The Internet of Things, or IoT, influences every aspect of our daily lives, from wearable technology to smart household appliances, industrial machinery, and municipal infrastructure. Strong IoT security measures become increasingly important as more devices are connected to the network.
Therefore, the blog will examine the details of the Internet of Things (IoTs), the methods needed to protect IoT devices, IoT Security Standards, best practices, implementation, and challenges.
What Is an IoT Device?
An object that is connected to the Internet and gathers and shares data with other devices and systems is called an Internet of Things (IoT) device. An IoT device often uses sensors to collect data about itself or its surroundings.
Thus, it transmits this data to an IoT platform, combining data collecting and analysis from numerous devices. Businesses implementing IoT devices utilize analytics to produce insights that facilitate remote device control, enhance decision-making, or set off an automated reaction.
Why IoT Device Security is So Important?
IoT devices can act as entry points for cybercriminals to enter networks and obtain private information because of their connection. These devices are vulnerable to hacking without the proper IoT cybersecurity standards, which might result in serious data breaches and harm to the organization’s finances and reputation.
Cyber-attacks have the potential to entirely interrupt the functionality of IoT devices. For example, malicious operations such as distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks can be carried out through compromised IoT devices. Smart home appliances can be compromised to harm or spy on their users. Integrated medical devices, if compromised, can disrupt medical care.
Moreover, IoT security and monitoring are necessary for following data privacy laws. Because IoT devices frequently handle sensitive personal and corporate data, companies must adhere to all applicable cybersecurity and data protection regulations. Failing to comply with regulations can lead to fines and penalties, declining client confidence, and lost commercial opportunities.
To secure your IoT devices, click on the box below to schedule a call with the experts and seek our guidance.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
What are IoT Security Standards and their Purpose?
IoT security standards are the policies, rules, and best practices formulated by different organizations to enhance the security systems of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and networks. Such standards attempt to establish the minimum best practices in developing and deploying these devices.
The purpose of IoT Security Standards:
1. Mitigate Security Risks
IoT devices are prone to hacking through weak passwords, lack of updates, and generally have limited computing power. Security measures like strong authentication, secure boot, IoT standard protocols, and firmware updates manage these risks.
2. Boost Consumer Trust
Due to the ever-increasing privacy and security issues, consumers will not accept insecure devices. Adhering to Industrial IoT security standards can enable manufacturers to establish customer trust because of the focus on user data security and protection of device integrity.
3. Ensure Interoperability
Though not the principal goal, some standards are designed to enhance compatible security features of devices, so that they can function cohesively in a network.
How IoT Security Standards Help Ensure the Security of IoT Devices?
IoT security standards guide manufacturers in securing devices from the design phase to the disposal phase. Here’s how they help:
1. Baseline Requirements
Standards establish a basic level of security that must be incorporated into the design of all IoT devices to protect them from certain kinds of attacks. It, thus, entails aspects such as passwords and other login information, data and communication encryption algorithms, and boot protection mechanisms.
2. Focus Areas
They identify sections that require focus during the development phase, such as secure coding, vulnerability mitigation, and the procedures for applying patches. Therefore, by adhering to these guidelines, manufacturers can reduce the vulnerability of their devices and make it harder for attackers to crack into them.
3. Transparency
Some standards require manufacturers to provide the user with information regarding the security of the said IoT device. This allows users to come up with the appropriate decisions surrounding the amount of risk a specific device poses to them.
4. Interoperability
Standardization can also be significant in terms of the compatibility of different devices from different manufacturers. This means that the devices are in a position to improve and enhance communication and cooperation, thereby creating a safer environment.
Key IoT Security Standards
Some of the key IoT Device Security Standards are:
1. International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27001:
This standard gives a guide on how information security can be managed. It can be applied to assist organizations in building and deploying a security management system (SMS) that encompasses all aspects of IoT security, including device and data security.
2. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF):
This framework includes general best practices, recommendations, and options for organizations to enhance infrastructure security. Companies can use it to create a strategic plan to secure the IoT infrastructure of an organization.
Best Practices for IoT Device Security
The following are the best practices for securing IoT devices:
1. Vulnerability Assessment
They perform a comprehensive scan to check for vulnerabilities in the security of your IoT device. They look for standard risks such as low-security protocols, old and outdated applications, and improper configurations. Consider it as a broad scan to identify the device’s current security measures.
2. Penetration Testing
This is a more tactical approach where security experts simulate real-world attacks to assess whether they can exploit the weaknesses discovered during assessment. It is like practicing to test how much the device’s security system can withstand hacking. This process is known as Penetration Testing.
3. Security Audit
This is an audit of your IoT device security policy, including all the security measures and protocols in place. It considers restrictions for who can enter certain areas, how information is protected, and what steps must be taken during an attack. It’s like a safety check you need as a business to ensure you are adequately protected. This process is known as a security audit.
4. Source Code Review
This means looking at your IoT device source code at a very micro level to try and spot any vulnerabilities. It is just like carrying out a security audit on the code of the device with the intent of knowing its vulnerabilities.
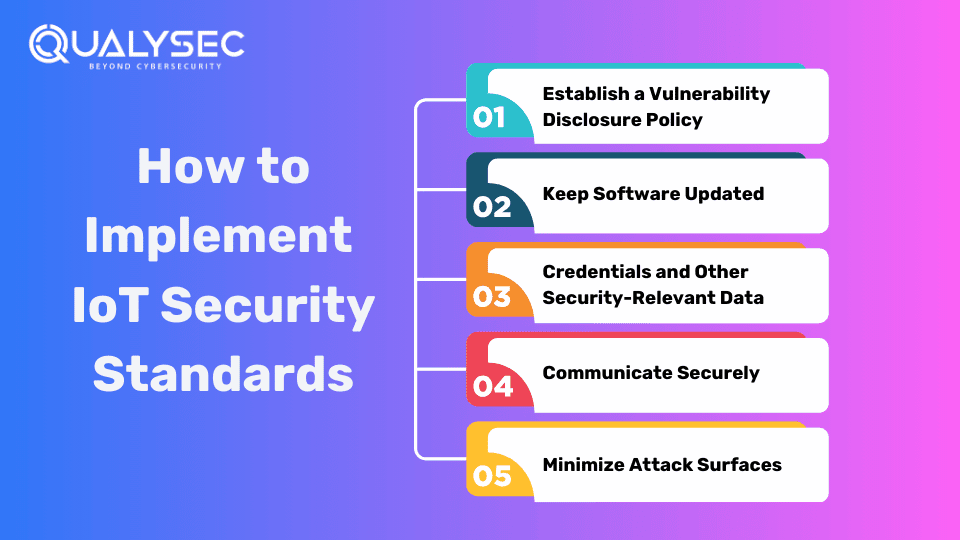
Implementing IoT Security Standards
Implementing IoT security standards is essential. Here are some of the areas to focus on:
1. Establish a Vulnerability Disclosure Policy
This is related to a corporate disclosure policy. This is to encourage a good relationship between the working partners and establish good communication.
2. Keep Software Updated
However, updating devices will be challenging, mainly due to the growing number of IoT devices deployed within organizations. Companies should consider the update issue in IoT software early in the deployment to ensure manageable tasks. Such updates shall be timely and should not hinder the device’s performance. The update policy should prevent potential attackers from exploiting older versions.
3. Credentials and Other Security-Relevant Data
This practice means that credentials should be safely kept within the services and devices. Thus, one should avoid using hardcoded credentials such as passwords or bank account numbers in device software. Always fully activate the device’s specific security measures and memory to protect any security-sensitive data.
4. Communicate Securely
All IoT devices must employ secure communications like TLS or LWC and preferably stay current with the latest versions. This means that you should encrypt data requiring enhanced security during transit and tightly protect the keys used for this process.
5. Minimize Attack Surfaces
The goal is to reduce the number of potentially exploitable entry vectors, and the vision is for every device and service to run with the minimum permissions required. This principle is critical to code quality because hackers exploit code weaknesses to compromise IoT devices.
Challenges in IoT Security Standardization
The biggest challenge that may prevent this vast network of devices from being secured is more standardization. Here’s how the lack of standard security protocols makes IoT security difficult:
1. Inconsistent Security Features
Many companies produce IoT devices, but they often lack essential security controls. These devices frequently do not have robust authentication processes or encryption, making them vulnerable to simple attacks.
2. Limited Resources
Many IoT devices are low power constrained, often with small form factors and low computing capabilities. This makes deploying intricate security measures or accommodating multiple security changes impractical.
3. Patching Difficulties:
One of the most significant challenges in today’s IoT environment is the complication of updating devices with security patches due to the system’s decentralized organization. At the same time, some IoT devices cannot update or receive updates.
4. Insecure Communication
Devices and networks sometimes need better encryption to prevent easy interception of communications. Since IoT devices constantly communicate through the internet, it is necessary to secure the communication channels.
Conclusion
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are becoming increasingly common in the daily lives of people. To guard against cyberattacks, these devices must have proper security mechanisms in place. IoT security standards offer recommendations and best practices for protecting these gadgets through their lifecycle. Implementing these standards and overcoming obstacles like lack of standardization will result in a more secure IoT ecosystem.
FAQs
1. Are there security standards for IoT devices?
A. Yes, there are security standards for IoT devices, including guidelines from ISO/IEC, NIST, and ETSI. These standards address data protection, device authentication, and network security to improve overall IoT security.
2. What are the three types of IoT security?
A. The three types of IoT Security are:
- Network Security
- Embedded
- Firmware Assessment
3. What are the critical elements of IoT security?
A. The critical elements of IoT security involve device authentication, data encryption, secure communication protocol, access control, regular software updates, intrusion detection, privacy control, and many more.




















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments