E-commerce revolutionizes people’s shopping by offering convenience, competitive prices, and a global marketplace. On the other hand, it has attracted cyber-crooks, placing this online marketplace at a fundamental risk and making security a top business and consumer concern. According to recent research by Juniper Research, more than 50% of online shoppers fear data breaches while global e-commerce fraud losses are projected at over $48 billion in 2023. These comprise phishing attacks, data breaches, and payment fraud which expose private customer information and hurt a company’s reputation and financial stability. One of the notable incidents was the data breach at Macy’s in 2019. Devastating results came from feeble security measures, business houses must come up with good e-commerce security best practices policies that include SSL encryption, two-factor authentication, and AI-based fraud detection to protect their web assets. Ensuring security while increasing online purchases would be an invaluable factor in maintaining customer confidence for the sustainable long-term prosperity of e-commerce.
Why Is E-commerce Security Important?
E-commerce is an area where people now shop. However, the growth in that area increases the chances of cyber threats. Therefore, businesses must be able to take security measures to protect themselves and their customers. Here is why e-commerce security is important.
1. Protection of Customer Data
E-commerce platforms hold very sensitive information from customers, such as names, addresses, credit card details, and login credentials. Data breaches may lead to identity theft, financial loss, and legal consequences, making data security a priority.
2. Maintaining Customer Trust
Trust is the core of online shopping. Based on a PwC study, 87% said they would stop doing business with a company if it does not properly protect their data. Years of trust and brand reputation can be destroyed in seconds of security lapse.
3. Avoid Financial Loss
Cybercrime will amount to $10.5 trillion annually in 2025 (Cybersecurity Ventures). Companies operating on e-commerce and with weak security lose their cash through fraud, fines, and claims.
4. Compliance
Some countries have very rigorous data protection for the e-commerce business. General Data Protection Regulation and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) are some examples of such regulations that demand high security. Therefore, compliance can’t be avoided.
Common E-commerce Security Threats
The awareness of threats enables companies to take precautions. The following are the common ones in e-commerce:
1. Phishing
Phishing is the act of stealing login details or financial information when fraudulent emails or websites that appear real dupe people into revealing them. For example, cybercriminals have used fake Amazon identities to steal people’s payment information through an Amazon phishing scam.
2. Payment Fraud
The compromised credit card data would be used to make unauthorized purchases. Therefore, it leads to chargeback, loss of finance, and other associated costs. Juniper Research stated that online payment fraud would cost businesses more than $362 billion between the year 2021 and 2025.
3. S/W Malware and Ransomware
Malware and ransomware attacks have been on the rise, targeting customer data and business operations. The July 2020 Magento attack compromised thousands of e-commerce stores, showing the severity of this threat.
4. DDoS Attacks
DDoS Attacks flood sites with excessive traffic, thus it or they end up crashing. In 2022, it was reported on Cloudflare whereby ransom DDoS attacks were up 175% wherein online e-commerce was primarily targeted.
5. SQL Injection
SQL Injection exploits the weak point of sites, and hence there is a theft of the customer’s information change to the transactions or deletion of important features. Such an attack can easily affect the key business functions profoundly.
E-commerce businesses must be concerned with security through SSL encryption, two-factor authentication, AI-driven fraud detection, and regular security audits. It will protect customer data, maintain trust, and ensure long-term business success in the digital marketplace through a proactive approach.
“Related Read: Top 10 Latest Security Threats in E-commerce and Their Solutions“
Best Practices for E-commerce Security
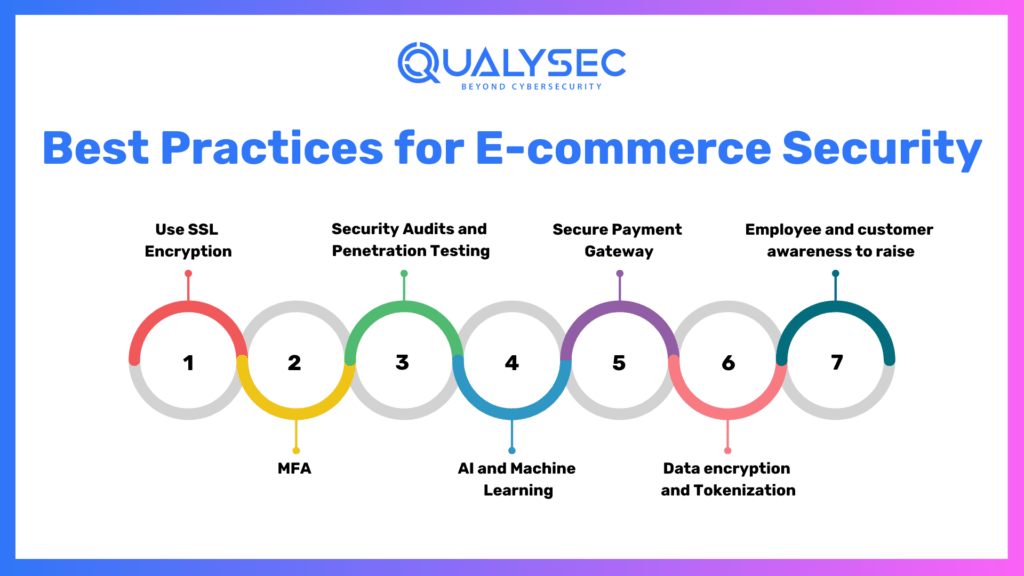
1. Use SSL Encryption
SSL encryption is an added layer, which guarantees security while making any data transfers between a website and its customers. Websites that make use of SSL display an HTTPS on the URL: one sure sign that affirms a safe connection.
2. MFA
MFA is another security measure because the users, for authentication, would need to undergo more than one mechanism of verifying themselves. That encompasses the mechanism of passwords as well as OTPs.
3. Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Security auditing and penetration testing find vulnerabilities even before hackers do. Shopify and WooCommerce spend a huge amount of money on proactive security measures.
4. AI and Machine Learning
AI-based security systems detect threats in real-time and respond to them. Both Amazon and Alibaba use machine learning for fraudulent transactions and unauthorized access.
5. Secure Payment Gateway
It guarantees its users a secure payment gateway like PayPal Stripe or Square, which can ensure that any transaction would require to be transferred encrypted and complies with PCI DSS norms.
6. Data encryption and Tokenization
Minimizing exposure through encryption and tokenization if ever there was an incidence of breaching into data.
7. Employee and customer awareness to raise
Human factors lead to the greatest security breaches. The best way to remedy risks is through employee education and publicity among customers concerning the proper purchase of online commodities.
“You might like to explore: E-commerce Penetration Testing: Securing Online Businesses“
Case Studies: Incidents Due to Security Breaches
1. Data Breach by eBay, 2014
The most massive e-commerce breach happened when the cyberattack on eBay exposed the information of 145 million users. The attack had significantly damaged the company’s reputation, and thus loss of customer trust and financial damage occurred.
2. Target Data Breach (2013)
Target is not an e-commerce business in itself; however, the data breach happened with the exposure of 40 million credit and debit card accounts. A malware attack led to a settlement of $162 million.
3. Magecart Attacks in 2020
Magecart cyber crooks launched the most massive attacks on e-commerce websites, based on Magento operating systems with malicious scripts to capture pay details. This attack mounted over 2,000 websites that became infected, resulting in regulatory pressures and loss.
The Future of E-commerce Security
Cyber threats associated with online transactions are growing in numbers. To gain a competitive advantage, e-commerce business needs to embrace innovative security technologies that will ensure smooth transactions. Here’s how things look for the future of e-commerce security:
1. Blockchain for Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology brings e-commerce toward decentralization and encryption with further transparency. However, blockchain breaks the single-point failure characteristic and eliminates the existence of data breaching and fraudulent activities, even in a traditional database. Presently, larger companies – Walmart and IBM – are being utilized for blocking supply chains to ensure transactions will be tamper-proof, safe, and payments secure. Tomorrow, the blockchain-driven smart contract will aid a lot in executing e-commerce transactions with proper automaticity-fraud proof to assure agreement between the buyers and the sellers.
2. Biometric Authentication
Passwords are now increasingly becoming vulnerable to phishing and brute-force attacks. E-commerce websites are also introducing biometric authentication to enhance the security standards with:
- Fingerprint scanning to enable secure login and payments
- Facial recognition to verify identity and thus not permit hijacking of the account
- Voice recognition is the third element in authentication.
Already, such giants as Amazon and Alibaba have taken up biometric verification as one of the safety measures and risk reduction of fraud on accounts. With the great spread of their usage, they will become increasingly integrated, having highly significant advantages in security and user experience
3. Zero Trust Architecture
The traditional security model of “intranet” assumes users within a network to be trustworthy. This is not the case. ZTA follows the rule of “never trust, always verify,” whereby no user and no device would be granted access without proper authentication. The critical components of Zero Trust in e-commerce are given below:
- Multi-Factor Authentication: This confirms the identity of a user.
- Least Privilege Access: It limits data exposure.
- Continuous Monitoring: This tracks real-time threat detection.
By adopting Zero Trust, e-commerce companies decrease insider threats, prohibit unauthenticated access, and safeguard sensitive transactions.
4. AI-Based Fraud Detection
Artificial Intelligence is changing the security landscape in e-commerce as it can detect fraud in real time. With this feature, AI-based fraud detection systems can do:
- Analyze the user behaviour trend that gives information on suspicious activities
- Detect unusual pay transaction patterns to inhibit fraud
- Continuous improvement in the accuracy of fraud detection with machine learning models.
Payment service companies like PayPal and Stripe apply artificial intelligence to flag fraudulent transactions and minimize chargebacks and payment security. Since AI is capable of processing so much information at a time, firms can be proactive regarding the threats rather than being reactive after it has occurred.
Conclusion
E-commerce security is no longer a luxury, but the question of survival in the new economy. The cybercriminals just won’t stop and thus need some very tight security measures on the art of the business to avoid financial losses while preserving customer confidence by not divulging their sensitive information.
Blockchains, biometric authentication, Zero Trust security, and AI-based fraud detection will enable online shoppers to enjoy secure and seamless shopping. Investment in security technologies ensures not only the success of warding off cyber threats but also customer confidence.
“Explore: AI-Based Application Penetration Testing and Its Importance“
Key Takeaways
✔ Cybercrime is expected to cost businesses $10.5 trillion a year by 2025. (Cybersecurity Ventures).
✔ The most pressing security concerns in electronic commerce are phishing, malware, and payment fraud.
✔ Uses of Secure Sockets Layer encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication, artificial intelligence-based fraud detection, and secured payment gateways to improve security.
✔ Cases like the eBay and the Magecart attacks reflect the worst outcome that may occur during any breach of e-commerce.
✔ Online transactions will be defined by future technologies that are blockchain, biometrics, artificial intelligence, and Zero Trust security.
With security-first strategies at the top of the priorities, this online e-commerce business can easily create a safer digital marketplace for its customers while generating customer confidence in its ever-changing virtual platforms. Check out the best cyber security companies that offer E-commerce security services.
































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments