Imagine how much data your enterprise handles. Every day there are likely many internal emails, customer transactions, and perhaps some performance reporting — all critical to the business and needing to be secured.
The information security compliance keeps your organization data information safe. It is compliance with some specific regulations or standards which guarantee the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Information has brought a recognized benchmark that assists in measuring and evaluating security best practices to avert data breach and promote safety, thus leading to an improvement in the security posture of the organization.
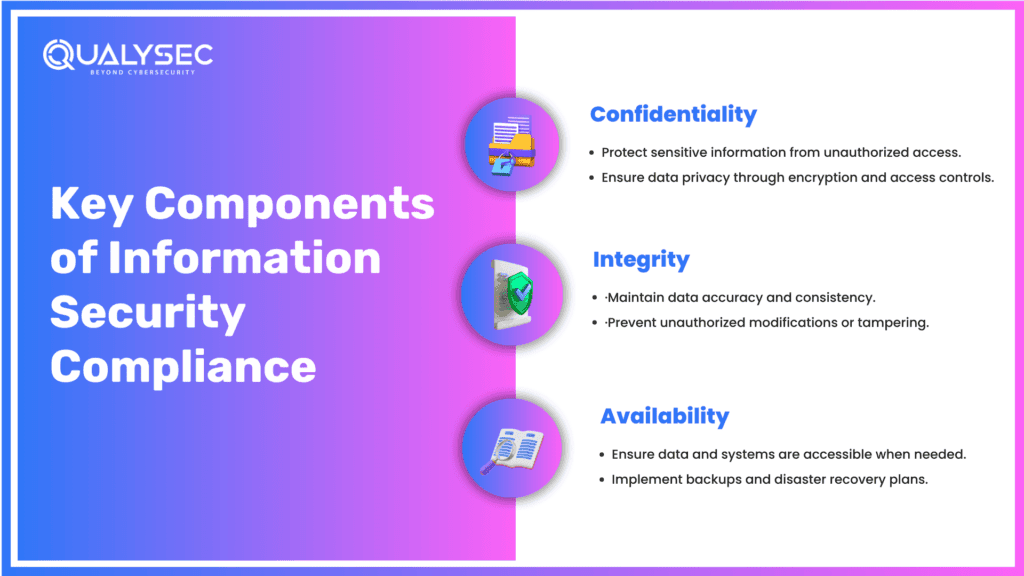
What do you mean by information security compliance?
Information security compliance or InfoSec compliance actually means complying with the conditions established by a third party, on which an organization will ensure adequate protection of its data and IT assets. Through the introduction of the recommended controls and processes, the main goals to be achieved can be to ensure that any information within the organization is kept confidential, maintained at its integrity, and made available when required.
Usually, an organization can ensure compliance requirements according to certain industries, geographical areas, or types of data which have been processed or stored by an organization. For instance, health care providers in the United States must abide by [HIPAA], while entities processing credit card transactions. Need PCI compliance-the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.
The InfoSec compliance would provide the organization with protection from risks of unauthorized access and data breaches due to a combination of evidence collections, risk assessments, and regular auditing. As far as profit is concerned, the enterprise would be shielded from an impact on its reputation.
What is the difference between IT security and IT compliance?
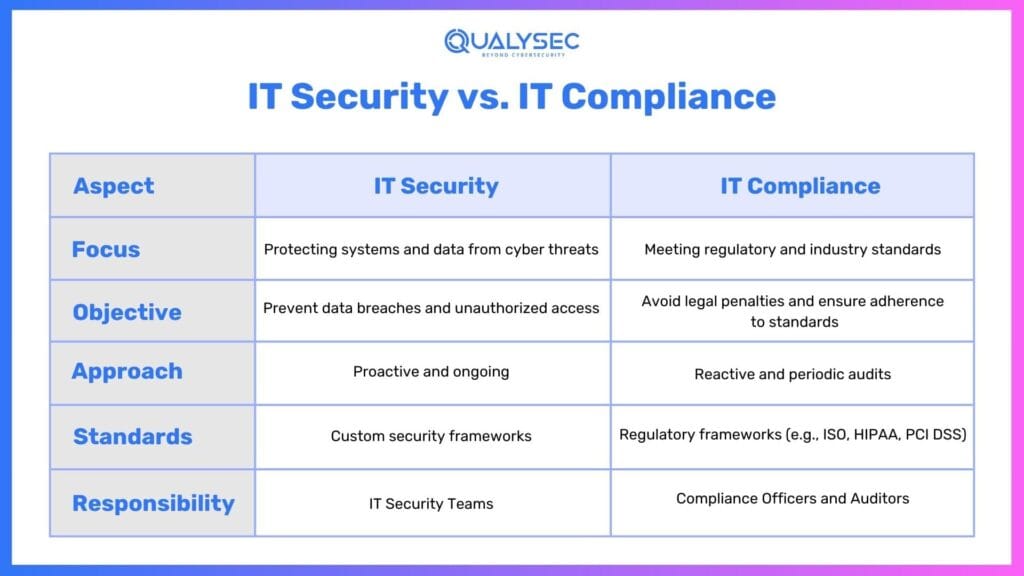
IT security is homegrown, not borne out of any third-party requirement. The other aspect of it is that such activities are usually under the ambit of the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or the whole IT security team and run for a continuous maintenance-improvement effort. On the other hand, IT compliance makes sure that the IT security measures adopted by an organization are good enough for meeting industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Even though IT compliance is audited according to third-party standards, there are not all security frameworks audited or certified by a regulatory body. For example, NIST CSF, which gives industry standards and best practices to cybersecurity risk, and CIS 18, which ensures the integrity of financial reports and business practices are both voluntary and self-assessed through internal compliance teams.
Whether it is compulsory or voluntarily IT compliance, the main purpose is to show that an organization, either in compulsory or voluntary compliance, has information security management system (ISMS) that matches the industry standards and demonstrates to stakeholders that it is capable of protecting all sensitive information.
What types of data involved in information security!
An important question to address when implementing an InfoSec program would be, what data does your company collect, store, process, or transmit?
Different types of data are likely to pose different types of information security risks. Data is usually classified according to type, satisfaction-risk or vulnerability, and the value it holds for the organization when it comes to security.
Knowing a lot about the different types of data being collected and stored would greatly help in implementing an effective InfoSec program, controls, and eventually, compliance to industry-specific regulations.
Most regulatory frameworks concern themselves with different degrees of sensitive data like personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), or some level of “secret” information such as controlled unclassified information (CUI).
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- Names
- Current address
- Date of birth
- Social security number (SSN)
- Passport number
- Taxpayer identification number
- Driver’s license number
- Car plate numbers
- Biometric data
Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Medical history
- Laboratory outcomes
- Health plan and insurance documentation
- Appointment history
- Prescriptions
- Hospital admissions
Other sensitive data protected under cybersecurity compliance are:
- Racial or ethnic origin
- Religious or philosophical beliefs
- Political opinion
- Marital status
- IP addresses
- Sexual orientation
- Biometric data (fingerprints, facial recognition and voice prints)
- Financial information (bank account numbers and credit card numbers) .
Importance of Information Security Compliance
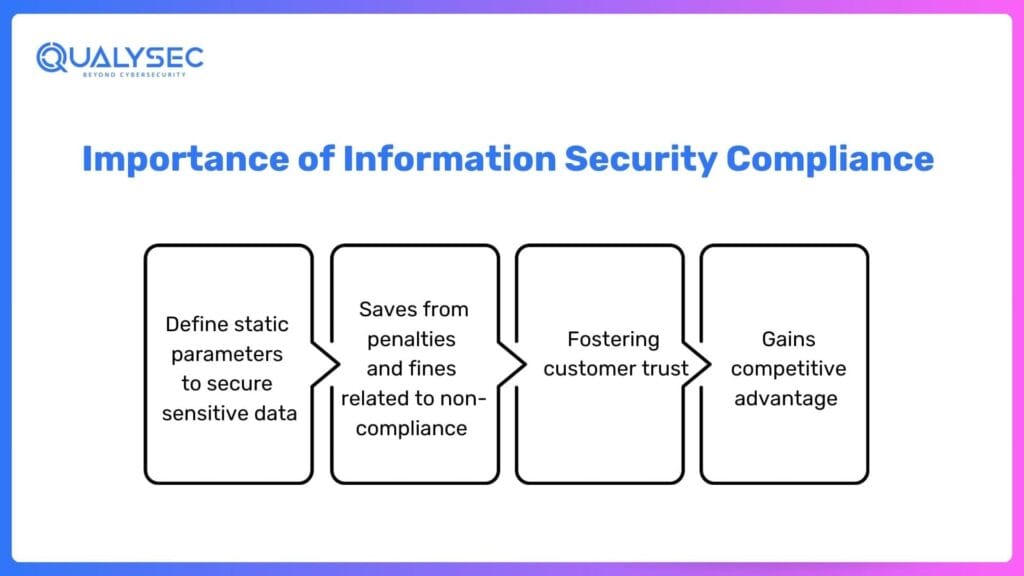
Well, the nitty-gritty importance of information security compliance is this.
“But even though an organization is doing a good job in implementation of controls and management of risk, things sometimes remain inefficient in the documentation of the same in terms of a compliance program to measure and communicate their risk posture.” Depending on the markets or segments, information security compliance may sometimes legally be a requirement before an organization can operate (e.g., PCI DSS). But observing and measuring one’s program against applicable compliance standards does come with some very significant benefits:
1. Define static parameters to secure sensitive data
Information security compliance programs are probably the best ways to protect and preserve an organization’s sensitive data over time. When data is collected and stored all over the network, information security compliance ensures that the controls and policies exist at different places within the organization to safeguard against occurrences of security incidents and mitigate against negative consequences that may arise if they do occur.
2. Saves from penalties and fines related to non-compliance
Failure to comply with the applicable regulations usually incurs substantial fines or even criminal charges in certain industries and places. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes maximum penalties for major violations not exceeding €20 million or 4% of the global annual revenue of the organization. In addition to the regulations and penalties for them, organizations suffering from data breaches bear very high remediation and business interruption costs.
3. Fostering customer trust
Compliance with information security is thus a means for companies to gain the confidence of their clients, partners, employees, and other stakeholders. In a survey conducted by McKinsey, 87% of the respondents from a survey carried on consumers said they “would not do business” with a company which had any concerns with its security practices. Half of the respondents also believe that they will be more inclined to trust companies that could quickly respond to breaching incidents as well as hacks and those that actively disclose such incidents to the public.
4. Gains competitive advantage
Regulatory compliance management proves an organization to be committed and ready to invest with all seriousness in the security of customer data. This is very fundamental in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance. Organizations can, henceforth, build a major competitive advantage by promoting risk-based culture and coming up proactively on the InfoSec compliance.
5 ways to become compliant with Information Security
Here are the general steps to take, together with the questions to ask, to prove compliance with Information Security while making the journey smoother:
1. Scoping the program and assessing risk
- What are the top security requirements that apply to your company based on: industry, geography, customer specific requirements, etc.?
2. Conducting a gap analysis
- Where does your company currently achieve Compliance standards?
- What areas of the business would require security controls that have not yet been implemented?
3. Mitigation of gaps
- What business processes and documentation do you need to meet compliance requirements?
- Who are the stakeholders that are necessary to implement those activities?
4. Manage and monitor the program
- How are you collecting evidence?
- What is the process to validate if controls are operational?
5. Perform the audit
- How do you export or disclose privy information to your internal or third-party audit team.
Who are the standards of compliance regarding information security?
Hundreds of information security standards exist all over the globe, but here are a few:
1. SOC 2
SOC 2 restricts the way that service organizations manage their client’s important data by improving the well-defined standards set forth by the American Institute of CPAs regarding the service audience. Security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy are the categories of the Trust Services criteria.
“Also check out: A detailed guide to SOC 2 Penetration Testing.“
2. HIPAA
HHS issued HIPAA, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, for rules governing the privacy of an individual’s protected health information (PHI). It encourages secure transfer of necessary health-related information to improve quality health care delivery.
“Also check out: A detailed guide to HIPPA Penetration Testing.“
3. GDPR
GDPR or General Data Protection Regulation is referred to as the most critical data protection laws in Europe on online privacy. According to this rule, any organization that deals with a resident of EU must comply with very strict guidelines as given. Also, those that collect and manage this data must protect it from misuse and exploitation.
“Also check out: A detailed guide to GDPR Penetration Testing.“
4. International standard ISO 27001
The International Organization for Standardization has released widely endorsed international standards regarding information security protection recognized by the International Electrotechnical Commission. It provides guidance to businesses on protecting their most vital information, from customer data through financial records to the intellectual property rights.
“Also check out: A detailed guide to ISO 27001 Penetration Testing.“
What Are the Legal Prerequisites for Information Security Compliance?
Legal requirements of information security compliance vary by standard and jurisdiction. Some of the more general requirements are as follows-
1. Laws for Data Protection
Data protection laws regulate the collection, use, transfer, and disclosure of personal information and the security of such information. People enter the power to hold up their data, accountability requirements for the companies protecting it, and remedies on the issue of improper or harmful processing of this data.
2. Laws on Notification After Data Breaches
It describes who could be applicable to the compliance rules, such as natural persons, legal persons, or the state, and what would constitute a breach. Such compliance rules prescribe that the organization that suffered a breach needs to inform the aggrieved individual regarding the violation of his or her data and to communicate the notification also to other important parties.
3. Data Retention and Destruction
The term data retention refers to maintaining different types of data for a defined period of time. Data destruction (sifting and shredding), in contrast, deems to be no longer beneficial for the organization. These personal data security policies include regulations on how to collect, maintain, or destroy personal data.
4. Contractual requirements
Contracts with clients, business partners, and suppliers often impose specific information security requirements upon an organization. Certain policies concerning security audits, incident response, confidentiality of data, and protection could form parts of such contracts.
Types of Information Security
These are the key aspects of information security that people apply and many countries have thus adopted them to protect data from theft and destruction in the areas concerning these.
- Network Security: Protects the external networks from threats and malicious activities. Typical measure of security here includes firewalls, intrusion detection shows, and security monitoring tools
- Application Security: Ensures the absence of threats and vulnerabilities in software and APIs and implements authentication, encryption, and secure coding practices.
- Endpoint Security: Protects end users- laptops, smartphones, and tablets against attacks. This includes setup of endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, web content filtering, and application control.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Checks who has information access and makes sure that only the right people have access to sensitive data-inspectorate. One should check and authorize such access.
- Cloud Security: Protects data, applications, and services, since it is stored and accessed, in cloud environments. This covers measures like data encryption, access controls, and regularity in security auditing.
- Cryptography: It makes use of techniques like encryption to ensure that the data being passed is private and set and that one cannot read it without an encryption key associated with it.
Conclusion
For organizations handling all the confidential data of customers and intellectual property, they must have adequate security measures to prevent data breaches. This is what achieving information security compliance does to your business. By following the guidelines of the specific industry standard your business is relevant for, you can not only protect sensitive information but also enhance your overall security, avoid legal penalties, and build trust among your customers and stakeholders.
FAQs
Q: What are the 4 pillars of information security?
A: The four pillars of information security are:
- Security reminders
- Protection from malicious software
- Log-in monitoring
- Password management
Q: What is information security policy compliance?
A: The information security policy (ISP) is a set of rules and procedures that ensure compliance with minimum IT security and data protection standards for all organizations, creating customer and stakeholder confidence.
Q: How often should I perform compliance audits?
A: Compliance audits should be performed at least once a year to stay one step ahead of potential threats. You can also perform a compliance audit if your region or industry has a new standard.
Q: Who can perform an information security compliance audit?
A third party company for data security auditing is best fit to carry out the information security compliance audit, but it can also offer other relevant services that can enhance the measures for securing your data.




















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments