnerabilities are identified during healthcare device penetration testing?
Exploitation. Once vulnerabilities have been discovered, it is time to exploit them. During this phase of penetration testing, the penetration tester attempts to get access to the target system and exploit the found vulnerabilities, generally by simulating real-world assaults with a program like Metasploit.
Ensure your healthcare solution is globally compliant.
Qualysec helps you meet HIPAA, FDA, ISO, and more. Contact us today!


















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments