A comprehensive cloud infrastructure security includes a broad set of technologies, policies, and applications. It involves security measures that help identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that could prove to be security threats to the cloud infrastructure. These measures also help business continuity by eliminating security issues and supporting regulatory compliance across multiple cloud infrastructures.
Though cloud services offer many benefits for business operations, 96% of organizations have faced severe challenges while implementing cloud strategies. As per IBM, 82% of beaches that occurred were for data stored in the cloud. This shows the severity and necessity of cloud security.
This blog will explain everything you need to know about cloud infrastructure security, including best practices and possible challenges organizations face with cloud services.
What is Cloud Infrastructure Security?
Cloud infrastructure security secures cloud resources and supporting systems from internal and external attacks. It involves several procedures, technologies, and guidelines that protect applications and sensitive data stored in cloud infrastructures. Cloud security prevents data breaches and unauthorized access by focusing on authentication and limiting authorized users’ access to resources.
3 Types of Cloud Security:
- Public Cloud Security: Security measures provided by third-party cloud service providers, for example: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Private Cloud Security: Security protocols for a cloud infrastructure hosted exclusively for or by a single organization. This offers greater security control and customization.
- Hybrid Cloud Security: A combination of public and private cloud security, which allows organizations to use both environments for different needs while maintaining data security.
Depending on the type of cloud model used, specific cloud infrastructure security measures are primarily the responsibility of the cloud service provider (CSP) or the user. However, maintaining the integrity of the cloud environment is not the sole responsibility of one party. Cloud service providers and their users work together to implement best security practices to avoid attacks on cloud data, services, and applications. This is briefly mentioned in the shared responsibility model.
“Also Read: Cloud Penetration Testing: The Complete Guide
Why is Cloud Infrastructure Security Important?
More than 92% of organizations use cloud computing. As cybercriminals become more tech-savvy, new and unique cyber threats are being used to target a costly cloud attack. This could compromise sensitive data and the business’s reputation.
Cloud computing gives companies a lot of benefits, such as:
- Customer service through enhanced data storage
- Flexibility through remote working
- Fast scalability
- Convenience through interconnected systems with fast data sharing
However, due to several risks like misconfiguration and lack of encryption, cloud infrastructure is prone to significant cyberattacks. With cloud infrastructure security, you can enhance the protection of cloud data and applications and avoid unauthorized access and data breaches.
Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure Security
Implementing the best cloud security practices offers the cloud service providers and the user a lot of benefits, such as:
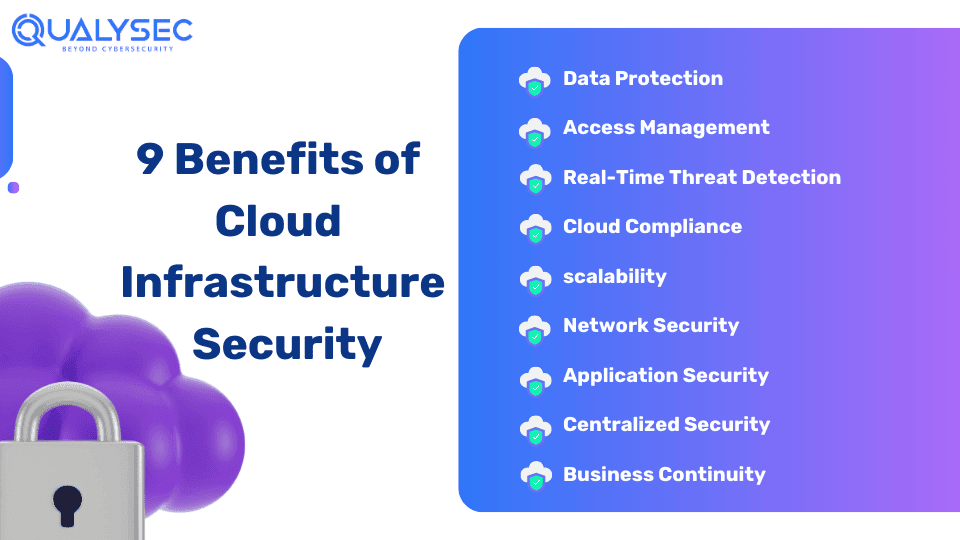
- Data Protection: Cloud infrastructure security solutions are specifically designed to ensure data security through proper access controls and data loss prevention. The data remains secure from unauthorized access both at rest and in transit.
- Access Management: Cloud security includes multi-factor authentication, which ensures that only authorized members can access the cloud.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Cloud security methods like vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT) detect real-time vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure. Additionally, the method provides the impact of those vulnerabilities and their remediation steps.
- Cloud Compliance: Cloud security solutions like penetration testing often align with international and industry regulatory requirements like ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR, etc. Organizations need to comply with these standards to avoid legal penalties and fines.
- Scalability: No matter the business size, cloud infrastructure security solutions are easy to scale. If needed, security controls can be expanded to include a growing infrastructure without making significant changes to the cloud architecture.
- Network Security: Cloud security ensures data flows safely between devices and servers through encryption, firewalls, and VPNs.
- Application Security: Cloud applications are protected with security measures like firewalls and VAPT, which help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Centralized Security: Cloud monitoring solution assesses potential threats to multiple areas from a centralized place. This helps organizations maintain timely software updates and establish disaster recovery plans.
- Business Continuity: Cloud infrastructure security ensures business continuity by making cloud services available all the time, even during some component failures.
| You May Like: Everything About Cloud Application Security Testing |
The Need for Cloud Infrastructure Security: Latest Cloud Security Challenges
Organizations looking to enhance their cloud infrastructure security can expect to face these common challenges:
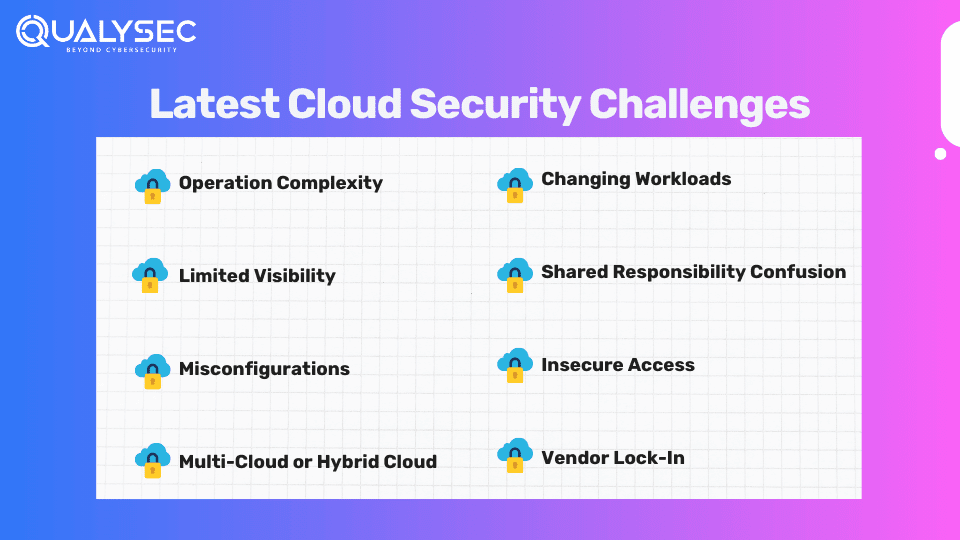
1. Operation Complexity
Cloud management requires certain solutions to access public and private providers, platforms, and deployments. This complicates the efficiency of business operations. Integrating every cloud security measure smoothly can be difficult to achieve.
2. Limited Visibility
Cloud solutions might not offer as much visibility as on-premises setups. When relying on third-party security solutions, transparency can decrease, which may impact the organization’s control over data and operations.
3. Misconfigurations
Lack of knowledge and expertise may lead to misconfigurations, which can potentially lead to data breaches and security vulnerabilities. For example, inadequate privacy settings configuration or failure to update administrative passwords may pose significant risks to data security.
4. Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Cloud
Using multiple cloud services from different providers or combining cloud and on-premises solutions creates difficulties while implementing security measures across these different environments.
5. Changing Workloads
Managing fluctuating workloads is a big challenge in cloud management. This becomes an issue when cloud services are not designed to adapt to these changes.
6. Shared Responsibility Confusion
To maintain cloud security, there are different responsibilities for cloud service providers (CSPs) and the users. Usually, the users are not well-educated with their part. This can create confusion, potential security gaps, and even compliance issues.
7. Insecure Access
Hackers are always looking for weak points in the public cloud (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS) to exploit and interfere with operations. This is especially risky for those companies that allow cloud access from all devices and locations.
8. Vendor Lock-In
Relying on the security tools of one cloud provider can make it challenging to implement advanced security measures or migrate to other platforms.
Qualysec’s cloud pentest gives you results—no endless emails, no digging through PDFs, no guesswork.

Cloud Infrastructure Security Best Practices
Cloud infrastructure is easier than you think – as long as you do your part. Organizations can protect their cloud infrastructure by implementing the following cloud security best practices. Although these security measures might not prevent every attack, they help businesses enhance their defenses, protect their data, and maintain their reputation.
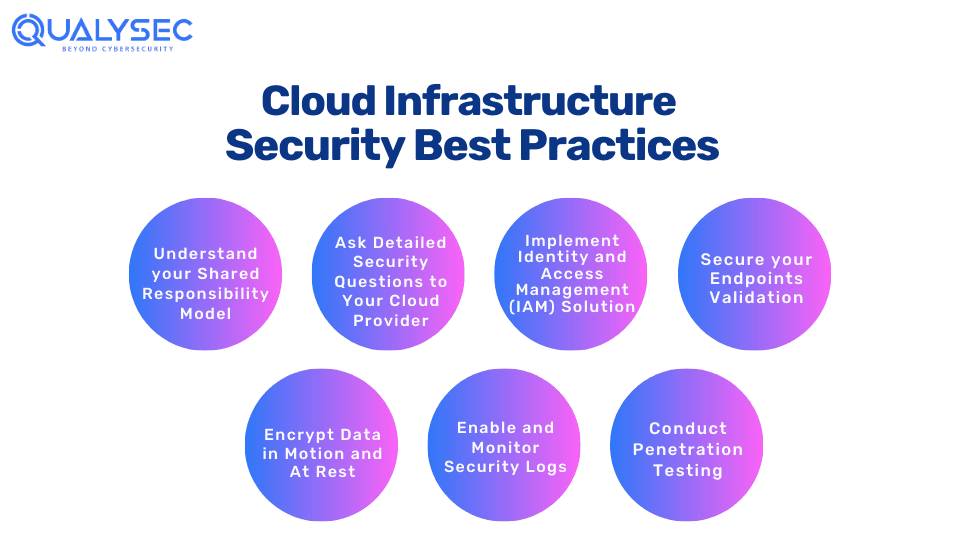
1. Understand your Shared Responsibility Model
Public cloud security differs a lot from private data centers. In the cloud, customers hold the responsibility to protect their data and applications, yet providers also share some duties in a shared responsibility model. Leading cloud providers like AWS and Azure clarify specific roles in their documentation. To ensure security, customers/users must follow encryption and configuration guidelines provided by the cloud vendor.
2. Ask Detailed Security Questions to Your Cloud Provider
To ensure cloud security, businesses must ask detailed questions to their public cloud providers. Leading providers may have different security measures. You should ask questions regarding:
- Server locations
- Incident Protocols
- Disaster recovery plans
- Access protection
- Support levels
- Penetration test results
- Encryption practices
- Data access
- Authentication methods
- Compliance support
3. Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solution
To enhance the security of public cloud infrastructure, organizations should implement identity and access management (IAM). Implementing principles like least privilege and zero trust ensures restricted access, while Privileged Access Management (PAM) secures sensitive accounts. Role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and cross-platform IAM solutions further enhance the security measures.
4. Secure your Endpoints
As endpoints directly connect to the cloud, their security should be a top solution. New cloud projects require new security strategies to counter changing threats.
Implement Endpoint security measures that include:
- Firewalls
- Anti-malware
- Intrusion detection
- Access control
You can use automated tools like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP). Additionally, implement patch management, endpoint encryption, VPNs, and insider threat prevention for further security enhancement.
5. Encrypt Data in Motion and At Rest
Encryption plays a vital role in any cloud security strategy. Data stored in public cloud services and during transit should be encrypted to prevent attacks. Certain cloud providers offer encryption and key management services, while third-party companies offer encryption too. Choose an encryption solution that integrates smoothly with existing workflows to ensure compliance without extra user effort.
6. Enable and Monitor Security Logs
This is one of the most effective cloud infrastructure security measures available today. Enabling logging in cloud services and integrating data into a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system is highly effective for cloud security. It helps monitor user activity, detect unauthorized changes, and enables quick remediation. Additionally, effective logging helps in addressing misconfigurations, tracking changes, and identifying excessive access rights.
7. Conduct Penetration Testing
If you use cloud services, the best way to keep your data and applications protected is by conducting regular penetration testing. Cloud penetration testing is usually conducted by third-party security firms, where ethical hackers simulate real attacks on the cloud infrastructure to find potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, they document the impact of the vulnerabilities they found and their remediation methods. Penetration testing is the best method to enhance the overall cloud infrastructure security.
Do you want to find vulnerabilities in your cloud infrastructure? Get quick vulnerability scanning and penetration testing (VAPT) services from Qualysec today! Just click the link below and talk to our cybersecurity consultant about your security needs!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Conclusion
Hackers are going to find new ways to penetrate cloud infrastructures. New threats are going to arise now and then to breach the security measures. Despite this, businesses can secure their cloud infrastructure by implementing the best security practices.
Typically, cloud security is based on a shared responsibility model, which states both the cloud service providers and the users actively contribute to the safety of cloud infrastructure. Hence, the cloud infrastructure must be designed in a way that supports secure operations, protects sensitive data, and safeguards applications.
FAQs
Q: What is the security of the cloud infrastructure?
A: The security of cloud infrastructure protects computing environments, sensitive data, and applications from unauthorized access by focusing on authentication and access limitations.
Q: How to secure cloud infrastructure?
A: Use the following seven cloud security tips to secure your storage:
- Understand your Shared Responsibility Model
- Ask Detailed Security Questions to Your Cloud Provider
- Implement Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solution
- Secure your Endpoints
- Encrypt Data in Motion and At Rest
- Enable and Monitor Security Logs
- Conduct Penetration Testing
Q: What is the role of cloud security?
A: Strong cloud security helps companies develop and build cloud security infrastructures, ensuring the companies can operate in a safe, secure cloud environment. It researches, monitors, and analyses security risks to mitigate threats and attacks that may occur within the cloud.
Q: What are the three categories of cloud security?
A: Cloud security is basically categorized into these three categories:
- Provider-based security measures
- Customer-based security measures
- Service-based security measures






















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments