Cybersecurity has undoubtedly emerged as one of the most important issues as new technologies develop. Given the current nature of cyber threats, organizations need to be security conscious to protect their data and systems. An essential factor of this protection strategy is a strong Threat and Vulnerability Management System (TVM). This Threat Vulnerability Management System provides crucial functions in defining, evaluating, and managing risks and threats that can threaten an organization’s security.
What is Threat Vulnerability Management?
Threat Vulnerability Management is an innovative system that seeks to address the threats and vulnerabilities affecting an enterprise IT system. It entails constant surveillance and assessment of links, frameworks, and programs to identify prospective threats and risks. According to these threats, the TVM systems assist organizations in applying security measures to manage risks.
It is important to note that while Threat Vulnerability Management is all about the identification of risks, it goes hand in hand with acknowledging threats that might exploit the risk. This dual focus allows organizations to think about cybersecurity both before and after the fact, preventing new kinds of attacks from arising before they can be used by attackers to infiltrate organizations
Why is Threat and Vulnerability Management Important?
In the cybersecurity context, Threat and Vulnerability Management (TVM) is a critical process that helps organizations beat cybersecurity threats. The significance of TVM cannot be overemphasized as it is a vital component of ensuring security and the sound functioning of an organization’s information and technological resources. undefined
1. Proactive Risk Mitigation
Threat and Vulnerability Management enables organizations to be more proactive as far as the issue of cybersecurity is concerned. In that way, TVM contributes to the minimization of risks involved in possible cyberattacks as it leads to the identification, evaluation, and control of threats before they are used against an organization. This is especially important in the present time where threat actors are also using more advanced strategies.
2. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Some industries have strict regulatory standards, especially on aspects concerning data privacy and security. Non-compliance with these regulations attracts severe penalties, legal implications, and a bad reputation for the organizations involved. More importantly, proper implementation of a TVM system guarantees that an organization complies with above stated regulations by constantly assessing and remediating vulnerabilities.
3. Protection of Sensitive Data
Now in the modern world, the biggest asset for any organisation is information. But as you will see, it is also one of the most vulnerable points for hackers. This is because a strong TVM system guards information that needs to be protected for instance consumer data, innovation, or even fiscal data to ensure that loopholes that cause penetrations are closed as early as possible. In this way, organizations can protect this data from being breached and therefore sustain the confidence of their customers, partners, and other stakeholders.
4. Enhancing Incident Response
A well-implemented Threat and Vulnerability Management (TVM) system not only focuses on preventing vulnerabilities but also plays a significant role in enhancing an organization’s incident response capabilities. By continuously monitoring and assessing threats, TVM provides critical insights that can be used to respond swiftly and effectively to any security incidents. This reduces the potential damage caused by cyberattacks and minimizes downtime, ensuring business continuity.
5. Cost Efficiency
Addressing vulnerabilities early in their lifecycle is significantly more cost-effective than dealing with the aftermath of a security breach. A successful cyberattack can lead to substantial financial losses, including costs associated with data recovery, legal fees, and reputational damage. By investing in a robust TVM system and conducting regular VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing), organizations can avoid these costly consequences by preventing attacks before they happen.
6. Competitive Advantage
In a world where cybersecurity is a top priority for consumers and business partners, organizations with strong TVM systems can gain a competitive edge. Demonstrating a commitment to security can attract customers, partners, and investors who are increasingly looking for companies that prioritize the protection of their digital assets. This can lead to increased trust and loyalty, ultimately benefiting the organization’s bottom line.
What Are the Steps of Vulnerability Management?
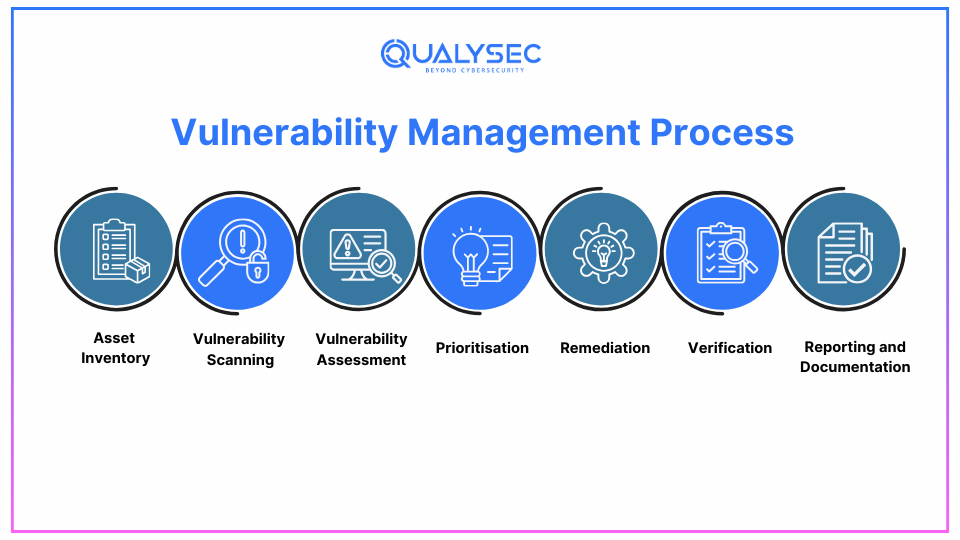
Effective vulnerability management is a systematic process that involves several key steps:
1. Asset Inventory:
The first action is the assessment of all available resources such as machinery, software, and information. This assists in establishing what must be protected.
2. Vulnerability Scanning:
Scanning the networks, the systems, and the applications that are in the company is useful in identifying some of the existing weaknesses. Many of these scans use tools such as Burp Suite or Nessus in the course of their execution.
3. Vulnerability Assessment:
When vulnerabilities are defined, their risks must be evaluated to understand how exposed they can be. This is because the VUCA model looks at the level of vulnerability and the probability of exploitation of such.
Conducting a thorough Vulnerability Assessment helps in computing these risks and provides a clearer picture of potential exposure and the likelihood of exploitation.
4. Prioritisation:
It is important to note that all sorts of vulnerabilities are not the same. It helps to prioritize the vulnerabilities according to the level of risks because this way only the most severe problems will be solved at first.
5. Remediation:
The next procedure that has to be implemented is the management of risks or, in other words, the treatment of the vulnerabilities. This could be in the form of patching, software updates, or changing some settings of the computer.
6. Verification:
In the case of remediation, it is equally necessary to check whether the vulnerability has remained active or not. This can be done through rescanning or penetration testing The present research may be conducted through rescanning or penetration testing.
7. Reporting and Documentation:
The last of them is to describe all actions, discover weak points, make measures, and the present situation. It is important as a guide to compliance during the execution of the project and for future use.
Common Challenges and Best Practices for Effective Threat and Vulnerability Management
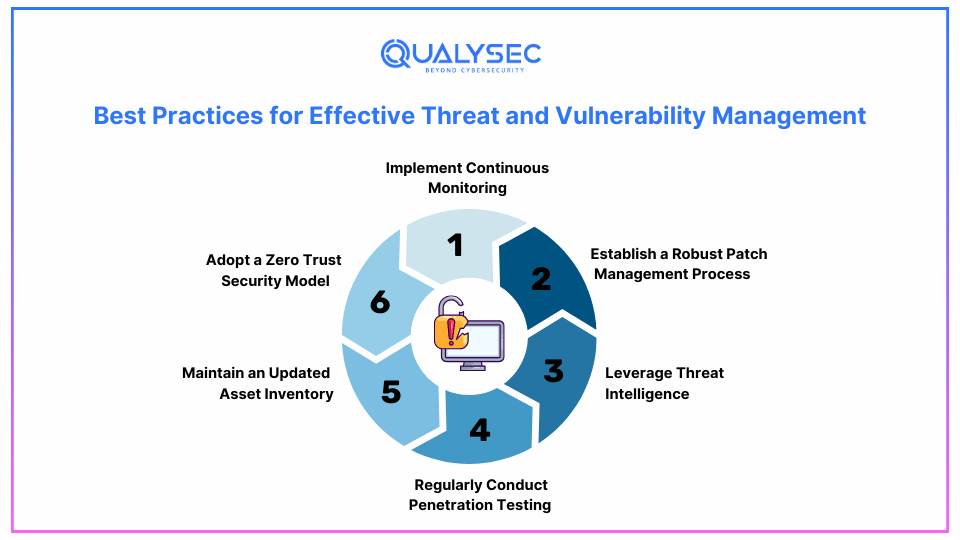
In the modern world, there are numerous threats, and an organization is exposed to many risks that may harm its security. What is apparent is that managing these risks is critical, though it is not without various considerations. Such practices, along with familiarity with these challenges, may help organizations configure their security measures and keep possible losses to a minimum.
1. Evolving Threat Landscape:
Categorically, therefore, the nature of the threats in cyberspace is quite dynamic, and new vulnerabilities are being unlocked and exploited regularly. Such an environment puts organizations under pressure to recognize emerging threats given the relative dynamism. Cyber attackers are increasingly becoming more innovative with new methods thus putting security personnel in a very complicated endeavor of trying to gauge possible breaches.
2. Resource Constraints:
Small and medium businesses often face the problems of restricted funding as well as a lack of sufficient professional staffing. It is also common that threat and vulnerability management demands a lot of investments in terms of technologies, training, and workforce. This is so because; if organizations fail to acquire enough resources in implementing security measures they will not be in a position to achieve this goal of implementing the right security systems.
3. Complex IT Environments:
Today’s IT infrastructure is saturated and heterogeneous, meaning that it can be on-premise in the cloud, or even in-between. This complexity can lead to the fact that some other weaknesses can act unseen. Further, the use of third-party vendors and applications may bring some extra security problems that can complicate the situation with security.
4. Inadequate Patch Management:
Indeed, one of the most stressful issues in vulnerability management is the ability to apply patches on time. However, organizations might not opt to apply those respective patches for their systems, or do so only after a while, as they may also consider various problems, such as possible disruptions, compatibility issues, and others. Such delay can make systems vulnerable to certain known types of attacks, thus compromising their security.
5. Lack of Visibility:
Without a fully comprehensive picture of the organizational network, the systems in place, and the assets conceptualized, it is pretty much herculean to identify the possible weakness. Organizations rarely have a good audit of their assets, which implies that they do not know which systems to patch nor which ones they cannot.
Best Practices for Effective Threat Vulnerability Management
1. Implement Continuous Monitoring:
Constant monitoring of networks, systems, and applications becomes necessary because threats change with time. This proactive approach allows an organization to notice the threats being posed and effectively deal with them as soon as possible thus minimising the exposure time of the attackers. SIEM systems, for example, are an integration of security tools and it helps in consolidating security data that can be effective in a particular organization.
2. Establish a Robust Patch Management Process:
To tackle the identified problem, related to the lack of effective patch management, an organization needs to develop an effective procedure that has to cover the process of patch application. This should involve always looking for the vulnerabilities, testing of patches in the sandbox environment, and then the release of the patches. Some of the common challenges that patch management processes face can be solved by standardizing the tools involved so that patching is an automated process.
3. Leverage Threat Intelligence:
Threat intelligence is a process of identifying information and learning about threats that are current and progressive. It is possible to use threat intelligence as a way of identifying what attackers are doing in terms of TTP. These pieces of information can therefore be used in developing security measures and be able to prevent threats as seen from the threats above. The incorporation of threat intelligence in the vulnerability management processes is beneficial as it offers better results in decision-making and countermeasures.
4. Regularly Conduct Penetration Testing:
Ethical hacking, or penetration testing, is a procedure for testing the holes and cracks in the system that are not recognizable under normal scanning. The procedure of penetration testing when performed periodically can reveal hitherto unknown vulnerabilities and is a good way to assess the viability of present security systems.
5. Maintain an Updated Asset Inventory:
In the same way, there is a need to have a register of all assets within the organization that is well-updated. It should contain specifications of hardware, software applications, and other network devices. If an organization maintains inventory that is up to date, then it will be easier for them to determine the exposure they have to these vulnerabilities and then start working on correcting this wrong.
6. Adopt a Zero Trust Security Model:
The Zero Trust model of security works based on the fact that no one is trusted, whether or not they’re located within a network. Zero Trust requires the enhancement of controls at the application, system, or process level where every user and device must be validated before being granted access to resources. It reduces the probability of invasive penetration and confines the vulnerability which results from a breach of security.
Vulnerability Management Solutions from Qualysec
Qualysec provides several solutions that give organizations bespoke and proactive vulnerability management plans. Other services offered by their company are; Automatic Scanning, Comprehensive Reporting, and Advisory on Remedial Actions. With Qualysec, organizations will be in a position to effectively and efficiently implement their version of TVM therefore minimising the effects of a cyberattack.
That is why Qualysec’s tools are designed for the availability of a broad range of organizations, especially those with limited budgets. They provide some basic strategies that can be further adapted to meet the requirements of all organizations and allow them to find the critical issues and counteract their negative impact.
Talk to our Cybersecurity Expert to discuss your specific needs and how we can help your business.
Conclusion
In the modern world, effective threat vulnerability management is the most effective approach to secure the cyber environment. With a proper TVM system functioning in an organization, it is possible to safeguard the organization’s assets; meet the legal requirements; and retain customers’ confidence. However, it becomes difficult to combat and control such threats, and to reduce such risks, it will be better to follow the best practices and to utilize the solutions when available such as Qualysec.
FAQ
1. What are some types of vulnerabilities in cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities include poor coding, flawed system configuration, crap passwords, outdated systems, and more. Such issues can be utilized by the attackers to compromise the network’s security and access the facilities and resources without the right permission.
2. Why do we need vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is important for identifying and addressing security weaknesses before they can be exploited by hackers and attackers. It helps reduce the risk of cyberattacks, protect sensitive data, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. What is the difference between vulnerability management and assessment?
Vulnerability management is an ongoing process that includes the identification, assessment, prioritization, and remediation of vulnerabilities over time whereas Vulnerability assessment is a one-time process that identifies security weaknesses in a system.
4. What is vulnerability scanning in cybersecurity?
Vulnerability scanning is the process of using automated tools to identify security weaknesses in a network, system, or application. It includes scanning for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other potential security issues.
5. What are some common methods for managing vulnerabilities?
Common methods for managing vulnerabilities include regular patching, configuration management, network segmentation, and the use of security tools such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. These methods help reduce the attack surface and protect against potential threats.






















































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments