Black box penetration testing remains a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies, offering invaluable insights into an organization’s external defenses. Below is an updated overview that incorporates the latest information as of 2025, while preserving foundational knowledge.
What is Black Box Penetration Testing?
Black Box Penetration Testing is a cybersecurity assessment technique where ethical hackers simulate external attacks without prior knowledge of the system’s internal structures or codebases. This approach mirrors real-world hacking attempts, focusing solely on publicly available information and external interfaces to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
The primary objective is to evaluate the system’s security posture from an outsider’s perspective, uncovering weaknesses that may not be apparent through internal assessments. By employing various tools and methodologies, testers can identify and address potential security gaps, thereby enhancing the overall defense mechanisms of the organization.
Why Do You Need a Black Box Pentest?
- Simulating Real-World Attacks: Black box pentesting authentically replicates external threats, providing a realistic assessment of how an actual attacker might exploit system vulnerabilities. This method helps organizations understand potential attack vectors and prepare accordingly.
- Identifying Hidden Vulnerabilities: By operating without internal knowledge, testers can uncover security flaws that might be overlooked in other testing approaches, such as misconfigurations, unpatched systems, or exposed services.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Regular black box testing is often mandated by industry standards and regulatory frameworks to ensure organizations adhere to required security practices.
- Validating Security Measures: This testing approach assesses the effectiveness of existing security controls, ensuring that implemented defenses function as intended against external threats.
- Shaping Cybersecurity Strategies: Insights from black box testing inform the development of robust cybersecurity strategies, guiding resource allocation and risk management decisions.
Recent Developments in Black Box Penetration Testing (2025)
- Advanced Testing Tools: The evolution of sophisticated tools has enhanced the capabilities of black box testers. For instance, platforms like Scytale integrate automation with expert manual testing, streamlining vulnerability identification and remediation processes.
- Cost Considerations: The financial aspect of black box penetration testing varies based on the scope and complexity of the engagement. Prices typically range from $4,000 to $15,000, influenced by factors such as the environment’s intricacy and the expertise of the testers.
- Market Growth: The penetration testing market is experiencing significant expansion, with projections indicating an increase from $5.30 billion in 2025 to $15.90 billion by 2030. This growth reflects the escalating sophistication of cybersecurity threats and the growing need for robust measures.
Incorporating black box penetration testing into your cybersecurity framework is essential for maintaining a robust defense against evolving threats. By understanding its importance and staying abreast of current developments, organizations can better protect their assets and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Types of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing, commonly known as pen testing, is a cybersecurity practice that simulates cyberattacks to identify and address security vulnerabilities within systems, networks, or applications. As of 2025, the landscape of penetration testing has evolved to encompass various specialized types, each targeting specific areas of an organization’s infrastructure. Below is an updated overview of the primary types of penetration testing, integrating both foundational and contemporary practices:
1. Black Box Testing:
In black box testing, testers possess no prior knowledge of the target system’s internal workings, such as infrastructure, architecture, or source code. They emulate external attackers, utilizing publicly available information to probe for vulnerabilities. This approach effectively assesses how a system withstands real-world external threats.
2. White Box Testing:
Conversely, white box testing provides testers with comprehensive information about the target system, including source code, network diagrams, and infrastructure details. This thorough access enables precise identification of vulnerabilities, offering an in-depth evaluation of the system’s security from an insider’s perspective.
3. Gray Box Testing:
Gray box testing strikes a balance between black and white box methodologies. Testers have partial knowledge of the system, such as understanding its architecture or access to certain internal documents, but lack full access to source code or detailed internal configurations. This approach simulates scenarios where an attacker has limited insider information, providing a realistic assessment of potential security exposures.
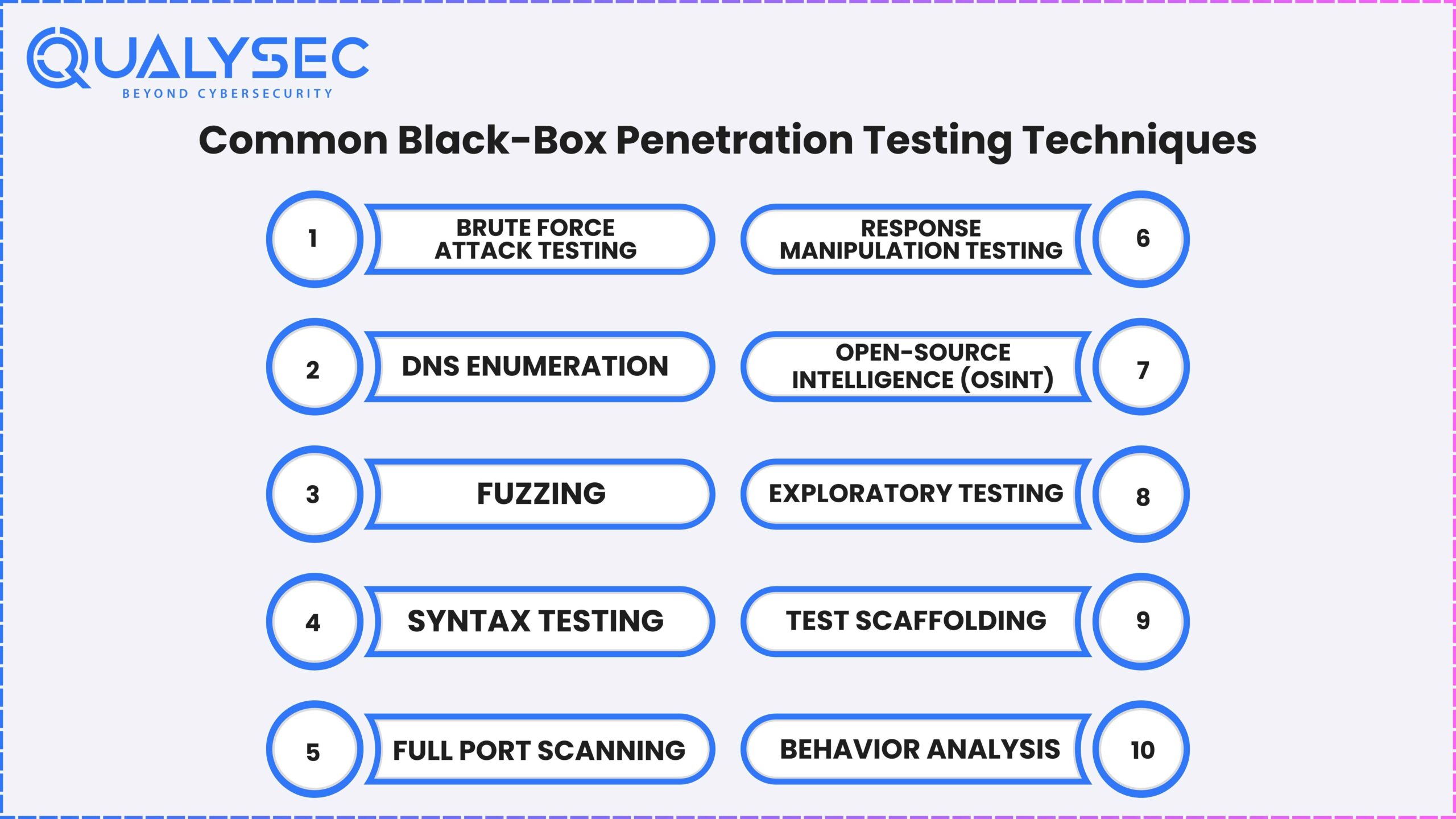
Common Black-Box Penetration Testing Techniques
Black-box penetration testing simulates real-world cyberattacks by evaluating a system’s security without prior knowledge of its internal structures. This approach identifies vulnerabilities that external attackers might exploit. Below are several key techniques used in black-box penetration testing, updated with the latest information as of 2025:
1. Brute Force Attack Testing:
This technique involves systematically attempting all possible combinations of usernames and passwords or encryption keys to gain unauthorized access. It remains effective against systems with weak passwords or inadequate authentication mechanisms.
2. DNS Enumeration:
DNS enumeration involves gathering information about a target’s DNS servers, including hostnames, IP addresses, and mail servers. This data can reveal potential entry points for attacks. As of 2025, advanced DNS enumeration tools have enhanced capabilities to detect subdomains and misconfigurations more efficiently.
3. Fuzzing:
Fuzzing entails inputting unexpected or random data into a system to uncover vulnerabilities, particularly in software interfaces, APIs, or protocols. Modern fuzzing tools in 2025 utilize machine learning algorithms to generate more effective test cases, improving the detection of complex security flaws.
4. Syntax Testing:
Syntax testing involves providing inputs with specific syntax patterns to identify weaknesses such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). This method remains crucial for detecting input validation issues. Recent advancements have led to the development of automated syntax testing tools that can more accurately pinpoint vulnerabilities.
5. Full Port Scanning:
This technique scans all ports of the target system to identify open ports and the services running on them, helping to map the attack surface. In 2025, port scanning tools have become more sophisticated, offering faster and more comprehensive scanning capabilities while minimizing the risk of detection.
6. Response Manipulation Testing:
This method involves manipulating system responses to observe behavior under various conditions, identifying vulnerabilities such as improper input validation and error handling. Recent developments include automated tools that can systematically alter inputs and analyze responses to detect subtle security issues.
7. Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT):
OSINT refers to collecting publicly available information about a target, including employee names, email addresses, and software versions. This information aids in understanding the target’s infrastructure and potential attack vectors. As of 2025, OSINT tools have integrated artificial intelligence to automate data collection and analysis, providing more accurate and actionable intelligence.
8. Exploratory Testing:
Exploratory testing involves dynamically interacting with the system without predefined test cases to discover unexpected vulnerabilities. Testers adapt their strategies based on system responses, making this approach effective for uncovering issues that automated tools might miss.
9. Test Scaffolding:
Test scaffolding refers to creating a controlled environment to automate specific tests, facilitating the detection of critical program behaviors that may not be evident through manual testing. This technique enhances the efficiency and depth of penetration testing efforts.
10. Behavior Analysis:
Behavior analysis monitors how a system responds to various inputs and conditions, identifying anomalies that may indicate underlying vulnerabilities. This approach is particularly useful for detecting subtle security issues that do not manifest through standard testing techniques.
By incorporating these updated techniques, organizations can more effectively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities for overall security posture.
Black-Box Pen Testing Checklist
Black-box penetration testing is essential for evaluating security without prior knowledge of the internal architecture. The following checklist ensures a structured and effective approach:
1. Thorough Reconnaissance
Before starting the penetration test, gathering detailed information about the target system or network is crucial. Modern reconnaissance techniques now include:
- AI-Powered OSINT Tools – Automate intelligence gathering from public sources.
- Cloud Asset Discovery – Identify exposed cloud services, misconfigurations, and leaked credentials.
- Dark Web Monitoring – Detect breached data or credentials related to the target organization.
- Live Subdomain Enumeration – Continuous tracking of new subdomains to identify attack surfaces.
2. Methodical Vulnerability Assessment
Systematic vulnerability identification ensures critical flaws are prioritized. The latest approach includes:
- Zero-Day Threat Detection – Leveraging AI-driven tools to identify emerging exploits.
- Automated & Manual Testing Combination – AI-enhanced scanners with expert manual validation for accuracy.
- API & Mobile App Testing – Expanding beyond traditional web testing to cover mobile and API security.
- Supply Chain Risk Assessment – Identifying vulnerabilities in third-party integrations and software dependencies.
3. Effective Reporting and Remediation Guidance
A black-box penetration test is incomplete without clear, actionable reporting. Best practices now include:
- Executive & Technical Reports – Tailored insights for both leadership and IT teams.
- Risk-Based Prioritization – Highlighting vulnerabilities based on exploitability and business impact.
- Step-by-Step Fixes – Providing detailed remediation guidance with patching timelines.
- Attack Simulation Reports – Showcasing real-world exploitation scenarios to improve awareness.
Want to see a real-time black-box penetration testing report? Download the sample report now!
Latest Penetration Testing Report

Black-Box Penetration Testing Steps
Here are the typical steps involved in conducting black-box penetration testing:
Step- 1: Gathering Information
Since the organization doesn’t provide the testers with any knowledge of the environment being tested, they gather as much information as possible from publicly available web pages.
Step – 2: Planning
Here the testers define the scope and strategies of the pentest. They plan which vulnerabilities to check and what technology to use.
Step – 3: Automated Tool Scanning
In this step, the testers use automated tools to scan known vulnerabilities. Since the tools follow a specific script, it is a quick but in-comprehensive process of finding vulnerabilities.
Step – 4: Manual Security Testing
Here the testers use human expertise to manually test the given software for hidden vulnerabilities. it is the most comprehensive way to find maximum vulnerabilities present in a software or network.
Step – 5: Reporting
The pen testers now generate a comprehensive report that is easy to read for developers, outlining every vulnerability they have found, their level of impact, and remediation steps.
Step – 6: Remediation
At this point, the developers use the pentest report to fix the vulnerabilities. If needed, the testers will help them locate the vulnerabilities over consultation calls.
Step – 7: Re-testing
The program is re-tested in the next phase to ensure that all the vulnerabilities are fixed and no new weaknesses have been found.
Step – 8: Security Certificate
Finally, the pen testers provide security certificates, which confirms that the organization has conducted black-box penetration testing.
Would you like to protect your website and online apps against cyberattacks? Connect to obtain our black box penetration services to discover and fix flaws in your web apps immediately. Click below to schedule a call!
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Black Box Penetration Testing Tools
Black box penetration testing approach uncovers vulnerabilities without prior knowledge of the system’s internal workings. To effectively conduct these tests, professionals rely on a variety of tools designed to identify and exploit security weaknesses. Below is an updated overview of prominent black box penetration testing tools as of 2025:
|
Tool |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Burp Suite |
A comprehensive web application security testing tool that includes components like a proxy server, scanner, intruder, repeater, sequencer, and decoder. These features assist in identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities within web applications. |
|
Metasploit |
A widely used penetration testing framework that simplifies the process of discovering, exploiting, and validating vulnerabilities. It offers a vast library of exploits and payloads, enabling security professionals to test various systems for weaknesses effectively. |
|
Kali Linux |
An advanced penetration testing and security auditing platform that comes pre-installed with over 600 security tools. It is highly customizable, allowing testers to tailor their environment to specific assessment needs. |
|
Nessus |
A leading vulnerability scanner that helps identify security vulnerabilities across various systems. With coverage for over 47,000 unique IT assets, Nessus provides accurate and fast assessments, aiding in risk mitigation and compliance efforts. |
|
Wireshark |
An open-source network protocol analyzer that captures and inspects network traffic in real-time. It provides detailed insights into network communications, assisting in the detection of anomalies and potential security issues. |
|
Acunetix |
A comprehensive web application vulnerability scanner that detects issues such as SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other vulnerabilities. It offers fast scans, detailed reports, and remediation guidance to enhance web application security. |
|
Cobalt Strike |
A threat emulation tool designed for adversary simulations and Red Team operations. It enables testers to mimic advanced persistent threats (APTs) by using post-exploitation agents and covert channels, providing a realistic assessment of an organization’s defense mechanisms. |
|
OpenSSL |
An open-source implementation of the SSL and TLS protocols, providing essential command-line tools for cryptographic operations. It is primarily used in penetration testing for tasks such as certificate management, encryption, decryption, and digital signatures. |
Integrating these tools into a black box penetration testing strategy enhances an organization’s ability to identify and address security vulnerabilities effectively, thereby strengthening its overall cybersecurity posture.
Conclusion
Black box penetration testing is critical to upgrading an organization’s cybersecurity defenses. This methodology identifies flaws by creating real-world attacks that mirror the perspective of external hackers. Furthermore, organizations may improve their security posture and resistance against cyber threats by using a systematic strategy that includes reconnaissance, vulnerability assessment, and repair assistance. Black box pen testing uses manual approaches and automated vulnerability scanning tools such as the Burp Suite, OpenSSL, and Metasploit. Hence, integrating black box pen testing is a requirement and a strategy for safeguarding sensitive data and digital assets.
FAQs
1. What is a black box in penetration testing?
In penetration testing, a black-box approach is where testers have no information about the system to be investigated. Therefore, this emulates the outsider’s point of view, enabling simple and transparent examination and detection of weaknesses.
2. What is the difference between Whitebox and Blackbox pen test?
Whitebox penetration testing is where the testers get access to the internal architecture and code of the computer network system. Whereas, Black box penetration testing mirrors the outsider’s viewpoint with no previous knowledge and checks the security of an external outsider. Both techniques allow the evaluation and detection of system vulnerabilities.
3. Who does black box testing?
Primarily, cybersecurity experts or ethical hackers perform black box penetration testing. It involves evaluating a system’s security without understanding its internal code. Additionally, it focuses on inputs and outputs, mimicking user interactions to detect flaws and guarantee that the software fits needs and standards.
































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments