Ethical hacking or Cybersecurity pentesting has arisen as a crucial activity in the field of cybersecurity to examine and improve the security of digital systems. This blog will go into the depth of ethical hacking, digging into the notion of penetration testing and its usefulness in cyber threat protection. We’ll also cover the process and approach of pentesting, its main types, and major challenges in penetration testing. Let’s dig in.
According to statistics, pentesting is used by 62% of businesses to assist vulnerability management. Furthermore, during penetration testing, 9% of firms prioritize risk assessment and remediation. Even after recognizing the underlying issues, 58% of businesses have difficulty getting sufficient resources for rehabilitation. Around, 30% of businesses struggle to find qualified third parties to do pen testing.
Organizations are continually engaged in a high-stakes struggle to protect their digital assets against an ever-evolving and increasingly sophisticated threat landscape in their persistent quest for cybersecurity resilience. Penetration testing in cyber security develops as a strategic and proactive strategy that goes beyond surface-level security examinations in this digital arms race.
Understanding the Depth of Cybersecurity Pentesting
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing, also known as “pentesting” or “ethical hacking,” is a systematic and controlled method of examining an organization’s cybersecurity posture. Cyber security pentesting mimics real-world cyber-attacks to detect flaws and vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, applications, and other assets. In contrast to hostile hackers who utilize these vulnerabilities for bad means, ethical hackers employ their talents and expertise for a great cause – to strengthen an organization’s security.
The Purpose of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing’s primary purpose is to identify possible vulnerabilities before hackers can exploit them. Organizations receive vital insights into their security flaws by simulating real-world assaults, allowing them to apply appropriate actions to minimize risks and reinforce their defenses.
Penetration testers conduct examinations using a range of methodologies. They seek to uncover vulnerabilities that might be exploited by attackers, such as weak passwords, misconfigurations, or obsolete software. By simulating attacks, penetration testing in cyber security assists businesses in evaluating their level of risk and prioritizing security changes.
Read More: What is the Purpose of Penetration Testing?
What are the Approaches Used for Penetration Testing in Cyber security?
Penetration testing differs in its technique as well as the holes it seeks to attack. The pen tester’s strategy and the scope of the project will be determined by the degree of information supplied to them. For example, will the penetration tester know how a network is mapped, or would they have to figure this out on their own? Among the several ways of penetration testing are:
Black-Box Testing
This method simulates the viewpoint of external attackers, with testers having little or no prior knowledge of the target environment. Black-box testing evaluates an organization’s capacity to detect and counter unexpected threats in a real-world situation.
White-Box Testing
White-box testers are well-versed in the target environment’s system architecture, source code, and network configurations. This method allows for a thorough analysis of the inner workings of systems and applications.
Gray-Box Testing
Gray-box testing is a hybrid of the black-box and white-box methodologies. A cyber security company operates with a limited understanding of the environment, imitating the perspective of an attacker armed with insider information.
What are the Types of Cybersecurity Pentesting?
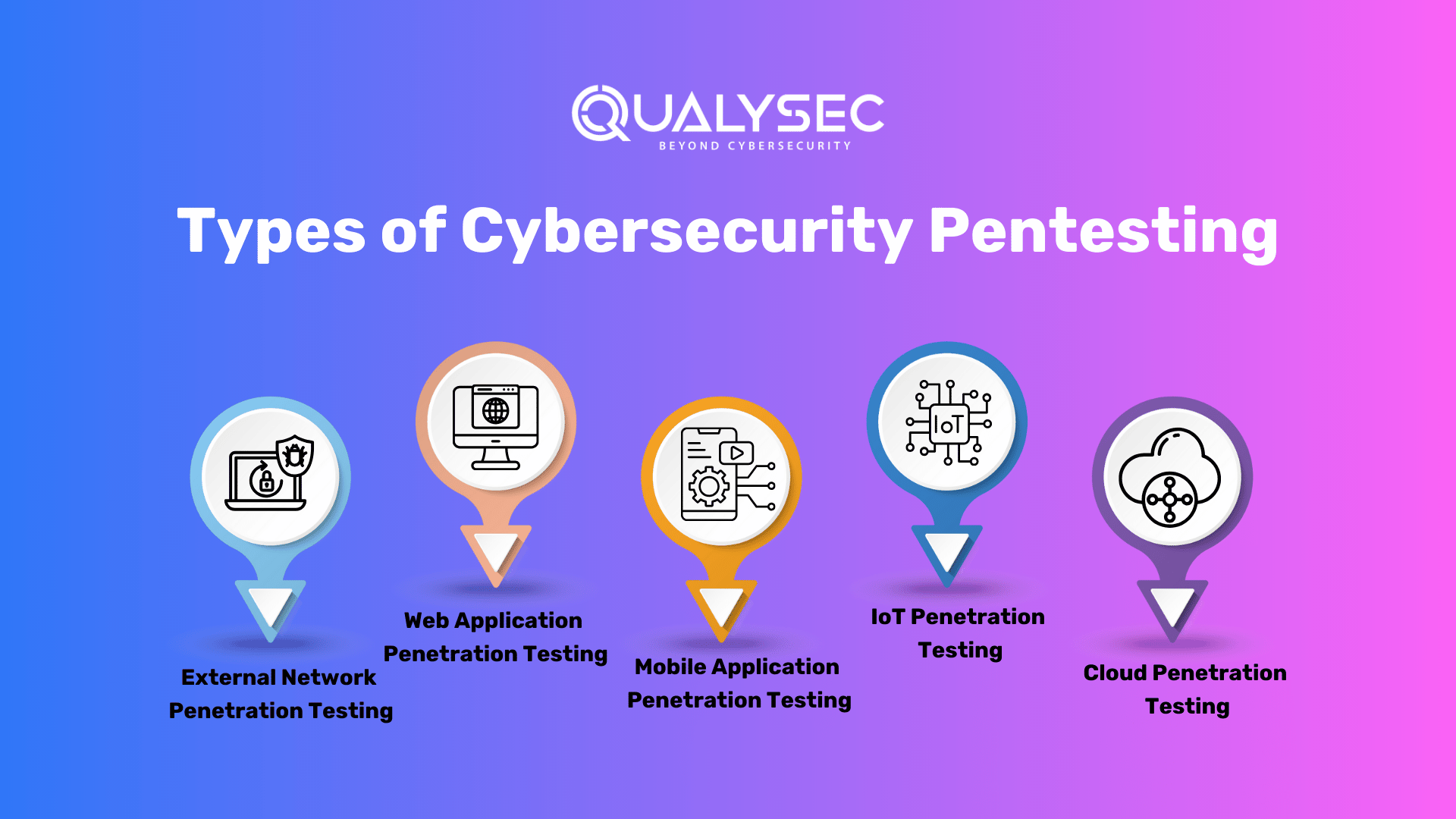
There are several types of penetration testing. Each sort of penetration test necessitates specialized expertise, methodology, and tools, as well as alignment with a specific business purpose.
These objectives might range from increasing employee understanding of assaults to adopting secure code development to discover defects in software code in real-time, or satisfying legal or compliance needs. Here are some of the main types of cyber security penetration testing:
1. External Network Penetration Testing:
External network penetration testing examines your present richness of publicly available information or assets. The assessment team seeks to acquire access to data via external-facing assets like as corporate emails, cloud-based apps, and websites by exploiting vulnerabilities discovered when screening your organization’s public information.
2. Web Application Penetration Testing:
Web application penetration testing identifies security flaws or vulnerabilities in web-based applications. It employs several penetration techniques and assaults in order to get access to the web application itself. This includes examining online applications, APIs, and web services for flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and weak authentication systems.
3. Mobile Application Penetration Testing:
Mobile application penetration testing includes both static and dynamic analysis:
- Static analysis gathers source code and metadata and then reverse engineers it to find flaws in application code.
- While the program is operating on a device or server, dynamic analysis detects application vulnerabilities.
This sort of testing examines mobile applications’ code and data storage for security weaknesses and potential data leaking.
4. IoT Penetration Testing:
IoT penetration testing searches for security flaws in linked ecosystems, such as flaws in hardware, embedded software, communication protocols, servers, and IoT-related online and mobile apps. The types of hardware, firmware, and communication protocol tests performed vary depending on the linked device.
5. Cloud Penetration Testing:
Cloud penetration testing is a sort of security testing that looks for weaknesses in a cloud computing environment that hackers may exploit. It is an important component of a cloud security strategy since it identifies possible flaws in cloud security mechanisms. Cloud penetration testing seeks to detect vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure and assess the efficiency of security protections in place.
Why is Penetration Testing in Cyber Security Important for Businesses?
Cybercrime is expected to cost $10.5 trillion per year by 2025. Cyber security penetration testing, which is already a prevalent security practice among big corporations, is projected to expand in popularity as the frequency and complexity of assaults increase for firms of all sizes. Despite the hazards, penetration testing has a lot of important advantages.
1. Identify and Fix Vulnerabilities
Hackers can locate weaknesses in places you might not think to explore. Penetration testers do important work by identifying weaknesses in your company’s digital systems and data. One of the primary benefits of penetration testing is that pentesters put themselves in the shoes of hackers. By illustrating what a bad actor may do to your organization in its present condition, you will be able to identify areas where your digital systems may require further protection and areas where you are currently effectively secured.
2. Avoid Costly Data Breaches
It is undeniably expensive to recover from the effects of a data breach. Legal fees, IT cleanup, client protection programs, lost revenue, and dissatisfied customers may cost businesses millions of dollars. Penetration testing regularly is a proactive strategy to remain on top of your security and may assist in preventing financial damage from a breach while safeguarding your brand and image.
3. Recognizes System’s Strengths
A penetration test’s ability to show you where your system is weak is also advantageous. This allows you to devote more time and effort to portions of your system that aren’t functioning properly. It also displays strategies you’ve used that have paid off. Now that you know they operate, you may use them on other platforms in the future. This capacity to accept both positive and negative results is what allows these types of testing to produce a thorough report. A penetration test, rather than merely addressing flaws, allows you to see what truly works.
4. Increases Customer Loyalty and Trust
Another advantage of IT penetration testing is that it may comfort your consumers. If the findings of your penetration test are positive, you will be able to issue a press release. If they are unfavorable, you can give them revised specs after any concerns are fixed. In this regard, penetration testing is useful since it may assist you in gaining more consumers. It’s all about proving that you’re correcting any problems and working hard to give your consumers the finest service possible.
5. Observe Industry Standards and Regulations
Penetration testing in cybersecurity aids in meeting the compliance and security duties imposed by industry standards and laws such as PCI, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Having these tests on a regular basis helps to demonstrate due diligence and your commitment to information security, all while avoiding the significant fines that associates with noncompliance.
Why not do frequent penetration tests if you aren’t already?
The first step is simple: Locate a qualified cyber security penetration testing specialist and collaborate to determine which form of pen test is appropriate for your firm.
Here’s the FREE Catch: Discover a free call with our expert security consultants to get a brief checklist on penetration testing today!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
How to Perform Cyber Security Penetration Testing: A Detailed Guide
There are usually 8 phases of pentesting. Here is the step-by-step process of penetration testing containing the phases of the testing:
1. Information Gathering:
The initial intent of penetration testing is to obtain as much information as can. This includes a two-pronged approach: utilizing readily available information from your end, as well as utilizing numerous ways and tools to get technical and functional insights. The cyber security company collaborates with your team to gather critical application information. Understanding user roles, permissions, and data flows is critical for building an effective testing strategy.
2. Planning
The penetration testing process begins with the service provider defining the objectives and goals. They delve extensively into the technical and functional complexity of an application. Furthermore, this allows testers to adjust the testing strategy to target specific vulnerabilities and threats in your environment.
A comprehensive penetration testing plan is created, outlining the scope, methodology, and testing criteria. To lead the testing process, the business will give a high-level checklist. This checklist provides a solid foundation by addressing crucial subjects such as authentication mechanisms, data processing, and input validation.
They acquire and prepare the essential files and testing instruments. This procedure includes configuring testing settings, checking script availability, and designing any unique tools needed for a smooth and effective review.
3. Auto Tool Scan
During the penetration testing process, especially in a staging environment, an automated and intrusive scan is necessary. This scan comprises utilizing specialized tools to seek vulnerabilities on the application’s surface level carefully. The automated tools mimic prospective attackers by crawling through every request in the application, uncovering potential weaknesses and security gaps.
By running this intrusive scan, the business proactively finds and addresses surface-level vulnerabilities in the staging environment, acting as a protective measure against potential assaults. This strategy provides not only a thorough review but also quick rectification, boosting the application’s security posture before it is deployed in a production environment.
4. Manual Testing
The cyber security company conducts a thorough examination of the apps at this step. The purpose is to detect weaknesses both inside and outside the organization. During deep manual testing, testers actively interact with equipment to uncover nuanced flaws that automated methods may miss. Testers simulate real-world scenarios, study user interfaces, and assess device compatibility to uncover potential vulnerabilities and usability concerns. This manual testing technique is crucial for increasing overall application quality and contributing to a more robust and secure environment.
5. Reporting
The cyber security pentesting team detects and categorizes vulnerabilities discovered throughout the assessment, ensuring that potential risks are fully recognized. A senior consultant does a high-level penetration test and reviews the entire report.
This ensures the highest level of quality in testing methods as well as the accuracy of reporting. This thorough documentation is a valuable resource for understanding the security state of the application.
Key Report Components:
- Vulnerability Name: Provides a clear identity for each vulnerability, such as SQL Injection.
- Likelihood, Impact, and Severity: Assesses the likelihood, impact, and severity of each vulnerability to quantify the possible risk.
- Description: Provides a summary of the vulnerability, allowing stakeholders to better understand it.
- Consequence: Explains how each vulnerability may affect the application and emphasizes the significance of mitigation.
- Instances (URL/Place): Identifies the location of vulnerabilities, allowing for more targeted repair efforts.
- Steps and Proof of Concept (POC): Provides a step-by-step tutorial as well as a Proof of Concept (POC) for validating and reproducing each vulnerability.
- Remediation: Provides concrete solutions for eliminating discovered breaches and fostering a secure workplace.
- CWE No.: Assigns IDs for Common Weakness Enumeration for exact classification and referencing.
- OWASP TOP 10 Rank: Indicates the vulnerability’s position in the OWASP TOP 10, emphasizing its importance in today’s threat landscape.
- SANS Top 25 Rank: Indicates the vulnerability’s position in the SANS Top 25, which helps to contextualize its significance.
- Reference: Additional materials and references are provided for a better knowledge of vulnerabilities and relevant remedial techniques.
This comprehensive reporting method ensures that stakeholders receive relevant insights into the application’s security condition as well as practical recommendations for a solid security posture.
If you’re searching for the best pentest report to get clarity, it’s a finger tip away.
Latest Penetration Testing Report

6. Remediation Support
If the development team requires support in reproducing or reducing reported vulnerabilities, the service provider delivers a critical service through consultation calls. Penetration testers with in-depth knowledge of the discovered issues promote direct engagement to aid the development team in effectively analyzing and addressing security threats. This collaborative approach ensures that the development team receives competent advice, allowing for the seamless and speedy resolution of vulnerabilities to enhance the overall security posture of the application.
7. Retesting
Following the completion of vulnerability mitigation by the development team, a vital stage of retesting happens. Testers undertake a thorough evaluation to validate the efficacy of the treatments used. The final report is lengthy and includes:
- History of Findings: This section has a complete record of vulnerabilities uncovered in previous assessments, making it easy to track the progress of security solutions.
- Condition of Assessment: Specifies the condition of each vulnerability, whether it is corrected, ignored, or declared out of scope, and provides a detailed overview of the remediation outcomes.
- Screenshots: Physical evidence and images are added to the retest report, giving visual validation of the fixed vulnerabilities. This verifies the approach and ensures that the application’s security status is thoroughly and accurately assessed after repair.
8. LOA and Security Certificate
The cyber security penetration testing company goes above and above by providing a Letter of Attestation, which is an important document. Furthermore, this letter, which is supported by evidence from penetration testing and security assessments, has numerous purposes:
- Confirms security Level: Use the letter to acquire physical confirmation of your organization’s security level, assuring stakeholders of the robustness of your security procedures.
- Stakeholder Security: Use the letter as a tangible testimony to the depth of your security practices to demonstrate to clients and partners your commitment to security.
- Satisfies Compliance: Address compliance issues as soon as possible, as the Letter of Attestation is a valuable resource for meeting regulatory requirements and proving compliance with industry-specific security procedures
Furthermore, the testing company will provide a Security Certificate, which will enhance your ability to represent a secure environment, reinforce confidence, and meet the expectations of various stakeholders in today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape.
Here’s a catch: If your clients ask for any authentication of the security of your digital assets, you can show them this certificate. A security certificate is proof that your assets are fully secured from cyber threats.
What are the Common Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities?
While a vulnerability may provide a danger to an organization, it does not constitute a threat in and of itself. When a vulnerability is exploited, it becomes a problem. This vulnerability might be carried out either maliciously by an attacker or accidentally by a normal user. A vulnerability is a major danger regardless of how it is exploited.
Data breaches, malware outbreaks, and the loss of vital services can all result from vulnerabilities. The following are the most typical forms of cyber vulnerabilities:
1. Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations are the single most dangerous to cloud and app security. Furthermore, many application security technologies involve manual configuration, which can be error-prone and time-consuming to administer and update. These mistakes turn cloud workloads into clear targets that may be found with a simple web crawler. The absence of perimeter protection within the cloud increases the danger of misconfigurations. To that end, enterprises must use security tools and technologies that automate the configuration process and limit the risk of human mistakes in the IT environment.
2. Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
A zero-day vulnerability is a security issue identified by a threat actor but not known to the company or software manufacturer. Companies are highly vulnerable to zero-day attacks since they may be exceedingly difficult to detect. To identify and neutralize zero-day attacks successfully, a coordinated defense is required, one that comprises both preventative technologies and a comprehensive reaction strategy in the case of an assault. Organizations may prepare for these attacks by implementing a comprehensive endpoint security solution that integrates technologies.
3. Unpatched Software
Failure to update software patches, as well as running software past its specified service life, is a vulnerability with potentially disastrous consequences. The good news is that normal patching may easily avoid these zero-day attacks. When businesses fail to apply patches regularly or employ software that is no longer maintained and updated regularly, they become exposed to all future zero-day attacks as well as all existing exploits that had not been resolved by the time of the last patch.
4. Unauthorized Access
Employees are frequently given greater access and permissions than are required to accomplish their job tasks. In the case of a data breach, this enhances identity-based dangers and gives adversaries more access. To overcome this issue, businesses could use the principle of least privilege (POLP), a computer security concept and practice that grants people restricted access permissions depending on the activities required for their employment. Furthermore, POLP guarantees that only authorized users whose identities have been validated are granted access to certain systems, applications, data, and other assets.
5. Weak or Stolen Password
Many users fail to generate strong and unique passwords for each of their accounts. Reusing or recycling passwords and user IDs provides attackers with another possible path of exploitation. To mitigate this specific cybersecurity weakness, businesses should establish and enforce explicit policies requiring the use of strong, unique passwords and prompting users to change them regularly. Organizations can also consider establishing a cybersecurity pentesting, multifactor authentication (MFA) policy, which requires more than one form of identification to authenticate the user, such as a password and a fingerprint or a password and a one-time security token.
What are the Challenges in Cyber Security Penetration Testing?
Because penetration testing is so “mainstream” these days, it’s easy to miss some of the important issues it poses. These difficulties, if not addressed properly, can leave your business exposed to attack, incur unnecessary costs, and reduce the value of your cybersecurity expenditures. Here are the top 5 challenges in cybersecurity pentesting:
1. False Positives
It is all too usual for penetration testing firms these days to run an automated tool against a client’s IT infrastructure and offer the results in the form of an altered report. These automated methods offer several advantages, such as faster scanning and updated signatures for the most recent vulnerabilities. Their major disadvantage is that they will generate several false positives. You may believe that this isn’t your problem. Yes, it is. A competent penetration testing firm will utilize both human and automated tests and understand how to eliminate or reduce false positives.
2. Quality Control Crisis
Companies that pass off vulnerability scans as penetration tests, use unqualified testers or depend too much on automated technologies may produce poor-quality findings, resulting in false positives or negatives, or engagements that do not fulfill legal standards such as PCI or HIPAA. Check that the cyber security company you choose has a proven track record and employs trained personnel with appropriate industry expertise. Inquire about their testing procedures and obtain recommendations from former clients when choosing a company.
3. Limited Test Accounts
Client companies frequently provide test user credentials for penetration testing. These test accounts are vital because they allow penetration testers to undertake a deep-dive test of the web application’s internal workings. However, it is also critical that they test using numerous test accounts with varied permission levels to evaluate privilege escalation attacks across accounts. Unfortunately, corporations may only supply one test account, resulting in a substandard test. This is low-hanging fruit, and we strongly advise the use of more than one test account.
4. Restricting the Scope
Modern times have brought with them modern technology. Everything from vehicles and pacemakers to cameras and printers now connects to the Internet. These IoT devices frequently have inadequate cybersecurity protections, making them ideal access sites for hackers. Furthermore, we always advocate including all devices and IP addresses that may connect to the Internet in penetration testing. Your security is only as good as its weakest link. Limiting the scope of your penetration testing to exclude such gadgets may give you a false feeling of security.
5. Complex Network Architectures
Organizations have extended their networks to accommodate the rising number of linked devices and systems. The evolution of diverse settings, virtualization, and dynamic infrastructure has made determining network borders and vulnerabilities more difficult. When traversing the complexity of architecture, penetration specialists encounter the following challenges:
- Inadequate visibility
- Expansions of the attack surface
- Resources are limited.
- Rapid evolution
The Future of Cyber Security Penetration Testing
As technology evolves, so do the tools and strategies at the disposal of cybercriminals. Penetration testing’s future depends on its continuous evolution to stay up with developing threats. Furthermore, machine learning and artificial intelligence, are becoming essential components of ethical hacking, allowing for quicker and more effective vulnerability detection.
Furthermore, the transition to DevSecOps, a methodology that incorporates security into the development lifecycle, emphasizes the importance of continuous testing. Because businesses constantly update their apps and systems, penetration testing must be a continuous activity rather than a one-time exercise. In addition, this guarantees that security measures grow in tandem with the digital world, therefore narrowing the window of opportunity for prospective attackers.
Read more: Discover the top cyber security Companies
Why Should You Trust a Cyber Security Company for Penetration Testing?
Cybersecurity pentesting firms are becoming increasingly vital in today’s digital environment. In reality, many transactions, not just monetary, but also data or product exchanges, are now conducted via the Internet. As a result, many hackers see the network as a vulnerable target. As a result, it is critical to spend wisely on networks and cybersecurity.
- A Strong Portfolio: A pentesting company has a great background in testing applications, networks, and IT infrastructure with years of experience and trusted client books. Check that, you can always trust them for penetration testing.
- Expert in Testing: A company that provides penetration testing as a service employs professional and ethical pen-testers to manually test your digital assets to get zero false positives and accurate results.
- Follows Regulatory Compliance: A cyber security company always follows the guidelines and meets compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, etc. which show the authenticity of the testing.
With these criteria, QualySec is the best choice for you to perform penetration testing services for your digital assets. We employ professional and certified pen-testers to conduct deep manual testing and automation testing on your assets.
We assure Zero False Positives with our process-based testing. Furthermore, we follow a hybrid approach to testing i.e., combining both manual and automation testing to get accurate results of vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, with our comprehensive and development-friendly report, we provide consultation to the developer for fixing those vulnerabilities. We have a strong portfolio of serving 20+ countries with 100+ global partners securing 250+ applications in our 3 years of journey.
You can sleep in peace with your applications secure. Contact us to safeguard your digital asset today with cyber security penetration testing!
Conclusion
Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, is an important discipline for detecting and mitigating vulnerabilities in applications and networks. Your business can proactively enhance its security procedures, comply with legislation, and increase consumer trust by simulating assaults. Furthermore, ethical hackers are critical in protecting against cyber-attacks and providing strong digital defenses. Secure your business with penetration testing in cyber security, testing companies are here to help!
FAQs
1. What is security testing cybersecurity?
Security testing is a type of software testing that is used to assess a system’s or application’s security. Security testing protects the system from hackers, viruses, and cyber dangers. Only by assessing the system against all security-related requirements can such protection be realized.
2. Is pen testing the same as security testing?
No. Security testing does not exploit security flaws (apart from pentesting). As a result, they lack a thorough process on how to resolve the difficulties. Penetration testing, on the other hand, constantly exploits security holes and gives a full fixation guide.
3. What is OWASP security testing?
OWASP security testing is a standard cybersecurity pentesting firms follow. The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a worldwide free and open community dedicated to enhancing application software security. Their objective is to make application security “visible” so that individuals and organizations can make educated decisions regarding application security threats.
4. Why is cyber security testing important?
The fundamental goal of security testing is to identify any potential ambiguities and vulnerabilities in the program so that the product does not cease to function. When we undertake security testing, we are able to uncover potential security dangers and assist the programmer in correcting such flaws.






















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments